
A crisp, juicy pear offers a simple delight. This delicious and versatile fruit packs essential nutrients. Exploring pear nutrition reveals surprising health power. Pears support gut health and heart protection, contributing to overall wellness. This guide uncovers the many health benefits of pears and their amazing benefits for your diet.
Key Takeaways
Pears are full of good nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and fiber. They have about 100 calories and no fat or cholesterol.
Eating pears helps your gut stay healthy because they have a lot of fiber. This fiber helps you digest food well and keeps your gut bacteria happy.
Pears are good for your heart. They have things that help lower blood pressure and keep your heart strong.
Pears can help you lose weight. The fiber in them makes you feel full, so you eat less food.
Pears can help lower your risk of getting type 2 diabetes. They do not make your blood sugar go up too fast.
Pear Nutrition: Key Facts
Pears offer more than just a sweet taste. They are a rich in nutrients and provide many health benefits. A medium-sized pear contains approximately 100 calories. It also has a high water content, which helps with refreshment and energy. Pears are naturally free from fat and cholesterol. This makes them an excellent choice for a healthy diet. This section explores the key facts about pear nutrition.
Vitamins and Minerals
Pears are a nutritious source of vitamins and minerals. They provide essential nutrients vital for body functions.
Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
Calcium | 16mg |
Iron | 0.3mg |
Potassium | 206mg |
Copper | 0.1mg |
Folate (B9) | 12µg |
Magnesium | 12mg |
Manganese | 0.1mg |
Niacin | 0.3mg |
Pantothenic acid | 0.1mg |
Phosphorus | 21mg |
Riboflavin (B2) | 0mg |
Selenium | 0.2µg |
Thiamine | 0mg |
Vitamin A | 2µg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.1mg |
Vitamin C | 8mg |
Vitamin E | 0.2mg |
Vitamin K | 8µg |
Zinc | 0.2mg |
Alpha carotene | 2µg |
Beta carotene | 25µg |
Choline | 9mg |
Fluoride | 4µg |
A medium-sized pear also provides important daily values. It offers:
Vitamin C: 9% of the Daily Value (DV)
Vitamin K: 7% of DV
Potassium: 4% of the DV
Copper: 16% of DV This serving also provides small amounts of folate, provitamin A, and niacin. These beneficial plant compounds contribute to overall wellness.
Fiber Content
Pears are packed with fiber, making them a true fiber powerhouse. Fiber is crucial for healthy digestion. Most American adults should consume between 21 and 38 grams of fiber per day. This amount depends on age and gender. One medium pear provides 6 grams of dietary fiber. This is about 21% of the Daily Value. This makes pears a good source of fiber. Including this tasty fiber in your diet helps meet daily requirements. The high fiber content in pears also supports gut health.
Carbohydrates and Fructose
Pears contain carbohydrates, primarily in the form of natural sugars like fructose. They also contain beneficial plant compounds. The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar. Pears have a relatively low glycemic index. This means they cause a slower, more gradual rise in blood sugar compared to high-GI foods.
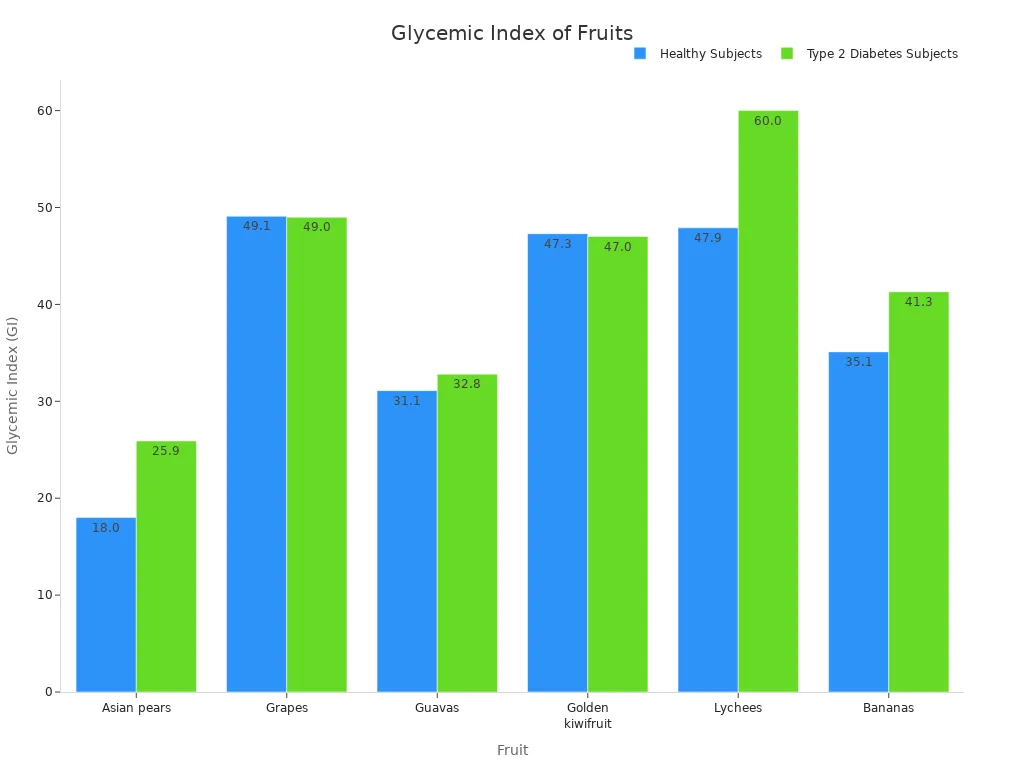
The chart above shows Asian pears have a low GI. For healthy subjects, the GI is 18.0 ± 5.4. For those with Type 2 diabetes, it is 25.9 ± 2.9. This low GI makes pears a suitable fruit choice for many people. This detailed look at pear nutrition highlights its many benefits.
Health Benefits of Pears
Pears offer many impressive health benefits of pears. They provide essential nutrients and powerful plant compounds. These benefits contribute to overall wellness and help protect the body.
Boost Gut Health
Pears are excellent for your digestive system. They promote gut health in several ways. Pears contain both insoluble and soluble dietary fiber. Insoluble fiber makes up about 71% of the total fiber in pears. It adds bulk to stool. This helps promote regular bowel movements and relieves constipation. Soluble fiber makes up about 29% of the total. The large intestine digests soluble fiber. It nourishes beneficial gut bacteria and can slow digestion. Pears also contain lignins. Gut bacteria convert lignins into lignans, which act as antioxidants.
Studies show pears can positively change gut bacteria. One study looked at different pear types. It found significant effects on gut microbiome composition. The ‘PremP009’ pear cultivar increased butyrate production. It also enriched Acidaminococcus intestini, a butyrate-producing species. This cultivar also enriched Akkermansia muciniphila. This may be due to pears having more insoluble fiber than apples. Another study used pear pomace soluble dietary fiber. It helped maintain gut microbiota diversity in mice on a high-fat diet. This intervention increased Lachnospiraceae_UCG-006, Akkermansia, and Bifidobacterium spp. These findings show pears support gut health and improves digestive health.
Boost Heart Health
Pears are truly heart smart. They boost heart health through various components. Pears contain flavonoids, dietary fiber, and antioxidants. These beneficial plant compounds work together to protect the cardiovascular system. Pears also provide potassium. Potassium helps reduce high blood pressure. A large clinical trial showed a link between eating pears and a lower risk of dying from heart disease.
Another study focused on middle-aged men and women with metabolic syndrome. Participants ate two medium-sized fresh pears daily for 12 weeks. This led to a significant reduction in systolic blood pressure and pulse pressure. The control group showed no such changes. This evidence confirms that pear consumption promotes heart health.
Lower Risk of Diabetes
Pears can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes. They have a low to moderate glycemic index (GI) of 38-50. This means they do not cause a rapid spike in blood sugar. Their high dietary fiber content also helps. Fiber slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. This regulates blood sugar levels. Pears contain natural sugars, but their low GI and fiber make them a safe choice for people with diabetes when eaten in moderation.
Research shows pear pomace ethanol extract (PPE) can improve insulin sensitivity. It activates the insulin signaling pathway. This was seen in both lab studies and animal models. PPE also helped reduce body weight and fat in animals on a high-fat diet. It showed hypolipidemic effects and reduced insulin resistance. These benefits come from polyphenols and triterpenes in pear pomace. These compounds have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory actions. Eating pears can therefore lower the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Help You Lose Weight
Pears can help you lose weight. Their fiber content makes you feel full longer. This feeling of fullness, or satiety, helps reduce overall calorie intake. Reducing calorie intake is key for managing body weight. Studies show fiber consumption predicts weight loss, even without strict calorie counting.
A clinical trial compared apples, pears, and oat cookies in overweight women. Pears, like other fruits, have a lower energy density than oat cookies. This means you can eat a larger volume of pears for fewer calories. This lower energy density led to a significant reduction in energy intake and body weight. Eating low-energy-dense foods like pears helps promote weight loss by increasing satiety without adding extra calories.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Pears possess strong anti-inflammatory properties. They are rich in flavonoid antioxidants. These compounds help ease inflammation throughout the body. This may decrease your risk of various diseases. Pears also contain vitamin C, which is known for its anti-inflammatory effects. Polyphenol antioxidants in pears protect against oxidative damage. Oxidative damage often links to inflammation. These beneficial plant compounds contribute to overall wellness by fighting inflammation.
Cancer Protection
Pears may offer cancer protection. They contain bioactive compounds that fight cancer. A study in Northern Italy found that dietary proanthocyanidins, found in pears, may protect against pancreatic cancer. Danish women who regularly ate pears as part of a healthy diet showed a lower risk of colorectal cancer. Data from the NIH-AARP study also suggested pears protect against esophageal cancer. These findings highlight the potential anticancer effects of pears.
Pears contain many compounds being studied for their anti-cancer mechanisms. These include arbutin, oleanolic acid, ursolic acid, chlorogenic acid, epicatechin, and rutin. Pear pomace also contains phenolic acids, flavonoids, and triterpenes. These beneficial plant compounds can inhibit MMP-9 activity. Dysregulated MMP-9 activity plays a role in cancer. Nutraceuticals from pears offer a non-invasive way to protect against certain diseases, including cancer.
Pear Varieties and Uses

Pears come in many types, each offering unique flavors and textures. People enjoy them fresh, in cooking, or paired with other ingredients.
Common Pear Types
Several popular pear varieties exist. Bartlett pears are bell-shaped. They have a sweet flavor and a smooth, buttery texture. Their skin changes from green to yellow as they ripen. Anjou pears are refreshingly sweet and juicy, often with a hint of lemon-lime. They have an egg shape. Green Anjou pears stay firm as they ripen and do not change color much. Red Anjou pears are dark maroon. Bosc pears have a distinct bronze color and an elongated neck. They offer a crisp, woodsy texture with honey sweetness. Their firm, dense flesh makes them ideal for cooking.
Fresh Eating and Snacking
Many pear varieties are perfect for eating fresh. Comice pears are juicy, sweet, and aromatic. People often serve them on cheese boards or in salads. Forelle and Seckel pears are small and sweet, excellent for snacking. Starkrimson pears are juicy and sweet with a floral aroma, great in salads. Asian pears are crisp, juicy, and refreshing when eaten fresh. These pears provide a good source of dietary fiber.
Cooking and Baking Uses
Some pears excel in cooked dishes. Bosc pears hold their shape well. This makes them ideal for baking, poaching, and roasting. They are great for tarts and pies. Anjou pears are versatile for baking and poaching. Bartlett pears are excellent for canning, preserves, and purees. Concorde pears maintain their firm texture when cooked.
Flavor Pairings
Pears pair well with many flavors. For savory dishes, they complement goat’s cream cheese, truffle oil, and honey. They also go well with Roquefort cheese, Gorgonzola, radicchio, and walnuts. Sweet pairings include cranberries, cinnamon, honey, and brown sugar. Spices like cardamom, cloves, and nutmeg also enhance their flavor. Honey and rosemary create a lovely savory-sweet combination.
Selecting, Storing, and Preparing Pears
Knowing how to choose, store, and prepare pears ensures you enjoy their best flavor and texture. These simple steps help maximize your pear experience.
Choosing Ripe Pears
Pears do not ripen on the tree. They ripen best after picking. A perfectly ripe pear feels soft at the neck. Gently press near the stem. If it yields to light pressure, the pear is ready. For Asian pears, look for specific signs.
Aspect | Perfectly Ripe Asian Pear |
|---|---|
Color | Golden, light brown with slight warmth; no bright green patches |
Firmness | Firm but has slight give near stem; remains firm and crisp |
Aroma | Subtle sweet pear fragrance; gentle pear aroma |
Skin Texture | Dry, slightly waxy finish; smooth and matte, not wrinkly or overly glossy |
Weight | Feels heavy for its size, signaling juiciness |
Ripening Tips
Pears often need a few days to ripen after purchase. You can speed up this process at home.
Paper Bag Method: Place pears in a paper bag. Leave the bag on your kitchen counter. Pears will ripen in about 2-4 days. The natural gases they produce get trapped, which helps them ripen faster. Check them daily to prevent over-ripening. Avoid plastic bags.
Paper Bag with Ripe Apples Method: For even quicker ripening, add a couple of ripe apples to the paper bag with your pears. Ripe apples release ethylene gas, which significantly speeds up ripening. Pears can ripen in 1-3 days using this method. Check them daily.
Storage Best Practices
Proper storage extends the life of your pears. Unripe pears store well in a cool, dark place. Once ripe, refrigerate them.
Store pears at a temperature between -1°C to 0°C (30°F to 32°F).
Maintain high humidity, specifically 90–95%.
To achieve high humidity, place fruit in unsealed or perforated plastic bags. You can also use an open pan of water in your storage area.
Keep pears at a constant 34 to 36 degrees F (1 to 2 degrees C) for the longest shelf life.
Simple Preparation
Pears are easy to prepare. Wash them thoroughly under cool running water. You can eat the skin, as it contains beneficial fiber. If you prefer, peel the pear. Cut the pear in half or quarters. Remove the core and seeds. Enjoy pears sliced in salads, added to oatmeal, or simply eaten out of hand.
Pears offer impressive pear nutrition. They provide essential fiber, vitamins, and minerals. These components support gut health, heart health, and overall wellness. Readers should embrace pears daily. They are a delicious and healthful addition to any diet. Enjoy them fresh, baked, or cooked. Their versatility is remarkable. Discover the sweet facts and amazing benefits of pears today.
FAQ
Are pears good for losing weight?
Yes, pears can help with weight loss. They contain high fiber content. Fiber makes you feel full longer. This reduces overall calorie intake. Eating pears helps manage body weight effectively.
Can people with diabetes eat pears?
Yes, people with diabetes can eat pears in moderation. Pears have a low to moderate glycemic index. This means they do not cause a rapid rise in blood sugar. Their fiber content also helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Should I eat the skin of a pear?
Yes, you should eat the skin of a pear. The skin contains beneficial fiber and antioxidants. These nutrients contribute to gut health and overall wellness. Always wash the pear thoroughly before eating.
How do you know when a pear is ripe?
A pear is ripe when it feels soft near the stem. Gently press the neck of the pear. If it yields to light pressure, it is ready to eat. Pears ripen best after picking.
Do pears have anti-inflammatory properties?
Yes, pears have anti-inflammatory properties. They are rich in flavonoid antioxidants. These compounds help reduce inflammation throughout the body. Pears also contain vitamin C, which fights inflammation.

