
Asparagus is a truly versatile and nutrient-packed vegetable. This green spear offers significant nutritional benefits, making it a valuable addition to your plate. You will find that asparagus nutrition is impressive. It is low in calories, with only about 20 calories per 5.3 oz serving, and contains no fat or cholesterol.
Beyond its basic asparagus nutrition facts, this asparagus provides a wealth of vitamins like K, A, and folate, plus essential minerals. The health benefits of asparagus extend far beyond basic benefits. Discover how this simple asparagus can boost your well-being.
Key Takeaways
Asparagus is a healthy vegetable. It has few calories and no fat. It gives you important vitamins and minerals.
Eating asparagus helps your body. It can make your digestion better. It also helps keep your blood pressure healthy.
Asparagus has special helpers called antioxidants. These protect your body’s cells. They also help make your bones strong.
Asparagus is good for pregnant women. It has folate, which helps babies grow healthy. It also helps control blood sugar.
You can easily cook asparagus. You can roast it or steam it. It is a simple and tasty food to add to your meals.
Asparagus Nutrition Facts

Calorie and Macronutrient Profile
You might wonder about the basic asparagus nutrition facts. This vegetable is remarkably low in calories. A cup of cooked asparagus (about 180g) contains only 40 calories. If you choose pickled asparagus, a 20g serving has just 6 calories. This makes asparagus a great choice for managing your asparagus calories intake. Understanding asparagus nutrition helps you make healthy food choices.
When you look at the macronutrients, asparagus offers a lean profile. You get minimal fat and carbohydrates, along with a small amount of protein.
Nutrient | Value (per 100g) |
|---|---|
Protein | 0.4g |
Carbohydrates | 0.4g |
Fat | 0.1g |
These nutrition facts show you get minimal fat and carbohydrates, along with a small amount of protein. This makes asparagus a smart addition to almost any meal. You can enjoy the benefits of low asparagus calories without guilt. |
Vitamins and Minerals
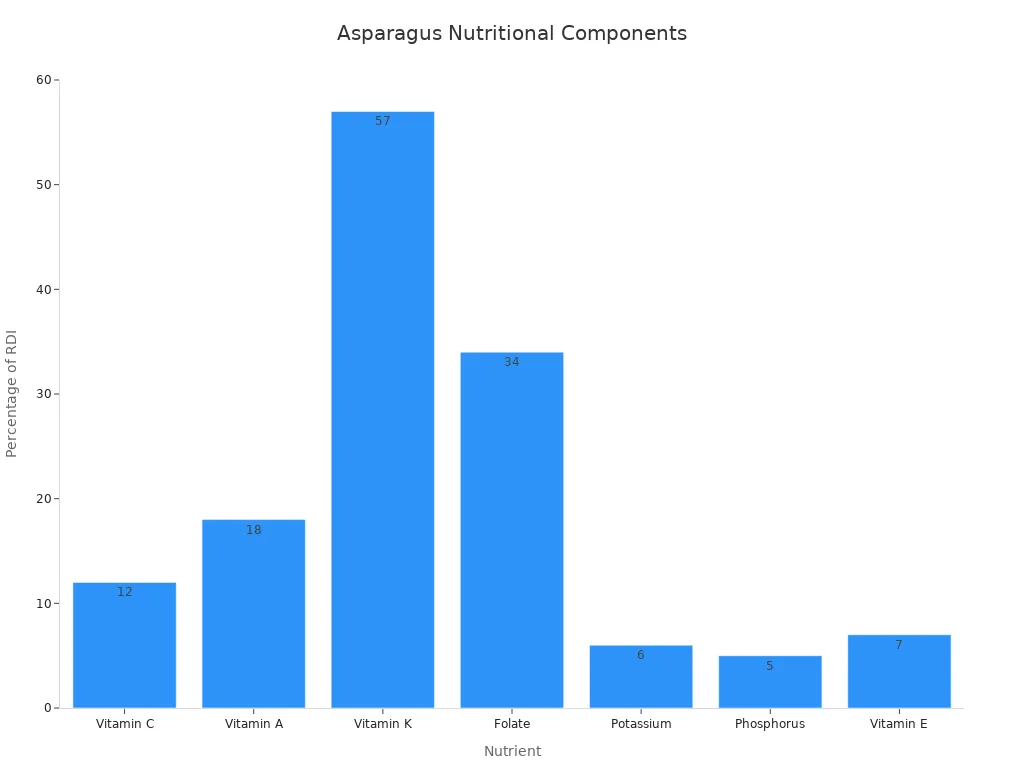
Beyond its low-calorie count, asparagus is an excellent source of vitamins. You get a nutritious source of vitamins and minerals from every serving. For example, a cup of cooked asparagus provides a significant amount of Vitamin K, giving you 76% of your daily value. This is a key nutrient for blood clotting and bone health.
You also find many other important vitamins in asparagus:
Vitamin K: 56 micrograms (46% daily value or DV)
Folate: 70 micrograms (18% DV)
Thiamine: 0.19 milligrams (16% DV)
Riboflavin: 0.19 milligrams (15% DV)
Vitamin E: 1.52 micrograms (10% DV) You also get B vitamins and Ergothioneine, sometimes called the “longevity vitamin.” These vitamins contribute to the overall nutrition of asparagus.
This vegetable also delivers essential minerals. You will find these in asparagus:
Calcium: 83 mg
Magnesium: 50 mg
Phosphorus: 194 mg
Potassium: 806 mg
Sodium: 50 mg These minerals support various body functions, from nerve signals to muscle contraction. The nutritional benefits of asparagus are truly impressive.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
Asparagus is also rich in antioxidants and beneficial phytonutrients. These compounds protect your cells from damage. You will find powerful antioxidants like flavonoids, saponins, and phenolic acids.
Specific antioxidants in asparagus include:
Lutein and Zeaxanthin: These are important for your eye health. They can help slow down macular degeneration.
Quercetin and Kaempferol: These flavonoids may have cancer-fighting properties.
Anthocyanins: If you eat purple varieties, you get anthocyanins. These can improve heart health and reduce inflammation.
Polyphenols: These bioactive compounds offer both antioxidant and anti-inflammatory benefits.
You also get important phytonutrients. Asparagus is a dietary fiber rich food. It contains saponins like asparanin A and diosgenin. Inulin, a prebiotic carbohydrate, is another key phytonutrient. This supports good gut health. The overall nutrition profile of asparagus makes it a superfood.
Health Benefits of Asparagus
You will find many health benefits of asparagus when you add this vegetable to your diet. The rich array of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytonutrients in asparagus contributes to your overall well-being. These nutritional benefits of asparagus make it a true superfood.
Digestive Health
Asparagus is a champion for your gut. It is rich in dietary fiber, which is vital for a healthy digestive system. This fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the good bacteria in your gut. These beneficial microbes then produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are important for gut health and have anti-inflammatory properties.
You get both insoluble and soluble fiber from asparagus. Insoluble fiber adds bulk to your stool, helping it pass through your gut easily. This promotes regular bowel movements and helps prevent constipation. Soluble fiber, on the other hand, becomes a food source for your gut bacteria, keeping them healthy and active. This combination leads to better digestion. Studies even suggest that compounds in cooked asparagus, like a flavonoid called rutin, might help reduce colon inflammation.
Blood Pressure
Keeping your blood pressure in check is another one of the many health benefits you gain from asparagus. This vegetable contains potassium, a mineral known for its role in regulating blood pressure. It also provides saponins and flavonoids. These compounds offer protective effects for your blood vessels.
Research supports these claims. One study showed that a diet including asparagus significantly lowered systolic blood pressure in animals. It also reduced activity of an enzyme linked to high blood pressure. Another clinical trial found that consuming powdered asparagus bottom-stems and cladophylls significantly lowered both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in healthy volunteers. This suggests asparagus can help improve hypertension.
Antioxidant Properties
Your body constantly fights off damage from free radicals. Asparagus helps you in this fight because it is packed with powerful antioxidants. These compounds protect your cells and DNA. You get antioxidants like Vitamin A and Vitamin E from asparagus.
Specific antioxidant compounds in asparagus include:
Flavonoids, especially quercetin
Glutathione
Vitamin C
Phytosterols, like b-sitosterol
Polyphenols, including phenolic acids and flavonols
Anthocyanins (found in purple varieties)
These antioxidants work in several ways. They can activate your body’s natural defense systems, leading to the production of antioxidant enzymes. This helps reduce harmful reactive oxygen species in your body. The benefits of these antioxidants extend to protecting against diseases like cancer and heart disease.
Bone Health
Strong bones are essential, and asparagus contributes to their health. It contains several nutrients crucial for bone density and strength. You get phosphorus, iron, and some calcium from asparagus. Most notably, it is an excellent source of Vitamin K.
A single cup of asparagus can provide almost half of your daily Vitamin K needs. Vitamin K is vital for creating proteins that build bones. It helps regulate cells involved in bone building and remodeling. Adequate Vitamin K prevents a higher risk of fractures and bone-related issues. Other minerals like potassium, phosphorus, zinc, and magnesium in asparagus also support bone health.
Prenatal Support
For pregnant women, asparagus offers significant health benefits. It is a rich source of folate, also known as folic acid. This B vitamin is crucial for fetal development, especially for the brain and spinal cord.
Folate helps prevent neural tube defects (NTDs) like spina bifida and anencephaly. These are serious birth defects. The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) recommends that all women of childbearing age consume enough folic acid daily. Beyond folate, asparagus provides other benefits for pregnancy, including:
Fiber, which helps prevent constipation
Vitamin K, supporting bone health
Antioxidants, boosting immune function
Vitamins A, C, and E, for overall health
This makes folate for healthy pregnancy a key reason to include asparagus in your diet.
Blood Sugar Control
If you are looking to manage your blood sugar levels, asparagus can be a helpful addition. It has a low glycemic index of 15. This means it does not cause quick spikes in blood sugar. Its fiber content also slows down how quickly your body absorbs food, helping to keep blood sugar stable.
Furthermore, consuming asparagus can increase insulin production. Insulin helps your body absorb glucose. Flavonoids in asparagus, such as quercetin, can also inhibit enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion. Research supports these health benefits. A 2006 study showed that asparagus consumption was linked to an 81% increase in the body’s ability to use glucose. Another study found that asparagus extract helped control blood sugar and increased insulin production in diabetic rats. These findings highlight the positive impact of asparagus nutrition on blood sugar management.
Uses and Preparation
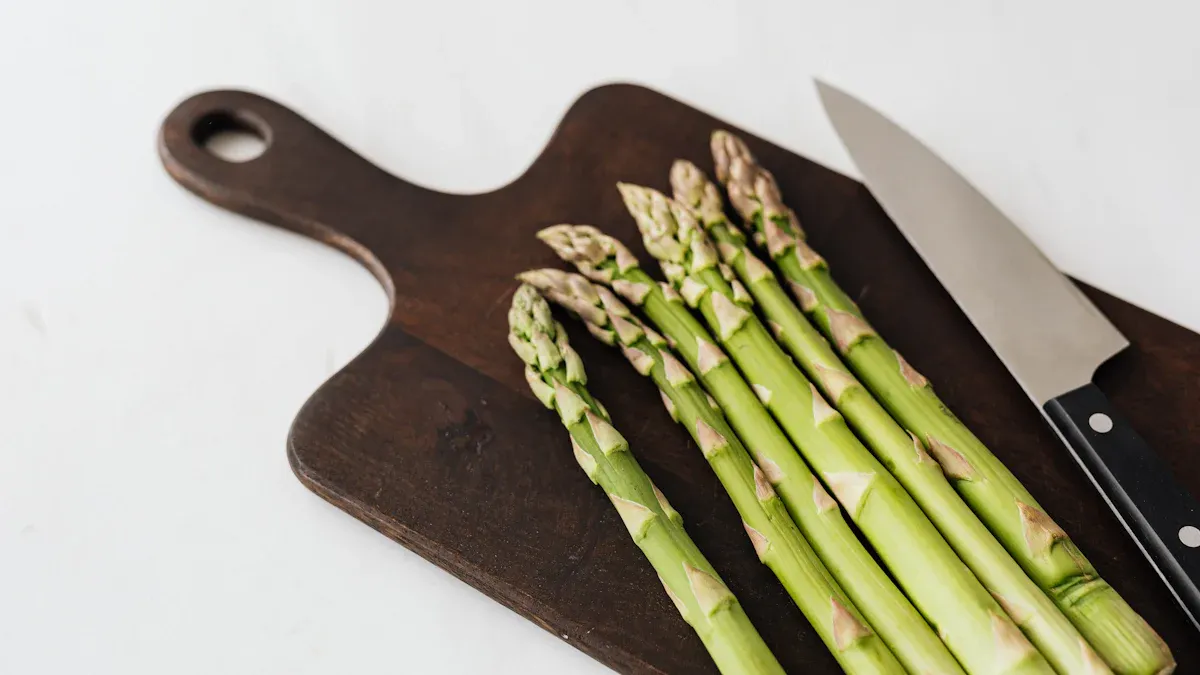

Choosing Fresh Asparagus
You want the best asparagus for your meals. Look for specific signs of freshness. Stalks should be firm, straight, and a vibrant green. They often have purplish tips. The tips must be tight and closed. They should resemble a compact bud. Avoid any stalks that appear flattened or misshapen. Healthy asparagus spears are typically 8 to 10 inches tall. They are at least half an inch thick. Uniformity within the bunch indicates good quality.
Storing Asparagus
Proper storage keeps your asparagus fresh longer. First, trim the ends of the asparagus spears. You can gather a bundle and cut them all at once. Place the trimmed asparagus upright in a deep container. A bowl or pitcher works well. Add fresh water to the container. The water should cover the ends by at least 2 inches. This ensures proper hydration. Store this container in your refrigerator. The top shelf is a good spot for this delicate vegetable. If you store it for more than a week, refresh the water after seven days. Rinse the asparagus ends under cold water before refilling.
Easy Cooking Methods
You have many easy options for how to cook asparagus. Boiling is a quick method. Bring a pot of water to a boil, then salt the water well. Boil the spears until they are tender. This takes a few minutes for thin stalks. Microwaving is even faster. Place asparagus in a microwave-safe dish with water and salt. Cover and cook for 2 to 4 minutes. Sautéing is another fast way to prepare asparagus. Cut the cleaned asparagus into 2-inch pieces. Heat oil in a large skillet. Cook for 3 to 5 minutes until crisp-tender. Roasting is also simple. Toss asparagus with oil, salt, and pepper. Roast in the oven at 425°F for 10 to 15 minutes.
Recipe Inspiration
You can enjoy asparagus in many delicious ways. Try sautéed asparagus with olive oil and lemon juice. Roasted asparagus is also a favorite. You can make air fryer asparagus for deliciously browned and crisp tips. Grilled asparagus makes an easy side dish. For a crunchy snack, consider pickled asparagus. An asparagus frittata is a quick, one-pan meal, great for brunch. You can also add asparagus to a bright spring salad. Explore these ways to eat asparagus for varied and tasty meals.
Asparagus offers impressive nutrition. It is low in calories and packed with essential vitamins like K and folate. You also get powerful antioxidants and fiber. These nutrients provide many health benefits. Asparagus supports your digestion and helps manage blood pressure. It also strengthens bones and aids prenatal health. You can even control blood sugar with this vegetable.
Nutrient | Value per 100g |
|---|---|
Calories | 20 kcal |
Carbs | 4 g |
Fiber | 2 g |
Sugars | 2 g |
Protein | 2 g |
Sodium | 2 mg |
Total Fat | 0 g |
Glycemic Index | 15 |
This versatile vegetable is easy to prepare. You can roast, steam, or sauté asparagus. Make asparagus a regular part of your meals. You will boost your well-being with this superfood.
FAQ
Can asparagus help you lose weight?
Yes, asparagus can support weight loss. It is very low in calories and high in fiber. Fiber helps you feel full longer. This can reduce your overall calorie intake.
Is it better to eat asparagus raw or cooked?
You can eat asparagus both raw and cooked. Cooking asparagus can increase the availability of some antioxidants. Raw asparagus retains more heat-sensitive vitamins. Both forms offer great nutritional benefits.
Why does asparagus make your urine smell?
Asparagus contains asparagusic acid. Your body breaks this compound down into sulfur-containing byproducts. These byproducts cause a distinct smell in your urine. This is a harmless and normal reaction.
How much asparagus should you eat daily?
You can enjoy asparagus regularly. A typical serving is about 5-6 spears. There is no strict daily limit. Incorporate it into your diet as part of a balanced meal plan.
Can you freeze fresh asparagus?
Yes, you can freeze fresh asparagus. Blanch the spears first in boiling water for 2-4 minutes. Then, quickly cool them in ice water. This helps preserve their color and texture. Store them in airtight containers in your freezer.

