
“Are refried beans healthy?” Many people ask this question. Their healthiness largely depends on preparation and ingredients. This post explores refried beans nutrition. It debunks common myths. We offer ways to enjoy refried beans as part of a healthy diet. Refried beans offer great versatility. They hold cultural significance. Understanding their nutritional value helps. You can make healthy refried beans.
Key Takeaways
Refried beans are good for you. They have protein and fiber. These help your body stay healthy.
Refried beans help your digestion. They also help your heart. They can keep your blood sugar steady.
Some refried beans have a lot of salt and fat. Read labels to pick healthier ones. Or, make them at home.
Make refried beans healthy at home. Use good oils. Add herbs and spices. This makes them taste great without extra salt.
What Are Refried Beans: The “Refried” Myth

Many people believe refried beans undergo a double frying process. This is a common misconception. The term “refried” comes from the Spanish “well-fried beans.” This phrase actually means “well-fried” or “thoroughly fried,” not “fried again.” The preparation involves only one frying step. This step gives the beans their distinct flavor and texture.
Understanding Preparation
The creation of refried beans begins with cooking dried beans until they become very soft. Pinto beans or black beans are common choices. Cooks then mash these soft beans. They often leave some beans whole for texture. Next, they fry the mashed beans in a pan with a type of fat. This frying process blends the flavors and creates a creamy consistency. The heat also helps to evaporate excess moisture. This results in a thicker, richer product.
Common Ingredients
Traditional refried beans use simple, wholesome ingredients. The base is always dried or canned beans, most often pinto beans. Cooks then add fat for flavor and texture. This fat can be lard, corn oil, canola oil, vegetable oil, or bacon grease. Aromatics like smashed garlic and quartered onion are essential. They provide a deep, savory base. Water helps achieve the right consistency during cooking. Salt enhances all the flavors. Some recipes also include bay leaf, Mexican oregano, or jalapeño for extra spice. These ingredients combine to create the beloved taste of refried beans.
Refried Beans Nutrition: Key Facts
Understanding the refried beans nutrition profile helps consumers make informed dietary choices. Refried beans offer a rich source of various nutrients. This section provides a detailed nutrition snapshot of a typical serving.
Macronutrients: Protein, Carbs, Fiber
Refried beans are a powerhouse of macronutrients. A typical serving provides approximately 13 grams of protein. This makes them a valuable plant-based protein source. They are also high in protein.
Nutrient | Amount per serving |
|---|---|
Protein | 6-7 grams |
The carbohydrate content stands at about 35 grams. A significant portion of this comes from fiber. Refried beans contain around 10 grams of fiber per serving. This high fiber content contributes to digestive health. This amount also represents a substantial part of the recommended daily intake for dietary fiber. The combination of protein and fiber helps promote satiety.
Essential Micronutrients
Beyond macronutrients, refried beans deliver many essential vitamins and minerals. They offer a comprehensive nutrition snapshot of vital compounds. These essential nutrients support various bodily functions.
Refried beans contain several essential micronutrients. Key vitamins include:
Vitamin C: 6.0mg (7% DV)
Vitamin B6: 0.1mg (8% DV)
Vitamin B1 (Thiamin): 0.1mg (6% DV)
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): 0.1mg (6% DV)
Vitamin B3 (Niacin): 0.4mg (2% DV)
Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid): 0.2mg (4% DV)
Vitamin K: 2.1µg (2% DV)
Vitamin E: 0.1mg (1% DV)
Choline: 21.2mg (4% DV)
Important minerals found in refried beans are:
Sodium: 370.0mg (25% DV)
Copper: 0.1mg (14% DV)
Manganese: 0.3mg (13% DV)
Selenium: 5.8µg (11% DV)
Phosphorus: 92.0mg (9% DV)
Iron: 1.4mg (8% DV)
Magnesium: 35.0mg (8% DV)
Potassium: 319.0mg (8% DV)
Zinc: 0.6mg (4% DV)
Calcium: 29.0mg (2% DV)
Refried beans are a source of various essential micronutrients. Notable vitamins include:
Vitamin C (Ascorbic acid): 14.8 mg (16% DV)
Vitamin B6: 0.255 mg (15% DV)
Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): 0.195 mg (15% DV)
Choline: 55.1 mg (10% DV)
Vitamin B3 (Niacin): 0.907 mg (6% DV)
Folate, DFE (Vitamin B9): 26.00 mcg (6% DV)
Vitamin K: 5.5 mcg (5% DV)
Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol): 0.23 mg (2% DV)
Key minerals present are:
Copper: 0.34 mg (38% DV)
Iron: 3.74 mg (21% DV)
Calcium: 75.40 mg (6% DV)
These nutrients contribute to the overall nutritional benefits of refried beans.
Calories and Portions
A typical serving of refried beans contains approximately 234 calories. This calorie density means portion control is important. Consumers should consider serving sizes when adding refried beans to their meals.
Here are common serving sizes:
Del Real Foods Refried Beans: 1/2 cup (130mg).
Santiago® Refried Beans: Approximately 1/2 cup dry (41g) or 130g prepared.
Understanding the nutrition of refried beans allows individuals to incorporate them wisely into a balanced diet. The protein and fiber content helps manage hunger.
The Health Benefits of Refried Beans
Refried beans offer many health benefits. They provide essential nutrients. These nutrients include iron, zinc, and magnesium. Iron helps transport oxygen in the body. Zinc supports the immune system. Magnesium is important for many body functions. Vitamin C also helps the body absorb iron. These nutritional benefits make refried beans a valuable part of a healthy diet.
Digestive Health Support
Refried beans are an excellent source of fiber. This high fiber content greatly supports digestive health. Beans contain oligosaccharides. These are a type of indigestible fiber. Beneficial bacteria in the large intestine ferment these oligosaccharides. This fermentation process means oligosaccharides act as prebiotics. Prebiotics support the growth of good gut bacteria. Good gut bacteria are linked to many health benefits. These benefits include reduced inflammation, better immune function, and increased calcium absorption. The dietary fiber in refried beans also helps keep bowel movements regular.
Heart Health and Cholesterol
Refried beans contribute to good heart health. The soluble and insoluble fibers in legumes help lower cholesterol absorption in the gut. These fibers also promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. This contributes to cholesterol reduction. Pinto beans, often used for refried beans, contain special compounds. These include polyphenols, flavonoids, and saponins. These active agents are known to lower cholesterol. Pinto beans reduce high cholesterol by decreasing cholesterol production in the liver. They also reduce cholesterol absorption in the intestines. These are important health benefits for your heart.
Blood Sugar Stabilization
Refried beans have a positive impact on blood glucose levels. They help with blood sugar control. Refried beans contain phenolic compounds. These compounds reduce blood glucose and high insulin levels. The protein content in beans helps slow down how quickly blood sugar rises. Studies show that whole black beans can significantly reduce insulin in adults with metabolic syndrome. Regular consumption of common beans is linked to a lower risk of type-2 diabetes. A study on 56 diabetic subjects showed that eating black beans regularly for three months reduces their glucose levels.
Dr. Sanjay Kapoor, an endocrinologist based in Delhi, emphasizes the importance of choosing complex carbohydrates like beans in a diabetic diet. “Refried beans, when prepared with healthy fats and eaten in moderation, can be part of a balanced meal. The fiber content in beans helps to regulate blood sugar and provide long-lasting energy without causing sharp spikes.”
Refried beans generally have a positive effect on blood glucose levels after eating. Their fiber and protein content slow digestion. This helps prevent rapid spikes in blood sugar after meals. They are a low-glycemic food. This means they have a much gentler effect on blood sugar than many other carbohydrate-rich foods. The glycemic load of beans is typically under 10. This is considered low. It makes them an excellent option for blood sugar control. The physical form of refried beans also affects digestion speed. Partially mashed beans help slow down the rise in blood sugar. These are significant health benefits.
Plant-Based Protein Source
Refried beans are an excellent plant-based protein source. They provide a substantial amount of protein. This makes them a great option for vegetarians, vegans, and anyone looking to increase their plant-based intake. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. It also helps make enzymes and hormones. The protein in refried beans contributes to feelings of fullness. This is another one of their many benefits.
Weight Management and Satiety
Refried beans are good for weight loss and weight management. Their high fiber and protein content helps you feel full for longer. This can reduce overall calorie intake. Refried beans are good for weight loss because they promote satiety. This means you feel satisfied after eating them. This helps prevent overeating.
Here is how baked beans compare to other foods in terms of satiety:
Baked beans: 168%
White bread: 100%
French fries: 116%
White pasta: 119%
Brown Rice: 132%
White rice: 138%
Grain bread: 154%
Whole meal bread: 157%
Brown pasta: 188%
Potatoes, boiled: 323%
The high satiety index of refried beans shows their benefits for weight management. They help you feel full and satisfied. This makes them a smart choice for those aiming for good for weight loss. These health benefits make refried beans a valuable addition to your diet.
Potential Downsides of Refried Beans
While refried beans offer many health benefits, consumers should be aware of potential downsides. These concerns often relate to how manufacturers prepare them. Understanding these aspects helps people make healthier choices.
High Sodium Concerns
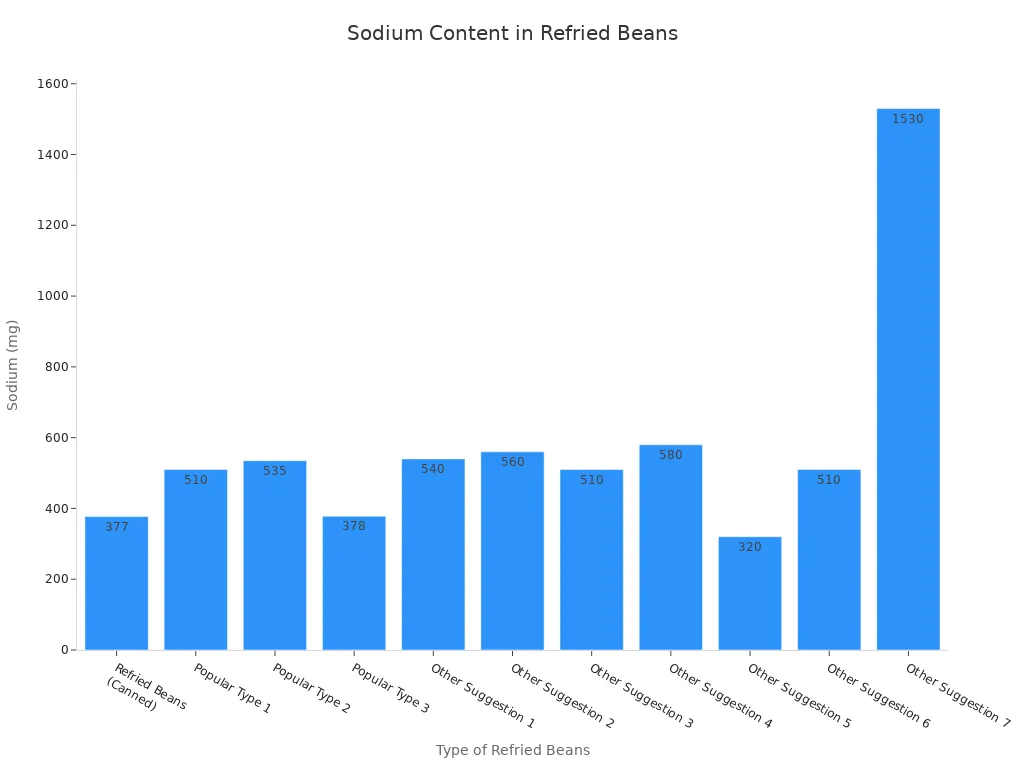
Many commercially prepared refried beans contain high levels of sodium. High sodium intake can contribute to hypertension. It also increases cardiovascular risks. For example, many canned refried beans contain over 900 mg of sodium per cup. This amount is more than half the daily ideal intake. Traditional refried beans can contain 553 mg more sodium per cup compared to low-sodium alternatives. This shows a significant difference.
Here is a look at sodium content in various refried beans:
Type of Refried Beans (1/2 cup serving) | Sodium (mg) |
|---|---|
Refried Beans (Canned) | 377 |
Popular Type 1 | 510 |
Popular Type 2 | 535 |
Popular Type 3 | 378 |
Other Suggestion 1 | 540 |
Other Suggestion 2 | 560 |
Other Suggestion 3 | 510 |
Other Suggestion 4 | 580 |
Other Suggestion 5 | 320 |
Other Suggestion 6 | 510 |
Other Suggestion 7 | 1530 |
Saturated Fat Content
The fat content in refried beans varies greatly. Some recipes use lard or other animal fats. These fats increase the saturated fat content. For instance, refried beans made with animal fat or meat drippings can contain 4.7g of saturated fat per cup. General refried beans typically have about 1.5g of saturated fat per cup. High saturated fat intake can negatively affect heart health.
Calorie Density
Refried beans are calorie-dense. A typical serving contains around 230-240 calories per cup. This means portion control is important. While they are good for weight loss due to fiber and protein, excessive portions can lead to higher calorie intake. The calorie density is about 1.4 cal/g, which equals 140 calories per 100g. This density helps with satiety but requires mindful eating for effective weight management.
Additives in Canned Varieties
Canned refried beans often contain more than just beans, water, and salt. Manufacturers sometimes add other ingredients. Common additives include:
Lard
Soybean oil (as an alternative to lard)
These additives can change the nutritional profile. Consumers should read labels carefully. This helps them choose healthier options.
Making Healthy Refried Beans
Consumers can easily make refried beans a healthy choice. Thoughtful preparation and smart shopping are key. These methods allow people to enjoy the nutritional benefits of beans.
Smart Shopping: Label Reading
When buying canned refried beans, always read the labels carefully. Look for products with lower sodium and fat content. Many brands offer healthier versions. This simple step helps manage your intake of less desirable ingredients.
Low-Sodium and Low-Fat Options
Choosing low-sodium varieties of refried beans significantly reduces sodium intake. Traditional refried beans often contain much more sodium than reduced-sodium versions. For example, Amy’s Organic Vegetarian Traditional Refried Beans, Light in Sodium, contain 210 mg of sodium. Amy’s Regular Traditional Refried Beans have 450 mg. One cup of traditional refried beans can contain 553 mg more sodium than the same portion of reduced-sodium refried beans. It is wise to select low-sodium options when purchasing pre-made refried beans.
Healthy Home Preparation
Preparing refried beans at home gives you complete control over the ingredients. You can choose healthier fats and reduce salt. This ensures your refried beans align with your dietary goals. Making them from scratch is often the best way to create healthy refried beans.
Reducing Salt and Fats
When cooking at home, you can easily reduce salt and unhealthy fats. Instead of traditional lard or butter, use healthier oils. Avocado oil or olive oil are excellent choices. You only need a few tablespoons of these oils. This eliminates the need for a full stick of butter often found in other recipes. You can also control the amount of salt you add.
Flavor with Herbs and Spices
Enhance the flavor of your refried beans without adding extra sodium. Many herbs and spices offer delicious alternatives. For heat, use cayenne pepper or dried chiles. Mild spices like paprika, oregano, garlic powder, onion powder, cumin, and coriander add depth. Fresh aromatics such as garlic and onion also boost flavor. Consider fresh chiles like jalapeño or serrano for a kick. Aromatic herbs like cilantro, rosemary, and thyme provide fresh notes. Epazote is a unique herb often used in Mexican cuisine. You can also create homemade chili powder blends without salt.
Flavorful Uses for Refried Beans

Versatile Meal Ideas
Refried beans are a staple in many kitchens. They offer incredible versatility for various meals. People enjoy refried beans in countless dishes. They serve as a hearty base or a flavorful topping. Some common uses of refried beans include:
Mexican Pizza: A delicious twist on a classic, using refried beans as a savory layer.
Four Bean Chili: Refried beans add thickness and richness to this comforting stew.
Beef Tacos: They provide a creamy, satisfying filling alongside seasoned beef.
Layered Taco Dip: Refried beans form the essential first layer of this popular appetizer. These examples show how easily this versatile ingredient fits into different culinary creations. They add flavor and substance to any meal. Their creamy texture also binds ingredients together effectively.
Healthy Swaps and Recipes
You can make refried beans even healthier with simple ingredient swaps. These changes enhance both nutrition and taste.
Substitute pinto beans with black beans. This offers a different flavor and texture. Black beans also provide a slightly higher antioxidant content.
Incorporate finely chopped bell peppers (any color) or jalapeño peppers with the onion. This adds flavor and texture. Bell peppers bring vitamins and a subtle sweetness. Jalapeños offer a pleasant heat. Remove seeds and membranes from jalapeños to control spiciness. These healthy swaps make your refried beans more nutritious. They also introduce new dimensions of taste. Experiment with different vegetables to find your favorite combinations.
Pairing with Whole Grains
Pairing refried beans with whole grains creates a complete and balanced meal. Whole grains provide complex carbohydrates and additional fiber. This combination boosts satiety and provides sustained energy. Serve refried beans with brown rice, quinoa, or whole wheat tortillas. This enhances the nutritional value of your meal. For example, a burrito bowl with brown rice, this bean dish, and fresh salsa makes a satisfying lunch. You can also spread them on whole-grain toast for a quick breakfast. These common uses of refried beans make them a healthy and delicious choice for any time of day. They contribute to a well-rounded diet.
Refried beans can be a highly nutritious and beneficial food. Thoughtful preparation makes them healthy. Understanding refried beans nutrition helps consumers make informed choices. Making conscious decisions about ingredients ensures healthy refried beans. This knowledge answers the question, “are refried beans healthy?” Enjoy refried beans as part of a balanced, healthy diet. Their versatility makes them a delicious and healthy choice. Informed food choices empower everyone.
FAQ
Are refried beans good for weight loss?
Yes, refried beans can support weight loss. They contain high amounts of fiber and protein. These nutrients help people feel full for longer. This reduces overall calorie intake. Portion control remains important due to their calorie density.
Can people with diabetes eat refried beans?
People with diabetes can eat refried beans. They have a low glycemic index. This means they help stabilize blood sugar levels. The fiber and protein slow digestion. Choose low-sodium and low-fat versions for better health benefits.
What is the healthiest way to eat refried beans?
The healthiest way involves homemade preparation. Use healthy oils like olive or avocado oil. Reduce salt content. Enhance flavor with herbs and spices instead of excess sodium. Pair them with whole grains for a complete meal. 🌿
Do refried beans have a lot of sodium?
Many commercially prepared refried beans contain high sodium levels. Some brands have over 900 mg per cup. High sodium intake can affect blood pressure. Look for low-sodium options or prepare them at home to control salt.

