
Shea nut oil comes from the nuts of the shea tree, found mostly in Africa. You see this natural oil in many skin and hair products today. People around the world choose shea nut oil because it offers benefits that come from its rich, natural ingredients. The global market for shea nut oil keeps growing, as shown below.
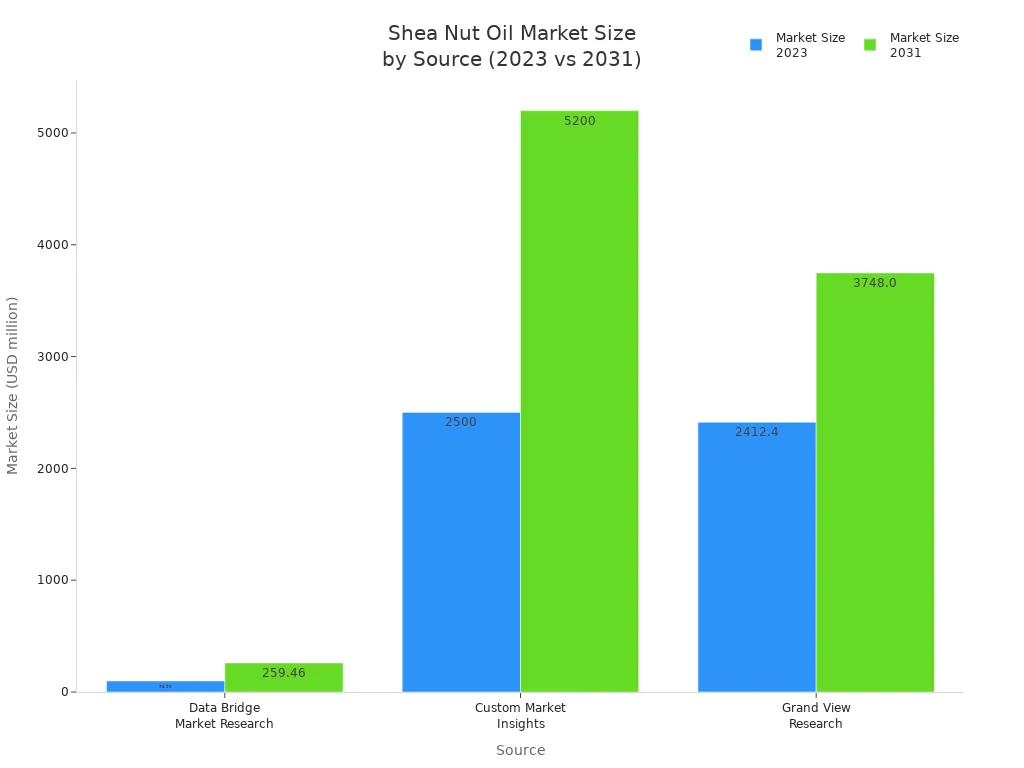
You can explore how natural products like shea nut oil fit into your daily routine.
Key Takeaways
Shea nut oil is a natural moisturizer that hydrates and softens skin, making it ideal for daily skincare routines.
Rich in fatty acids and antioxidants, shea nut oil supports skin repair, reduces inflammation, and promotes overall skin health.
Using shea nut oil in hair care helps lock in moisture, reduce breakage, and improve scalp health for stronger, shinier hair.
Shea nut oil is versatile; it can be used topically for skin and hair or included in cooking for its nutritional benefits.
Always perform a patch test before using shea nut oil, especially if you have allergies or sensitive skin.
Shea Nut Oil Overview

What Is Shea Nut Oil
Shea nut oil comes from the nuts of the shea tree, which grows wild in Africa. You find shea trees in regions where they mature over at least 20 years and produce about 20 kilograms of nuts each year. People use traditional methods to extract shea oil, such as de-pulping, boiling, drying, de-husking, and manual water extraction. Modern techniques include mechanical screw press expellers and solvent extraction, which help get more shea nut carrier oil from each nut.
Shea nut oil has a rich history. Ancient Egyptians used shea butter oil for skin protection and healing. Cleopatra’s reign saw shea butter as a prized ingredient for beauty and wellness. African women have relied on shea butter and shea nut carrier oil for centuries to moisturize and protect their skin and hair. Shea butter continues to help infants by reducing infection risk for umbilical wounds.
Shea nut oil production supports local communities. Women often lead the process, gaining economic opportunities and helping their families.
Shea Nut Carrier Oil Properties
Shea nut carrier oil stands out among carrier oils. You notice its mild scent, which makes it perfect for blending with essential oils. Unlike essential oils, shea nut carrier oil comes from fatty plant parts and does not overpower with fragrance. Shea nut carrier oil contains essential vitamins and antioxidants, which help heal and rejuvenate skin and hair. Shea butter oil also provides a soothing effect.
Shea nut carrier oil can go rancid over time, so you need to store it properly. Shea butter oil remains a favorite in African beauty routines because of its high fatty acid and vitamin content.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Environmental Sustainability | Shea trees grow wild and do not need fertilizers or pesticides, making shea butter production eco-friendly. |
Community Development | Profits from shea butter production support schools and health clinics. |
Cultural Heritage | Shea butter production preserves traditions and adapts to modern economies. |
Shea nut carrier oil offers you a natural choice for skin and hair care, while supporting communities and the environment.
Nutrition
Fatty Acids
Shea nut oil contains a unique blend of fatty acids that help support your skin and overall health. You find four main fatty acids in shea nut oil: palmitic, stearic, oleic, and linoleic acids. Each fatty acid plays a different role in skin care and nutrition. Stearic acid helps create a smooth texture and protects your skin barrier. Oleic acid keeps your skin soft and helps lock in moisture. Linoleic acid supports skin repair and helps balance oil production. Palmitic acid adds stability to shea nut oil and helps your skin stay hydrated.
Here is a table showing the fatty acid profile of shea nut oil:
Fatty Acid | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
Palmitic | 6.93 ± 1.68 |
Stearic | 38.83 ± 1.86 |
Oleic | 46.76 ± 0.82 |
Linoleic | 7.48 ± 0.35 |
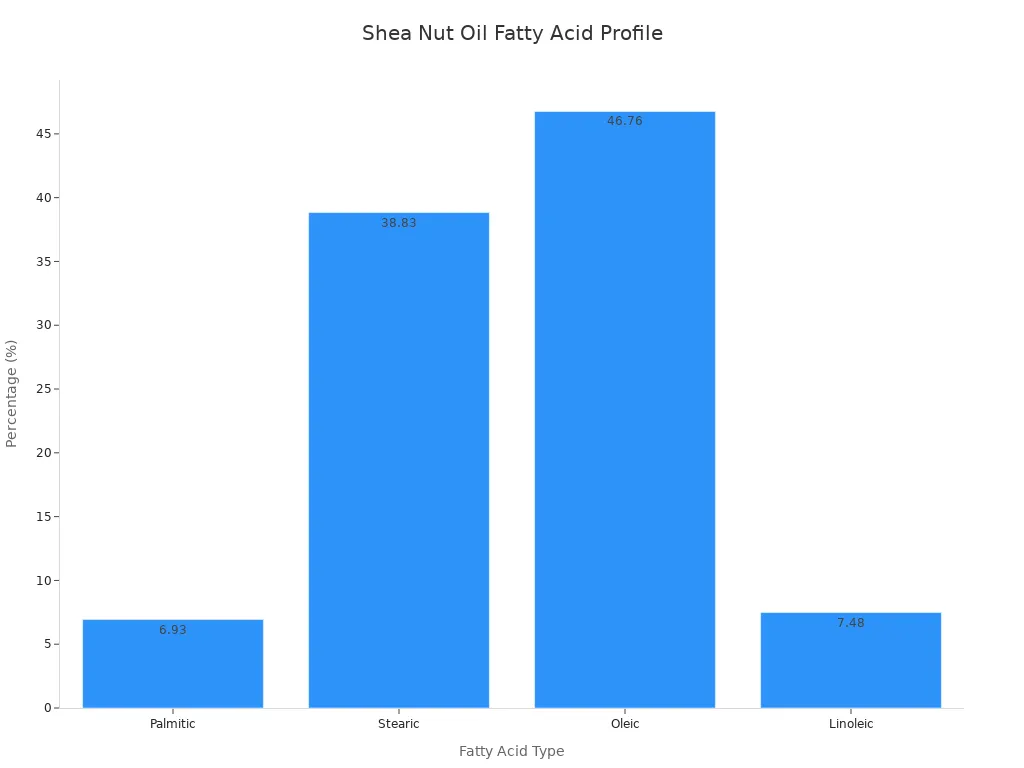
You see that shea nut oil has a high amount of oleic and stearic acids. These fatty acids help nourish your skin and support your health. Populations that use shea nut oil in their diets benefit from its rich stearic acid (52%) and oleic acid (30%) content. These nutrients help provide energy and support heart health.
Vitamin E and Antioxidants
Shea nut oil contains vitamin E and other antioxidants that protect your skin and body from damage. Vitamin E, also called tocopherol, helps fight free radicals and keeps your skin looking healthy. Shea nut oil has both α-tocopherol and β-tocopherol, which work together to boost antioxidant activity.
Here is a table comparing the vitamin E content in different types of shea oil:
Type of Shea Oil | α-Tocopherol (mg/100 g) | β-Tocopherol (mg/100 g) | Total Tocopherols (mg/100 g) |
|---|---|---|---|
Crude Shea Butter | 8.52 ± 0.03 | 1.04 ± 0.02 | 10.06 ± 0.06 |
Refined Shea Stearin | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 0.21 ± 0.04 | 1.27 ± 0.07 |
Refined Shea Olein | 8.28 ± 0.03 | 0.97 ± 0.05 | 9.25 ± 0.02 |
Mixture | 4.58 ± 0.08 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 4.94 ± 0.11 |
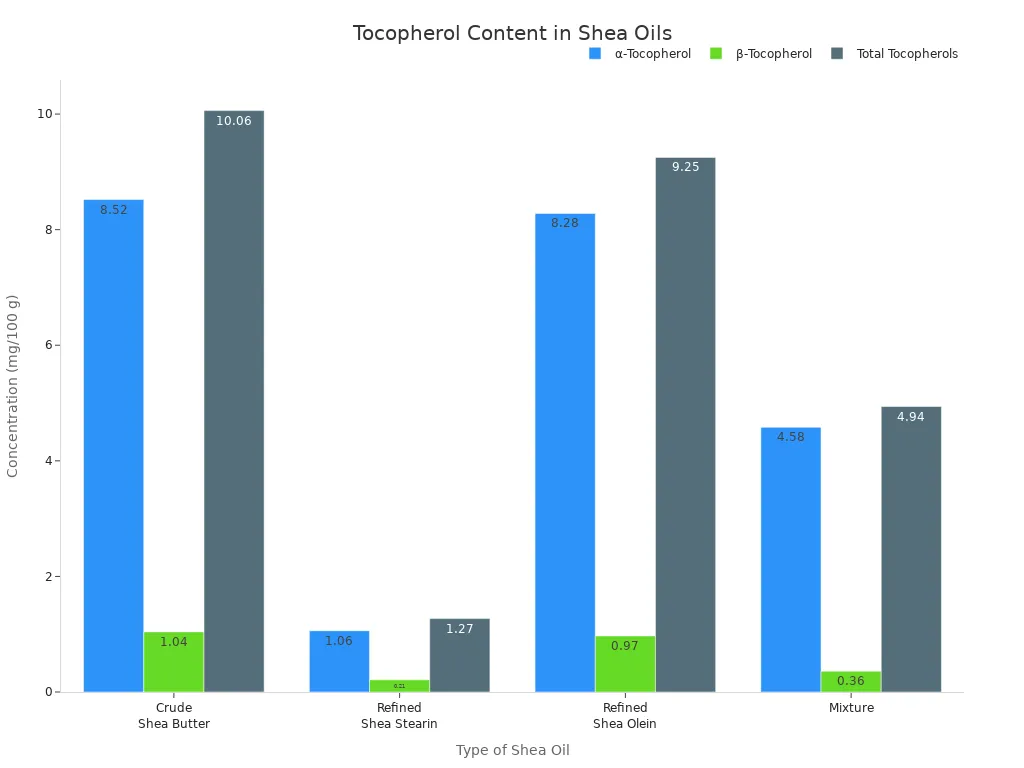
You get extra protection for your skin when you use shea nut oil with high tocopherol levels. Antioxidant compounds like catechins also help reduce inflammation and support your health. Shea nut oil’s nutrients make it valuable for both topical and dietary uses. You can enjoy softer skin and better overall health by including shea nut oil in your routine.
Benefits
Skin Benefits
Shea nut oil offers many benefits for your skin. You can use it as a natural moisturizer to help keep your skin soft and smooth. Shea butter for skin is popular because it acts as an emollient, filling gaps in dry skin and helping you retain moisture. The moisturizing effects of shea nut oil come from its rich blend of fatty acids, including stearic, oleic, and linoleic acids. These ingredients help protect your skin barrier and prevent water loss.
Shea nut oil increases skin hydration and improves softness.
It seals moisture into your skin and supports barrier function, similar to ceramides.
Topical shea butter helps heal lesions and improves skin appearance for people with eczema.
You can use shea nut oil in your skin care routine to soothe irritation and calm redness. Linoleic acid helps reduce inflammation and supports lipid synthesis, while stearic acid prevents dryness and enhances skin barrier function. Oleic acid provides hydration and antioxidant protection. Shea nut oil is a natural emollient, making it ideal for skin conditioning and daily moisturizing.
Shea nut oil calms eczema symptoms and helps your skin recover from dryness. You can rely on its soothing and healing properties for sensitive skin.
Shea butter benefits include reducing inflammation and supporting wound healing. The antioxidants in shea nut oil help protect your skin from environmental stress. You can enjoy healthier, more radiant skin by using shea nut oil as a moisturizer.
Hair Benefits
Shea nut oil provides important benefits for your hair. You can use it to lock in moisture and prevent breakage. Shea nut oil reduces water loss by up to 80%, which helps keep your hair strong and healthy. Vitamins A and E in shea nut oil offer antioxidant protection, supporting scalp health and promoting hair growth.
Shea nut oil strengthens hair and reduces breakage.
It contains triterpene esters that reduce scalp inflammation and create better conditions for hair growth.
You can use shea nut oil in hot oil treatments for deep moisturization and conditioning.
Shea nut oil has a lightweight texture that absorbs quickly, making it suitable for all hair types. The essential fatty acids, such as oleic and linoleic acids, penetrate the hair shaft and deliver hydration. Shea nut oil provides conditioning and helps you maintain soft, manageable hair.
Tip: You can use shea nut oil as a natural conditioner or add it to your hot oil treatment for extra hydration and shine.
Shea nut oil supports hair health by delivering nutrients and antioxidants. You can use it to improve scalp condition, reduce inflammation, and promote hair growth. Shea nut oil is a natural choice for conditioning and strengthening your hair.
Other Benefits
Shea nut oil offers additional health benefits beyond skin and hair care. You can use it to promote wound healing and protect your skin from environmental irritants. Shea nut oil has anti-inflammatory effects that help reduce swelling and support tissue remodeling.
Shea nut oil helps shield wounds and supports healing.
It provides basic sun protection, absorbing UV rays and offering a low SPF of 4.
Shea butter can enhance the effectiveness of other UV filters in sunscreen formulations.
Study Focus | Findings | SPF Value |
|---|---|---|
Use of Vegetable Oils to Improve the Sun Protection Factor of Sunscreen Formulations | Investigated the SPF of shea oil in sunscreen formulations | Increased SPF with 1% shea oil compared to formulations with only organic UV-filters |
Shea nut oil contains compounds that inhibit inflammatory pathways and reduce skin irritant reactions. You can use it to manage symptoms of osteoarthritis and reduce pain and stiffness. Shea nut oil supports your overall wellness by decreasing inflammatory markers and promoting healing.
Study | Findings |
|---|---|
Journal of Nutrition & Food Sciences | Shea butter inhibits inflammatory pathways (Inos, Cox-2, Cytokines) via the NF-kB pathway in macrophage cells. It reduces skin irritant reactions and shows anti-inflammatory effects through α-amyrin. |
Validating Efficacy of Shea Nut Oil Extract in Knee Osteoarthritis Patients | Significant improvement in knee OA symptoms after 16 weeks, with reductions in inflammatory markers (TNF-alpha, hsCRP, IL-6) by over 20%. |
Anti-inflammatory activity of fatty extract of Vitellaria paradoxa Kernel | Topical application inhibited acute edema and systemic inflammation in rodent models, supporting traditional use for arthritis. |
You can rely on shea nut oil for its natural healing and anti-inflammatory properties. Shea nut oil supports your skin, hair, and overall health, making it a valuable addition to your daily routine.
Uses

Topical Uses
You can find many uses for shea nut oil in your daily skin and hair care. People often apply shea nut oil directly to the skin to moisturize and soothe dryness. Shea butter works well in homemade soaps because of its saponification value and nutty aroma. You may see shea nut oil added to creams and lotions, making up 3-20% of the formula. Shea nut oil also helps treat irritated scalp and dry hair. Many people use it as a hot oil treatment, sometimes mixing it with essential oils for extra benefits.
Moisturizes skin and reduces irritation.
Diminishes dry hair and speeds up hair growth.
Treats scalp issues and supports healthy hair.
Tip: You can use shea nut oil as a natural conditioner for hair or as a soothing balm for skin.
Culinary Uses
Shea nut oil has a long history in West African cooking. You may see shea butter used as a traditional cooking oil in many dishes. Shea nut oil provides healthy fats, protein, fiber, and important vitamins and minerals. The table below shows some nutritional benefits:
Nutritional Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
High in Healthy Fats | Rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, beneficial for health. |
Protein Source | Contains significant protein, useful for dietary inclusion. |
Dietary Fiber | Provides fiber, important for digestive health and blood sugar regulation. |
Vitamins and Minerals | Contains vitamins E, K, B-vitamins, and minerals like calcium and iron. |
Traditional Cooking Oil | Used in traditional cooking in West Africa for various dishes. |
You can enjoy shea nut oil in your diet as a natural source of nutrition.
Choosing and Storing Shea Nut Oil
You should look for high-quality shea nut oil when shopping. Bright, solidified shea butter with a smooth texture is preferred. The drying method affects the oil’s yield and quality. Roasting or boiling shea nuts improves the stability and oil yield. The table below compares different drying methods:
Drying Method | Yield (%) | Density (g/cm³) | Iodine Value (g/100g) | Free Fatty Acid (%) | Peroxide Value (mEq/100g) | Impurity (%) | Refractive Index | Saponification Value (mgKOH/g) | Unsaponifiable Fractions (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Sun Drying | 20-37 | 0.894-0.980 | 23-34.6 | 3.99-6.91 | 2.42-5.20 | 1.0-2.00 | 1.465-1.468 | 178.12-293 | 5.07-9.31 |
Traditional Oven Drying | 21-42 | 0.896-0.991 | 26.6-40.43 | 4.62-7.51 | 2.99-4.95 | 0.69-2.0 | 1.465-1.469 | 173.4-287.4 | 4.78-9.2 |
Manually Operated Rotary | 25-32 | 0.898-0.988 | 22.01-46.020 | 3.05-7.32 | 2.99-5.82 | 1.05-2.00 | 1.4650-1.469 | 154.1-268.5 | 1.15-8.72 |
To keep shea nut oil fresh, follow these best practices:
Store shea butter in an airtight container.
Keep it in a cool, dry place away from sunlight.
Use a glass jar to prevent chemical reactions.
Refrigerate in hot climates, but always use an airtight container.
Store at room temperature if refrigeration is not possible.
Place in a pantry away from heat and moisture.
Note: Proper storage helps maintain the natural potency and shelf life of shea nut oil.
Safety
Side Effects
You may wonder what side effects can occur when you use shea nut oil. Most people find shea nut oil safe for skin and hair. However, some individuals may experience unwanted reactions.
People with latex allergies can develop skin irritation, redness, swelling, or itching after using shea nut oil.
In rare cases, contact dermatitis may appear. This condition causes red, itchy patches on your skin.
If you have eczema, you should watch for any signs of irritation when trying new products.
Note: Always perform a patch test before using shea nut oil on large areas of your skin. Apply a small amount to your inner arm and wait 24 hours to check for any reaction.
Research shows that allergic reactions to shea nut oil are extremely rare. The FDA classifies shea nut as a true nut, but studies have not reported allergies to shea nut or shea butter. Even children with peanut or tree nut allergies usually tolerate shea nut oil. Refined shea nut oil does not contain detectable proteins that trigger allergies.
Who Should Avoid
You should know what groups need to avoid shea nut oil. While most people can use it safely, some should take extra care.
Individuals with nut allergies, especially tree nut allergies, should use caution. Although no cases of allergy to shea nut oil have been reported, the risk may still exist.
People with latex allergies should avoid shea nut oil, as it can cause dermatitis or worsen eczema symptoms.
If you have a history of severe dermatitis or eczema, consult a healthcare professional before using new skin products.
Group | Reason for Caution |
|---|---|
Nut allergy sufferers | Possible cross-reactivity, rare risk |
Latex allergy sufferers | Increased chance of skin irritation |
Eczema or dermatitis | Risk of flare-ups or irritation |
Tip: Do not use shea nut oil as a substitute for prescribed treatments for eczema or dermatitis. Always seek advice from a healthcare provider if you have concerns.
Proper storage and sourcing from trusted suppliers can help reduce risks. You should always measure ingredients accurately and keep blends in airtight containers away from sunlight.
You discover many benefits when you use shea nut oil. The table below shows what you gain for nutrition, skin, and hair:
Benefit Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
Nutritional | Rich in unsaturated fatty acids like Oleic Acid and Linoleic Acid. |
Skin | Moisturizes, softens, and soothes; promotes repair and reduces inflammation. |
Hair | Conditions, protects, and adds shine; reduces frizz. |
You can try shea in your daily routine for healthy skin or hair. Always check with a professional if you have allergies or concerns.
Using natural oils supports self-care and helps you choose eco-friendly products.
FAQ
What is the difference between shea nut oil and shea butter?
Shea nut oil comes from the liquid part of the shea nut. Shea butter is the solid, creamy part. You use shea nut oil for lighter moisturization. Shea butter works best for deep hydration.
What can you use shea nut oil for?
You can use shea nut oil to moisturize skin, condition hair, and soothe irritation. Many people add it to lotions, shampoos, and homemade beauty products. Some use it in cooking for healthy fats.
What does shea nut oil smell like?
Shea nut oil has a mild, nutty scent. The aroma is gentle and does not overpower other ingredients. You can blend it easily with essential oils for a custom fragrance.
What should you look for when buying shea nut oil?
You should choose shea nut oil that is pure, unrefined, and free from additives. Look for a smooth texture and a light color. Check the label for sourcing information and expiration date.
What are the main nutrients in shea nut oil?
Shea nut oil contains fatty acids like oleic and stearic acid. You also get vitamin E and antioxidants. These nutrients help protect your skin and support overall health.

