
The culinary landscape is witnessing a surge in interest for plant-based alternatives, yet traditional beef continues to hold its strong appeal. Many consumers are exploring options like plant-based burgers or other vegan ground meat, with 19% of households purchasing plant-based burgers in 2021. This blog objectively compares Beyond Beef Vs Ground Beef across nutrition, ingredients, and flavor. Readers frequently inquire about which is healthier, what they contain, and how they truly perform in the kitchen and on the plate. We offer an in-depth analysis to help individuals make informed food choices for their burgers and other beef dishes based on their priorities.
Key Takeaways
Beyond Beef is a plant-based option. It has less saturated fat and more fiber than ground beef. It contains no cholesterol.
Ground beef offers important vitamins and minerals. These include B vitamins, iron, and zinc. It has a traditional meat taste.
Beyond Beef uses plant proteins like peas and avocado oil for fat. Ground beef comes from cows. It is a mix of muscle and fat.
Beyond Beef can taste like a fast-food burger. Its texture is similar to real ground beef. Some people might find it too realistic.
Your choice depends on your health goals and taste. Consider if you want plant-based food or traditional meat. Both options have different benefits.
Nutritional Comparison: Beyond Beef vs Ground Beef

Understanding the nutritional profiles of Beyond Beef and traditional ground beef helps consumers make informed choices. Both options offer significant protein, but they differ in fat content, micronutrients, and other key metrics. Many consider Beyond Burger patties to offer similar nutritional benefits and drawbacks to an 85% lean ground beef patty, particularly regarding protein and saturated fat.
Protein Content
Protein is a vital nutrient for muscle building and repair. Beyond Beef provides a substantial amount of plant-based protein. A single serving of Beyond Burger contains 20g of plant-based protein. Another source indicates 21g of plant-based protein per serving. This protein comes from peas, brown rice, and mung beans. Traditional ground beef also offers high-quality protein. An 80/20 ground beef patty typically contains around 20-25g of animal protein per serving. Both options are excellent sources of protein, making them suitable for those looking to meet their daily protein needs.
Fat Content
Fat content is a major difference between Beyond Beef and ground beef. Beyond Meat ground often has fewer calories, less total fat, and less saturated fat compared to some ground beef options. For example, Beyond Meat ground contains 230 calories, 14g total fat, and 5g saturated fat. In contrast, some ground beef options can have 332 calories, 30g total fat, and 11g saturated fat. Beyond Meat also contains no trans fat, which is a type of unhealthy fat. The latest Beyond Meat IV recipe further improves this, containing 75% less saturated fat and no cholesterol compared to 80/20 ground beef. Traditional beef, especially fattier cuts, can be high in saturated fat and cholesterol.
Sodium and Micronutrients
Sodium levels can vary between the two products. Beyond Meat generally has less saturated fat compared to beef, but it may have more sodium. Consumers should check labels for specific sodium content. When it comes to micronutrients, ground beef is a rich source of essential vitamins and minerals.
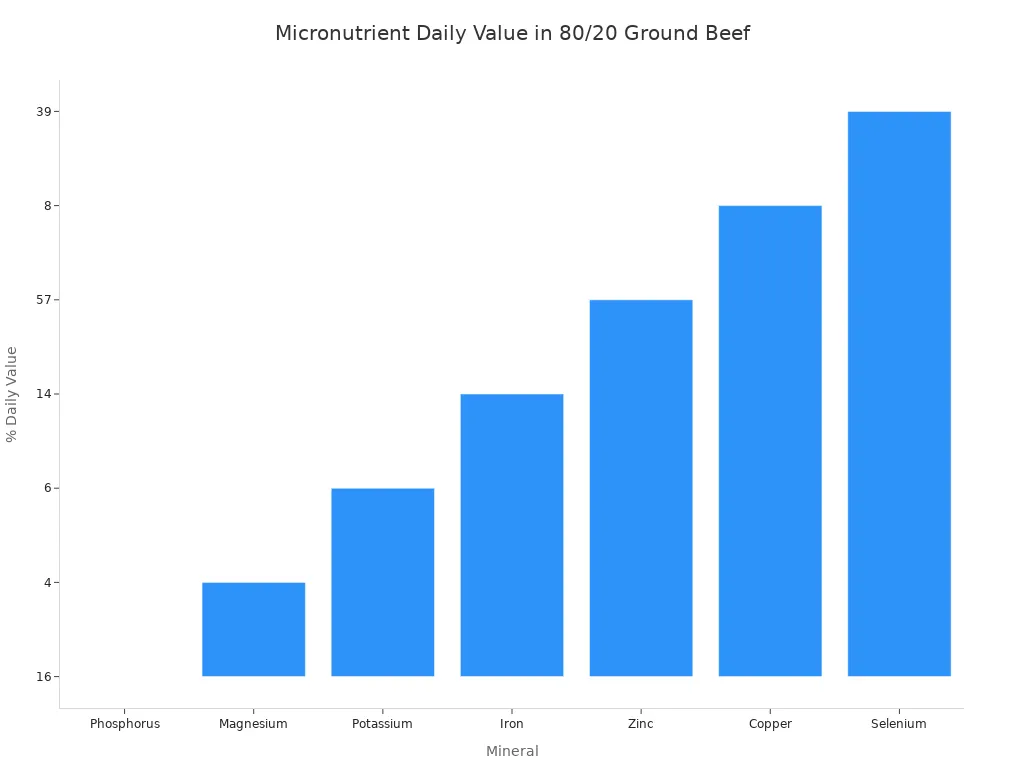
Here are some key minerals found in 80/20 ground beef:
Mineral | Amount per 100g (cooked) | % Daily Value (DV) |
|---|---|---|
Major Minerals | ||
Phosphorus | 194.1 mg | 16% |
Magnesium | 18.8 mg | 4% |
Potassium | 303.5 mg | 6% |
Trace Minerals | ||
Iron | 2.48 mg | 14% |
Zinc | 6.25 mg | 57% |
Copper | 0.07 mg | 8% |
Manganese | 0.01 mg | <1% |
Selenium | 21.2 mcg | 39% |
Ground beef is also a rich source of B-complex vitamins. These vitamins are crucial for energy metabolism and neurological function. It is a potent dietary source of Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin). This vitamin is essential for nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation. A 3-ounce serving provides approximately 97-99% of the Daily Value. It is also an excellent source of Niacin (Vitamin B3). Niacin is vital for converting food into energy and supporting nervous, digestive, and skin health, providing about 29% of the DV per 3-ounce serving. Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) supports amino acid metabolism, red blood cell production, and neurotransmitter creation. It contributes about 18% of the DV per 3-ounce serving. Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) is critical for energy production and cellular function, providing about 12% of the DV per 3-ounce serving. Additionally, ground beef contains Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5), Thiamin (Vitamin B1), Folate (Vitamin B9), and Choline. Choline is an essential nutrient for brain health, liver function, and nerve signaling. It contains modest amounts of Vitamin E and Vitamin K, but no Vitamin C or D.
Beyond Beef, as a plant-based product, does not naturally contain all the same micronutrients as beef. However, manufacturers often fortify plant-based burgers and other plant-based alternatives with certain vitamins and minerals, such as B12 and iron, to match the nutrition of animal products.
Calories and Fiber
Calorie counts also show some differences. Beyond Beef Plant-based Ground contains 230 calories per serving. Beyond Meat Beyond Beef Crumbles, Beefy, have 80 calories per 1/2 cup (1.9 oz) serving. As mentioned earlier, some ground beef options can have around 332 calories.
A significant nutritional advantage of Beyond Beef is its fiber content. Since it is plant-based, Beyond Beef contains dietary fiber, which is important for digestive health. Traditional ground beef, being an animal product, contains no dietary fiber. This is a key distinction for those looking to increase their fiber intake.
Ingredient Breakdown
This section details what each product contains. It also explains how manufacturers make these items.
Beyond Beef’s Plant Components
Beyond Beef uses various plant-based ingredients. These ingredients create a meat-like texture and flavor. Its primary protein sources include peas, lentils, brown rice, and faba beans. These plant proteins provide the bulk of the product’s structure. For fat, the fourth generation of Beyond Beef uses avocado oil. This change helped reduce saturated fat significantly. Manufacturers explicitly state the product is ‘Made with avocado oil.’ They removed coconut and canola oils from the ingredient list. Beyond Meat adds plant-based fats to mimic the juiciness and flavor of animal beef.
Ground Beef’s Animal Composition
Ground beef comes from cows. It is a blend of various cuts. These cuts often come from tougher parts of the cow. Common sources include chuck, round, and brisket. Butchers also mix fat trimmings with lean meats. This creates specific fat percentages, like 80/20 ground beef. Ground beef primarily consists of skeletal muscle and trimmings. It can also include head meat trimmings and cheek meat. Sometimes, added beef fat helps achieve the desired hamburger texture.
Additives and Processing
Beyond Beef contains several additives. These help with texture, flavor, and preservation. Common additives include cellulose, methylcellulose, and potato starch. Methylcellulose is a plant fiber derivative. It helps hold ingredients together, similar to cornstarch. The FDA recognizes methylcellulose as safe for food use. Other additives are natural flavor, salt, and beet juice extract. The processing of Beyond Beef involves separating protein from peas. Canola and coconut oils are produced by crushing or solvent methods. Manufacturing occurs in cool environments, below 40 degrees Fahrenheit.
Allergen Considerations
Consumers should know about potential allergens in plant-based burgers. Beyond Beef uses pea protein as its main protein source. Some people can have allergic reactions to peas or related legumes. Coconut oil is also present for fats and texture. A small number of people may experience allergic symptoms from coconut. Rice protein and canola oil are also ingredients. Natural flavors can sometimes contain traces from common allergens like soy or wheat. Manufacturers formulate these plant-based burgers without major allergens. However, cross-contamination risks can exist during manufacturing. This means traces of soy, gluten, or nuts might be present.
Taste Test: Flavor, Texture, Cooking

This section compares the sensory experience and cooking performance of Beyond Beef and traditional ground beef. A thorough taste test reveals key differences in how these products perform on the plate and in the kitchen.
Flavor Profile
Beyond Beef offers a distinct flavour profile. Many describe it as nutty, smoky-charcoal, musty/earthy, buttery, and having fat-like aromatics. It also presents salty and umami notes. However, Beyond Beef has a decreased beef flavor intensity compared to ground beef. The Beyond Burger also showed reduced meat flavor intensity and flavor liking when compared to a traditional beef burger.
When eaten plain, Beyond Beef does not taste exactly like beef. One tester suggested it could pass for a fast-food burger. When served as a burger with condiments, it surprisingly tasted very much like real ground beef, even fooling a tester. Despite this, it often lacks the depth and richness of traditional beef. It can have a slight hint of artificial smoke flavour.
Consumer Reports noted Beyond Beef as one of the most meat-like among plant-based burgers. While none were identical to real meat, some came very close. An expert panel judged at least one in each category to be very good, attributing this to the overall flavour profile giving the impression of meat. A study from Kansas State University offered a contrasting view. It indicated consumers rated plant-based alternatives “very low” for flavor and “extremely dry.” Only 18% of consumers expressed willingness to purchase them.
The study concluded these plant-based alternatives are “very different than ground beef” and do not compete on the same level playing field in terms of taste. The ground ‘beef’ version of Beyond Beef has a similar taste to their Beyond Beef burgers but is described as less smoky.
Texture and Mouthfeel
The texture of Beyond Beef also presents unique characteristics. When raw, Beyond Meat feels like many small nubs held together. This contrasts with Impossible meat, which feels mostly smooth. Once cooked, Beyond’s previously mentioned ‘nubs’ maintain a similar texture. This makes the overall texture comparable to real ground beef. Upon cooking, the Beyond Beef’s fat renders and sizzles. The burger changes from red to brown. When bitten into, the texture is exactly like beef, specifically loose and tender, with speckled pockets of juicy fat. One reviewer found it almost “too realistic” due to its beef-like texture. They, as a vegetarian, would avoid it because it was too much like real meat in texture, appearance, and flavor.
Cooking Performance
Cooking Beyond Beef requires attention to temperature. The recommended temperature for cooking meatless burgers can lie between 160°F and 165°F (71° and 74°C). A user named Ricardo emphasized the “importance of 165° temps” for “veggie type ‘meat'”. During cooking, the bottom of the Beyond Beef patty quickly turns a nice dark brown. The cooking process also produces an “old-school barbecue meat smell.” This mimics the experience of cooking traditional ground beef.
Aroma and Appearance
Before cooking, Beyond Beef has an aroma reminiscent of canned corn beef hash. As it cooks, the appearance changes significantly. The patty transforms from a reddish hue to a rich brown, similar to traditional ground beef. The cooking process also releases an appealing aroma, often described as an “old-school barbecue meat smell.” This contributes to the overall sensory experience, making it feel more like cooking conventional meat. Ultimately, the choice between Beyond Beef and ground beef involves a personal balance of taste, texture, and nutrition.
The comparison of beyond beef vs ground beef reveals distinct differences. Beyond Beef offers a plant-based alternative with lower saturated fat and fiber. Ground beef provides specific micronutrients and a traditional beef flavour. Neither is a definitive “winner.”
Your choice depends on nutrition goals, ethical views, and taste preferences. Those seeking plant-based burgers, lower saturated fat, or no cholesterol might prefer Beyond Beef. Consumers prioritizing traditional beef taste, specific micronutrients, or simpler ingredients may stick with ground beef. Consider your own values and needs when making food choices.
FAQ
What is the main protein source in Beyond Beef?
Beyond Beef primarily uses pea protein. It also includes protein from brown rice and mung beans. These plant-based ingredients provide its protein content.
Does Beyond Beef contain cholesterol?
No, Beyond Beef contains no cholesterol. It is a plant-based product. Traditional ground beef, an animal product, does contain cholesterol.
Which product offers dietary fiber?
Beyond Beef offers dietary fiber. It is made from plants. Traditional ground beef, an animal product, contains no dietary fiber. Fiber supports digestive health.
Is Beyond Beef considered a whole food?
No, Beyond Beef is not a whole food. It is a processed food. Manufacturers combine various plant ingredients to create its meat-like texture and flavor.
What is the primary fat source in the latest Beyond Beef recipe?
The latest Beyond Beef recipe uses avocado oil as its primary fat source. This change helped reduce its saturated fat content. Earlier versions used coconut and canola oils.

