
Do you love the tangy, salty kick of feta cheese? This versatile cheese is a true star of the Mediterranean diet. The global market for feta cheese is substantial, reaching an estimated $15.3 billion in 2025, showing its widespread appeal. Beyond its unique flavor, feta offers significant protein and calcium. You gain great feta cheese nutrition from this delicious feta. How exactly can this flavorful cheese benefit your health?
Key Takeaways
Feta cheese is a good source of protein and calcium. These nutrients help build strong bones and muscles.
Feta cheese has many vitamins and minerals. These include B vitamins, iron, and zinc, which support overall health.
Feta cheese can help with gut health and weight management. It contains good bacteria and makes you feel full.
You can enjoy feta cheese in many ways. Add it to salads, main dishes, or snacks for a tangy flavor.
Choose authentic Greek feta cheese. It is made with traditional methods and has the best quality.
What is Feta Cheese

Origin and History
Feta cheese has a long and rich history. Its origins trace back to ancient Greece. You can find mythological accounts, like those in Homer’s Odyssey, describing a Cyclops named Polyphemus making and storing cheese from sheep’s milk. Many consider this the mythological beginning of cheese making. Historically, cheese production in Greece dates back at least 8,000 years. The god Aristaios even received credit for the art of cheesemaking in Greek mythology. During Byzantine times, people knew a cheese called ‘prosphatos’, meaning fresh. This cheese was especially popular in Crete. The practice of preserving cheese in brine appeared as early as the 2nd century BC. The name ‘feta’ itself, meaning ‘slice’ in Greek, appeared in the 17th century. This likely referred to cutting the cheese into pieces for storage in barrels. By the 19th century, ‘feta’ became the common name for this traditional greek cheese.
Traditional Production
Making authentic feta cheese follows specific steps. Producers primarily use sheep’s milk, or a mixture with up to 30% goat’s milk. They heat the milk and add a bacterial culture. This helps convert lactose into lactic acid. Next, they add rennet to coagulate the milk. Once the milk sets, they cut the curd into cubes. The curds then drain in molds. Workers turn the molds regularly to help with drainage. After draining, they dry-salt the cheese blocks. Finally, they place the cheese into barrels or containers with brine, a salty solution. This allows the cheese to ripen for at least two months. This traditional process gives feta its rich taste and aroma. It also ensures a thick but creamy texture.
Types of Feta
Not all feta cheese is the same. The European Union granted ‘feta’ Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status in 2002. This means only cheese made in specific regions of Greece, using traditional methods and specific milk types, can bear the name. This authentic greek feta comes from areas like Thrace, Macedonia, and the Peloponnese. It uses 100% sheep milk or up to 30% goat’s milk. You will find it packed in brine.
Other countries also produce similar cheeses. French feta, often from producers like Valbreso, uses sheep’s milk and has a creamier, milder taste. Bulgarian feta, also called ‘sirene’ cheese, can use sheep’s, goat’s, or cow’s milk. It offers a firm yet creamy and very tangy flavor. American feta often uses cow’s milk. It typically has a drier texture and a milder flavor compared to the more traditional mediterranean cheese. You might find it not packed in brine. Each type offers a unique experience, but only the Greek version is true feta.
Feta Cheese Nutrition
Feta cheese offers a robust nutritional profile. You gain many essential nutrients when you include this delicious cheese in your diet. A typical serving of feta cheese provides a good balance of macronutrients and a wealth of micronutrients. You get significant protein and calcium, along with various vitamins and minerals.
Protein Content
Feta cheese is a good source of protein. A standard 1-ounce (28 grams) serving of feta cheese typically contains between 4 to 6 grams of protein. Some brands might offer 4 to 5 grams, while others provide 6 to 7 grams. The specific amount depends on the brand and the milk blend used. One source even indicates that feta cheese contains 11 grams of protein per serving. This high protein content supports muscle growth and repair. It also helps you feel full, which can aid in weight management.
Calcium and Minerals
You will find feta cheese rich in calcium. A 1-ounce serving provides around 70mg of calcium, which is about 5% of your daily recommended intake. This calcium strengthens your bones and teeth. It also supports proper muscle and nerve function. Beyond calcium, feta cheese contains many other important minerals. You get phosphorus, which is vital for bone and kidney health. It also includes iron, magnesium, manganese, selenium, zinc, and potassium. These minerals play crucial roles in various bodily functions, from energy production to immune support.
Vitamins and Other Nutrients
Feta cheese is a good source of B vitamins. You receive Vitamin B12, which is essential for brain function and red blood cell production. Riboflavin (B2) helps convert food into energy. You also get Vitamin B6. Other vitamins present in feta include Vitamin A, Vitamin K, Folate, and Pantothenic acid. These nutrients contribute to your overall health.
Here is a detailed look at the vitamins and minerals you find in feta cheese:
Micronutrient | Amount (per serving) |
|---|---|
Calcium | 739.5 mg |
Copper | 0.05 mg |
Folate | 48 mcg |
Folate dfe | 48 mg |
Folate food | 48 mcg |
Iron | 0.98 mg |
Magnesium | 28.5 mg |
Manganese | 0.03 mg |
Niacin | 1.49 mg |
Pantothenic acid | 1.44 mg |
Phosphorus | 505.5 mg |
Potassium | 93 mg |
Riboflavin | 1.26 mg |
Selenium | 22.5 mcg |
Sodium | 1674 mg |
Thiamin | 0.23 mg |
Vitamin A | 633 IU |
Vitamin A RAE | 187.5 mg |
Vitamin B12 | 2.54 mcg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.63 mg |
Vitamin D | 24 mcg |
Vitamin D3 Cholecalciferol | 0.6 mcg |
Vitamin D D2 and D3 | 0.6 mg |
Vitamin E | 0.27 mg |
Vitamin K | 2.7 mcg |
Zinc | 4.32 mg |
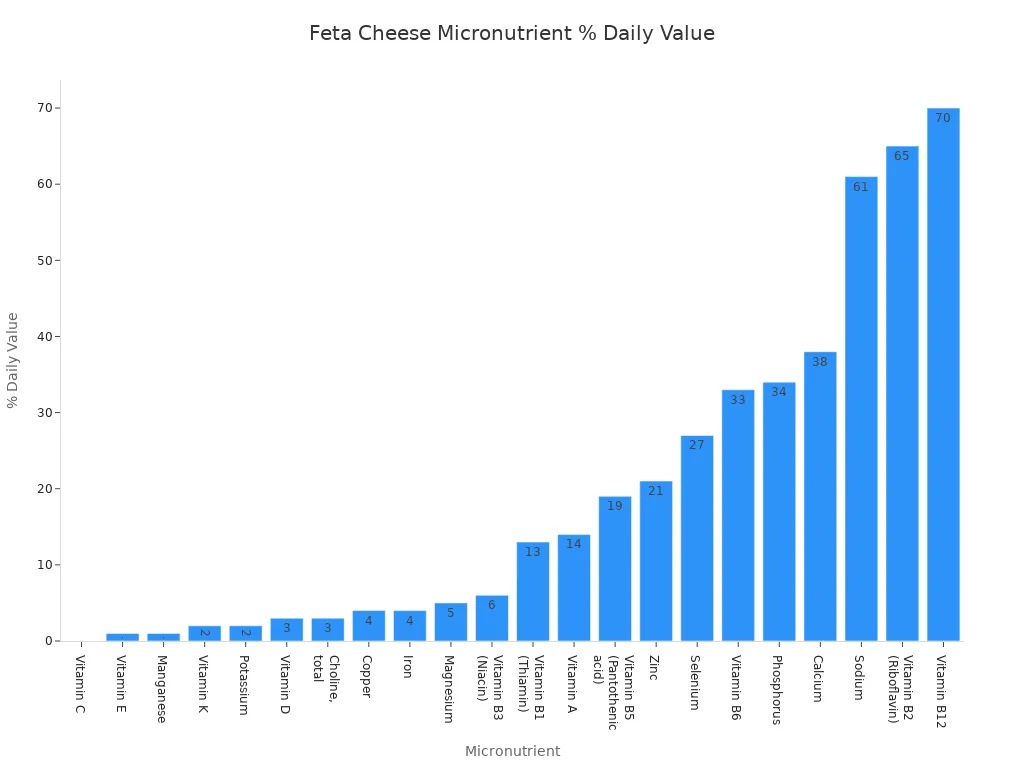
Calorie and Fat Profile
Feta cheese is a relatively low-calorie and low-fat cheese compared to many other aged cheeses. A typical 1-ounce serving contains about 70-76 calories. This makes it a lighter option for your meals. It has about 5.3 to 6 grams of fat per serving. A significant portion of this total fat is saturated fat. You should consume it in moderation for heart health.
Feta cheese is also suitable for low-carb diets. It contains only 1.1 to 1.56 grams of carbohydrates per 1-ounce serving, with about 0.45 grams of sugar. This provides flavor and essential nutrients without significantly increasing your carb intake. However, you should be aware of its sodium content. Feta cheese typically contains around 312 mg of sodium per serving. This can be a concern if you monitor your sodium intake.
Benefits of Feta Cheese
You gain many advantages when you include feta cheese in your diet. These are the key benefits of feta cheese that contribute to your overall well-being.
Bone Health Support
Feta cheese offers significant benefits for your bones. You get essential nutrients that strengthen your skeletal system. Feta cheese contains calcium. This mineral is crucial for strong bones and teeth. It helps reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Food Item | Serving Size | Calcium Content |
|---|---|---|
Feta Cheese | 4 oz | 140 mg |
This table shows you how much calcium you get from feta. Adequate calcium intake maintains bone density and strength. It also reduces the risk of fractures. Feta cheese is also a good source of phosphorus. This mineral is essential for bone health. Feta cheese contains higher levels of calcium compared to many other cheeses. This is vital for healthy teeth and bones. The combined consumption of phosphorus and calcium improves bone density. It also helps prevent osteoporosis. You can get this important calcium from dairy products like feta.
Muscle Maintenance
Feta cheese helps you maintain your muscles. It is a good source of protein. This nutrient is crucial for your overall health. Protein is the building block for muscles, skin, and blood. You need adequate dietary intake for cells and tissues to grow, develop, and repair. Muscles require this nutrient to increase and maintain their mass. If you want to maximize muscle growth and enhance recovery, eat a high-protein snack. Do this within 30 to 60 minutes after strength training. Feta cheese provides this important nutrient.
Gut Health
Feta cheese can support your gut health. It contains beneficial bacteria. These bacteria are good for your digestive system. You find lactic acid bacteria (LAB) in feta. Other beneficial bacteria include:
Bifidobacterium
Streptococci
Streptococcus thermophilus
Lactobacillus bulgaricus
Bifidobacterium bifidum
Bifidobacterium longum
These probiotics help balance your gut microbiome. A healthy gut contributes to better digestion and overall well-being.
Weight Management
Feta cheese can assist you with weight management. Its nutritional composition helps you feel full. Feta cheese has a high protein content. This helps you feel satisfied after eating. It is also a lighter option compared to many other cheeses. Feta is lower in calories and fat. This can aid in weight loss when you eat it in moderation. Feta also contains conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). This compound is beneficial for improving body composition. These are clear benefits of feta.
Antioxidant Properties
Feta cheese offers antioxidant properties. These properties protect your body cells. Feta cheese is a good source of vitamin B2 (riboflavin). This vitamin has links to a lower risk of degenerative eye diseases. These include cataracts, keratoconus, and glaucoma. Riboflavin provides antioxidant protection against aging, migraines, and fatigue. Feta also contains histidine and vitamin B6. When combined, these form histamines. Histamines contribute to immune strength. This is especially true when you consume them with other antioxidant-rich foods. You gain these health benefits from the feta cheese nutrition.
Potential Downsides
While feta cheese offers many benefits, you should also know its potential downsides. Understanding these aspects helps you make informed dietary choices.
Sodium Levels
Feta cheese is quite salty. Producers salt and brine it during production. A standard 1/4 cup serving of crumbled feta cheese contains around 400-418 mg of sodium. This high sodium content is a concern if you have high blood pressure or kidney issues. Excessive sodium intake can contribute to hypertension. Hypertension is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease. It can also lead to kidney damage by overworking your kidneys. High sodium intake may also negatively impact calcium retention. This can increase your risk of osteoporosis. You might also experience bloating and water retention. These are some of the potential risks of feta cheese if you consume too much.
Lactose Considerations
If you are lactose intolerant, you might wonder about feta cheese. Feta cheese is generally low in lactose. Hard and mature cheeses like feta contain almost zero lactose. This is due to their production process.
Dairy product | Lactose content /serve | Serving size | Lactose classification/serve |
|---|---|---|---|
Feta Cheese | 0.13g | 125g | Low |
Cheddar (tasty) Cheese | 0.04g | 40g or 2 slices | Low |
Camembert Cheese | 0.04g | 40g | Low |
Brie Cheese | 0.04g | 40g | Low |
Cottage cheese | 0.7g | 36g | Low |
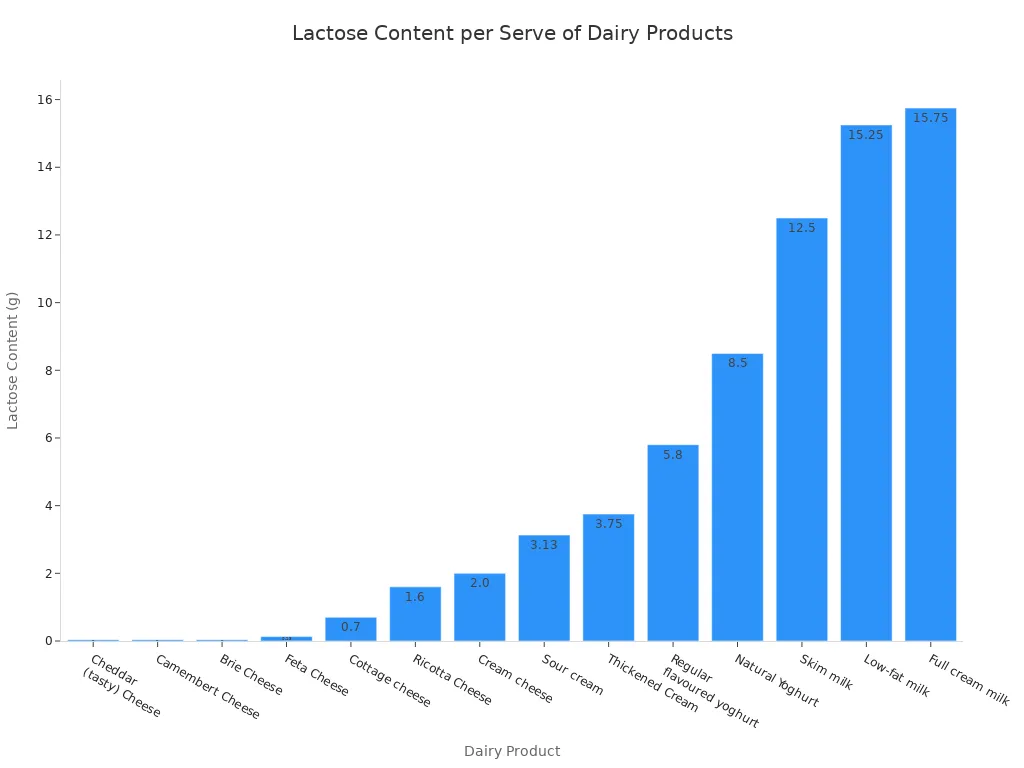
You can see feta cheese has a very low lactose content per serving. This makes it a more tolerable option for many people with lactose sensitivity.
Saturated Fat
Feta cheese contains saturated fat. One ounce of feta has about 4-6 grams of fat. A significant portion of this is saturated fat. You should consume saturated fat in moderation for heart health. It may contribute to high cholesterol if you eat too much. Saturated fat is a high contributor to daily nutrient intake from prepacked feta cheese. Your intake may even exceed the recommended daily limits. This is another of the potential risks of feta cheese if you do not watch your portions.
Choosing Quality
You want to choose high-quality feta. Authentic Greek feta carries a red and yellow label marked ‘DOP’ (Protected Designation of Origin). This means it comes from specific regions in Greece. It uses 100% sheep’s milk or a blend with up to 30% goat’s milk. High-quality feta cheese should always be packed in brine. It has a distinct salty and sour aroma. It also has a white color and a dry, crumbly texture. Avoid commercial feta cheeses with many preservatives. Traditional, high-quality feta is a better choice for natural ingredients and better health.
How to Enjoy Feta Cheese

You can easily add feta cheese to many meals. This versatile cheese brings a salty, tangy flavor. It enhances both simple and complex dishes. You will find many delicious feta cheese recipes.
In Salads and Sides
Feta cheese shines in salads. You can crumble it over a classic greek salad. This adds a creamy texture and sharp taste. Try it with fresh tomatoes, cucumbers, olives, and red onion. You can also toss feta with roasted vegetables. Think about zucchini, bell peppers, or eggplant. It makes a simple side dish more exciting. Feta also pairs well with spinach or kale salads.
Main Dish Integration
You can integrate feta into your main courses. It makes a great feta cheese dish. Stir it into pasta dishes with cherry tomatoes and basil. You can also bake it into savory tarts or quiches. Top grilled chicken or fish with crumbled feta for extra flavor. This is a good way to incorporate dairy into your protein. You can even add it to scrambled eggs or omelets for a quick breakfast. These feta cheese recipes are simple to make.
Snacks and Appetizers
Feta is perfect for snacks and appetizers. Spread it on crackers or crusty bread. Serve it with a drizzle of olive oil and a sprinkle of oregano. You can also cube feta and serve it alongside olives and cherry tomatoes. This creates a quick and healthy snack. You can also make small skewers with feta, watermelon, and mint. This offers a refreshing bite.
Mediterranean Pairings
Feta is a cornerstone of mediterranean cuisine. It naturally complements many mediterranean dishes. Pair it with olives, sun-dried tomatoes, and fresh herbs like dill or parsley. You can also combine this cheese with chickpeas or lentils. This creates a hearty and flavorful meal. Feta’s distinct taste elevates these simple ingredients.
Feta cheese offers excellent feta cheese nutrition. You get significant protein and calcium from this delicious cheese. Feta is a healthy and balanced diet component. It fits perfectly into the Mediterranean diet. You can easily incorporate feta into your meals. This adds both flavor and health benefits. Choose feta cheese to make informed decisions for your overall health.
FAQ
Is feta cheese healthy for you?
Yes, feta cheese offers many health benefits. You get protein, calcium, and essential vitamins. It supports bone health and muscle maintenance. Enjoy it in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Can you eat feta cheese if you are lactose intolerant?
Many people with lactose intolerance can eat feta cheese. It has a very low lactose content. The cheesemaking process removes most of the lactose. You might find it easier to digest than other dairy products.
How do you store feta cheese properly?
You should store feta cheese in its brine. Keep it in an airtight container in your refrigerator. This keeps the cheese fresh and moist. It also preserves its distinct flavor.
What makes authentic Greek feta special?
Authentic Greek feta has Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status. This means it comes from specific Greek regions. Producers use traditional methods and specific milk types. It uses sheep’s milk, or a blend with up to 30% goat’s milk.

