
Minced meat is a worldwide culinary staple. You find minced meat in countless recipes, from hearty beef dishes to quick weeknight meals. This versatile form of beef and other meats offers delicious possibilities. The global market for minced meat is vast, valued at approximately $150 billion annually, highlighting its immense popularity. Understanding minced meat nutrition is vital. Proper handling of minced meat is key for your health and culinary success. You ensure your beef meals are both tasty and good for your health. Knowing about the different types of beef helps you choose wisely. This knowledge improves your overall nutrition. Minced meat can be a great part of your diet.
Key Takeaways
Minced meat comes in many types, like beef, chicken, turkey, pork, and lamb. Each type has different amounts of fat and protein.
Lean ground beef has less fat and calories than regular ground beef. Chicken and turkey mince often have less fat than beef.
Plant-based minced meat can be a good choice, but check for high sodium levels. Some plant-based options have more salt than meat.
Always handle minced meat safely. Keep it cold, cook it fully to 160°F, and wash your hands and surfaces to stop germs from spreading.
You can make minced meat meals healthier. Choose lean meat, drain extra fat, and add lots of vegetables and whole grains.
Minced Meat Nutrition: Types and Profiles

You find many types of minced meat in stores. Each type offers unique nutritional values. Understanding these differences helps you make informed choices for your meals. This section explores the specific nutritional profiles of various minced meats, including plant-based options.
Ground Beef Nutrition: Lean vs. Regular
Ground beef is a popular choice for many dishes. Its nutritional values vary greatly depending on its fat content. You will find both lean and regular options.
Type of Ground Beef | Maximum Fat Content |
|---|---|
Lean | 17% (83% lean) |
Regular | 30% (70% lean) |
The main difference between lean and regular ground beef is the fat content. This directly affects the calorie count. Higher fat percentages mean more calories per serving. Fat provides about 9 calories per gram. Protein and carbohydrates offer about 4 calories per gram. Choosing leaner ground beef significantly reduces your overall calorie intake and fat consumption. For example, general ground beef nutrition shows about 218 calories, 13g fat, and 24g protein.
You can choose extra-lean beef. It has less than 5g total fat, less than 2g saturated fat, and less than 95mg cholesterol per 3.5-ounce serving. A raw 80% lean/20% fat ground beef contains 77.88g protein and 90.72g total fat per pound. This means 287 calories per 100g, with 28% protein and 72% fat. If you choose raw 95% lean/5% fat ground beef, you get 24.19g protein and 5.65g total fat per 4-ounce serving. Grass-fed ground beef, typically 15-20% fat, provides 250-300 calories per 4-ounce serving. A 3-ounce serving of lean beef offers 10 essential nutrients, around 150 calories, less than 10g total fat, and less than 95mg cholesterol. These options provide excellent protein and important nutrients, making them a good part of your nutrition plan. The health benefits of ground beef are clear when you choose leaner cuts.
Chicken and Turkey Minced Meat Benefits
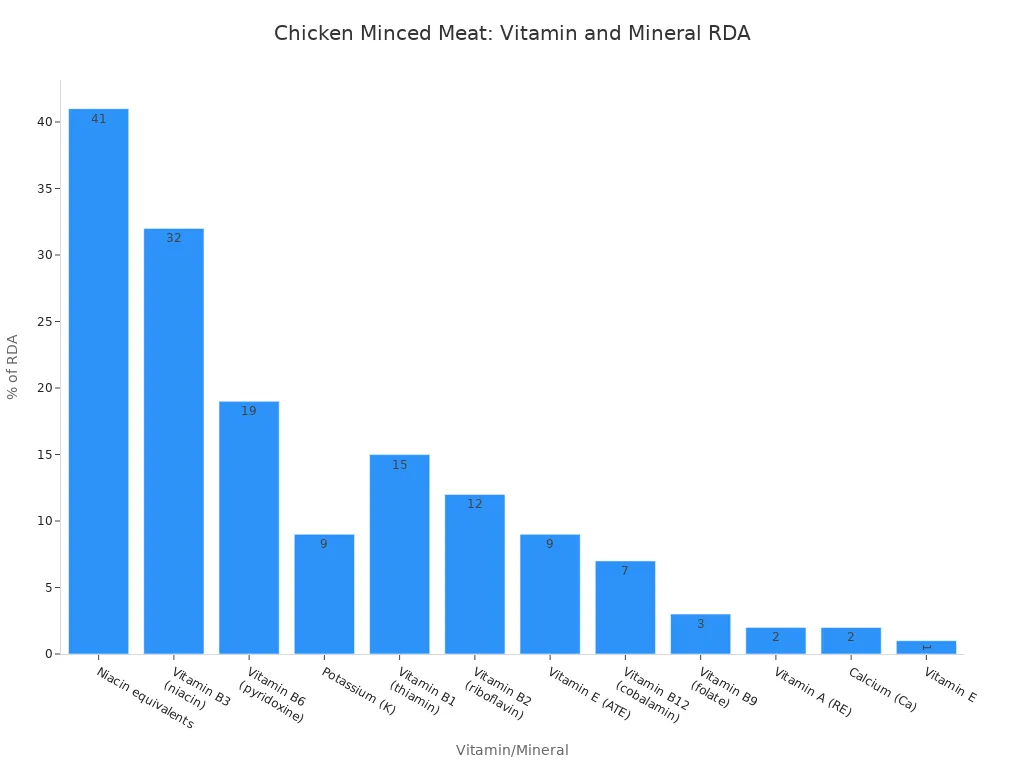
Chicken and turkey minced meat offer excellent alternatives to beef. They are often lower in fat and calories. Chicken meat is a great source of B complex vitamins, especially B12. It also provides essential minerals like iron, zinc, selenium, phosphorus. You get other important micronutrients from chicken.
Vitamin/Mineral | Quantity | % of RDA |
|---|---|---|
Vitamin A (RE) | 21 µg-RE | 2 % |
Vitamin E | 2 mg | 1 % |
Calcium (Ca) | 23 mg | 2 % |
Potassium (K) | 327 mg | 9 % |
Niacin equivalents | 8.4 mg | 41 % |
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 0.35 mg | 19 % |
Vitamin B9 (folate) | 12 µg | 3 % |
Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) | 0.3 µg | 7 % |
Vitamin E (ATE) | 1.1 mg-ATE | 9 % |
Vitamin B1 (thiamin) | 0.2 mg | 15 % |
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 0.2 mg | 12 % |
Vitamin B3 (niacin) | 5.1 mg | 32 % |
Turkey minced meat also offers significant benefits. Per 100g serving, ground turkey contains 27.4g of protein. Ground chicken contains 23.3g of protein. This means ground turkey offers 17% more protein than ground chicken. Both chicken and turkey minced meat contribute to your daily protein needs and provide valuable nutritional values for your health.
Pork and Lamb Minced Meat Nutrition
Pork and lamb minced meat bring different flavors and nutritional values to your table. High-fat minced pork can contain up to 300 calories per 100g. You should consider this when planning your meals.
Lamb is a rich source of high-quality protein. This is its main nutritional component. It contains iron, mostly heme iron. Your body absorbs heme iron more efficiently than non-heme iron from plants. Lamb is also a good source of zinc. Your body absorbs zinc better from meat than from plants. Zinc is essential for growth and hormone formation.
Other beneficial compounds in lamb include conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), creatine, and taurine. These compounds help maintain muscle, improve physical performance, and support heart health. Regular consumption of lamb can promote muscle growth, maintenance, and performance. It also helps prevent anemia due to its iron content. These benefits make lamb a valuable part of your nutrition.
Plant-Based Minced Meat Alternatives
For those seeking alternatives, plant-based minced meat options have become very popular. These products aim to mimic the taste and texture of traditional minced meat. They offer different nutritional values. Common protein sources for these alternatives include:
Soybeans
Peas
Wheat
Corn
Rice
Mung beans
Lentils
You should pay attention to the sodium and saturated fat content in plant-based minced meat.
Nutrient | Plant-based Mince (Median % DV) | Traditional Beef Mince (% DV) |
|---|---|---|
Saturated Fat | 4% | 19%–30% |
Sodium | 18% | 2%–4% |
A 2019 study in Australia found that only 4% of plant-based meats had lower sodium than their meat equivalents. The mean sodium content in plant-based products was generally less than 500 mg per 100 grams. Some products contained up to 1,200 mg per 100 grams. Plant-based mince had approximately six times the sodium content of its meat-based counterpart. While plant-based options often have lower saturated fat, you need to check their sodium levels. This ensures you make healthy choices for your nutrition.
Safe Handling and Storage of Minced Meat
You must handle minced meat correctly. This ensures your food is safe to eat. Improper handling can cause foodborne illness. Following simple rules protects your health.
Smart Purchasing and Inspection
You start with smart choices at the store. Always pick up minced meat last when you shop. Make sure it feels cold to the touch. Look at the packaging carefully. It should be sealed tightly. There should be no tears or holes.
You should also inspect the meat itself. A slimy or sticky texture is a bad sign. Discoloration can also mean spoilage. Raw beef should look bright red. Purple or brownish colors might appear from oxygen exposure. This does not always mean it is spoiled.
Raw chicken should be pink. If it turns grayish, it is spoiled. If the meat does not spring back when you press it, it might be bad. Watch for excessive liquid in the package. This can show temperature problems or bacterial growth. Green or iridescent patches almost always mean spoiled meat. Swollen or sticky plastic packaging can mean bacteria are active. Powdery residues or mold are also clear signs of spoilage.
Refrigeration Guidelines
You need to get minced meat into the refrigerator quickly. Perishable foods, including meat, should not stay at room temperature for more than two hours. If the room temperature is 90 degrees F or higher, this time drops to one hour. This rule applies to all time the food spends out of the fridge.
You should set your refrigerator to 40°F (4°C) or below. This slows bacterial growth. The University of Illinois Extension says you should keep uncooked ground beef in the refrigerator for only one to two days. You must cook or freeze it within this time. Healthline also advises keeping ground meat in the refrigerator for a maximum of one to two days. Use refrigerated ground beef within one to two days of buying it. Proper storage is key for your safety.
Freezing and Thawing Safely
Freezing minced meat is a great way to extend its life. You can store ground beef and pork in the freezer for 4 to 6 months. Make sure your freezer is at 0°F (-18°C) or below. This keeps the meat safe for longer storage.
Thawing frozen minced meat needs care. You must avoid the temperature danger zone. This zone is between 40°F and 140°F. Bacteria multiply fast in this range. The safest way to thaw meat is in the refrigerator. Keep your refrigerator at 41°F or below. Allow 24 hours for every five pounds of meat. Place sealed packages on a tray to catch any drips. Thawed ground beef can stay in the fridge for up to two days.
You can also thaw meat with cold running water. Seal the meat in a waterproof bag. Submerge it in cold tap water. The water should not be warmer than 70°F. This method thaws about one pound in 30 minutes. Cook the meat right after thawing.
Microwave thawing is fast. Use the defrost setting. Rotate and flip the meat to prevent hot spots. Cook the meat immediately after microwaving. Parts of it might start to cook during defrosting. You can also cook thin cuts, like beef patties, from frozen. Just add at least 50% more cooking time. This method avoids thawing altogether. It also reduces the risk of cross-contamination. You must cook thawed food fully if you plan to refreeze it. This principle is vital for food safety.
Preventing Cross-Contamination
Cross-contamination happens when bacteria spread from raw meat to other foods. You must prevent this for your health. Store raw minced meat, poultry, and seafood in sealed containers. This stops juices from dripping onto other foods.
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and hot water. Do this before and after handling any food. Wash them after using the bathroom or touching pets. Clean all kitchen surfaces, cutting boards, and utensils. Use hot, soapy water after preparing each food item. Use separate cutting boards for raw meat and fresh produce. Replace old, worn boards. Marinate food in the refrigerator, not on the counter. If you use a marinade on raw beef, boil it before putting it on cooked food. Always use a clean plate for serving cooked food. Never put cooked food back on a plate that held raw food. These steps ensure your food safety.
Minced Meat Culinary Uses and Preparation

Minced meat offers many cooking possibilities. You can create delicious and nutritious meals. Understanding proper cooking techniques helps you maximize flavor and nutritional value.
Essential Cooking Techniques
You can reduce fat content when cooking minced meat. This makes your meals healthier. One method is boiling. You place ground beef in a skillet. Cover it with water and bring it to a boil. Reduce the heat and continue boiling. Break up the beef as it cooks.
Drain the beef in a colander to remove rendered fat. Another technique is draining. Brown your ground beef in a skillet. After cooking, drain the fat using a colander. You can also soak up the fat with paper towels. Move the beef to one side of the skillet. Tip the skillet to collect fat. Absorb the fat with folded paper towels. Rinsing is another option.
Brown the ground beef in a skillet. Place it in a colander once cooked. Rinse it with hot water for about thirty seconds. Toss it to remove excess water. These methods show you how to prepare ground beef for healthier eating. Preparing minced meat this way helps manage fat intake.
Integrating Minced Meat into Balanced Meals
You can easily integrate minced meat into balanced meals. Mix ground beef with vegetables like bell peppers, onions, spinach, or zucchini. This boosts fiber and nutrient content. Serve your beef alongside whole grains. Brown rice, quinoa, or whole wheat pasta add fiber and nutrients. You can also combine ground beef with beans or lentils.
This increases volume, adds fiber and protein, and reduces overall fat content. A beef and lentil chili is a great example. It features ground beef with red lentils, black beans, tomatoes, and spices. This offers a protein-rich and comforting option. A study showed that replacing some red meat with non-soy legumes benefits heart health and weight.
Legumes are healthier and environmentally friendly. They have low saturated fat and high protein and fiber. Increased legume consumption links to reduced cancer risks and better cholesterol levels. This protects against cardiovascular diseases. Plant-rich diets also help with weight management. They improve blood sugar control for people with type 2 diabetes. This shows the benefits of preparing minced meat with legumes.
Flavor Pairings and Spice Ideas
Spices enhance the flavor of your minced meat dishes. For beef, classic pairings include black pepper, cumin, and oregano. Black pepper enhances robust beef flavors. Cumin gives an earthy taste. Oregano adds a Mediterranean touch. Mustard seeds add a mild tang. Thyme provides a subtle herbal note. Garlic offers a robust flavor.
A classic beef rub uses salt, pepper, and garlic. For chicken or turkey minced meat, you have many choices. Turmeric gives an earthy warmth. Basil offers a warm, sunny flavor. Cilantro provides an herbaceous taste. Lemongrass is lemony and grassy. Oregano pairs well with chicken in European dishes. Rosemary has a woodsy, lemon-pine character.
Sage is velvety and peppery. Tarragon offers a subtle licorice flavor. Thyme has a lemony top note. Coriander is sweet and citrusy. Cumin provides earthy notes. Fennel is warm and licorice-like. Garlic is a universal aromatic base. Ginger brings sweet and surprising heat. Dried lemon peel brightens dishes. Paprika offers gentle warmth. Saffron adds a delicate, honeyed floral note. These spices make your cooking exciting.
Creative Minced Meat Recipes
Minced meat is incredibly versatile. You can make many creative dishes. Spanish Beef Empanadas are handheld meat pies. Indian Beef Curry is a slow-cooked stew. English Shepherd’s Pie is a comfort dish with mashed potatoes. Swedish Meatballs are slow-cooked in a creamy sauce. Asian Dumplings are steamed with a spiced filling.
Other international dishes include Siniyeh from the Middle East. Phat Kaphrao is a Thai stir-fry. Sloppy Joes are an American classic. For quick weeknight meals, try Spicy, Creamy Weeknight Bolognese. Korean BBQ-Style Meatballs are ready in 20 minutes. Homemade Hamburger Helper takes a bit longer. Stuffed Peppers are also a good choice. Easy Skillet Spaghetti is simple to make. One-Pan Stuffed Pepper Casserole is kid-approved. Skillet Lasagna and Classic Sloppy Joes are also great. You can also make Ground Beef Stroganoff Noodles. Teriyaki Ground Beef Skillet is another quick option. These recipes show the endless possibilities for cooking ground beef.
You now understand the diverse minced meat nutrition profiles, from lean beef to plant-based options. Remember, safe handling and proper cooking are vital. Always wash your hands thoroughly, sanitize your cooking surfaces, and cook minced meat to an internal temperature of 160°F to prevent illness. Experiment with different types of minced meat in your kitchen. You can create delicious and nutritious meals. Embrace the versatility of minced meat for better nutrition and enjoyable eating.
FAQ
How long can I keep raw minced beef in the refrigerator?
You should keep raw minced beef in your refrigerator for one to two days. Store it at 40°F (4°C) or below. If you do not plan to use the beef quickly, freeze it. This keeps your beef fresh.
Can I refreeze thawed minced meat?
You should not refreeze raw thawed minced meat. Once you thaw it, cook it first. After cooking, you can safely refreeze the cooked beef. This prevents harmful bacterial growth.
How can I make minced beef dishes healthier?
You can make minced beef dishes healthier. Choose lean ground beef. Drain excess fat after cooking. Add plenty of vegetables to your meals. Serve your beef with whole grains for added fiber.
What is the ideal internal temperature for cooked minced beef?
You must cook minced beef to an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C). Use a food thermometer to check the temperature. This ensures your beef is safe to eat. Always cook your beef thoroughly.
Is grass-fed beef better than grain-fed beef?
Grass-fed beef often has more omega-3 fatty acids. It also contains more antioxidants. Some people prefer its taste. Both types of beef provide good protein and essential nutrients.

