
Chestnuts stand out in the nut family. Unlike typical nuts, they offer a unique nutritional profile. You will find them high in carbohydrates and rich in fiber. Importantly, chestnuts are notably low in fat. This distinct combination contributes to their growing popularity. The global chestnut market reached around $3.8 billion in 2024, reflecting this interest. Consumers increasingly look for foods with clear health benefits, and fiber is a sought-after nutrient. Chestnuts nutrition benefits align perfectly with these trends. Their unique nutrition makes them a valuable addition to your diet.
Key Takeaways
Chestnuts are different from other nuts. They have many carbohydrates and fiber. They are also low in fat.
Chestnuts give you steady energy. Their fiber helps your digestion. They also help control blood sugar.
Chestnuts are good for your heart. They have vitamins and minerals. These help protect your body’s cells.
You must cook chestnuts before eating them. You can roast or boil them. They are good in many dishes.
Understanding Chestnuts Nutrition Benefits

Chestnuts offer a unique nutritional profile that sets them apart from other nuts. You will find them packed with beneficial components. This distinct makeup contributes to the many chestnuts nutrition benefits you can enjoy.
Carbohydrates for Energy
Chestnuts are a great source of carbohydrates. You get a significant amount of energy from them. For example, 100 grams of chestnuts can provide around 45.54 grams of carbohydrates. These are not simple sugars. Chestnuts contain complex carbohydrates. Your body takes longer to break down these complex structures. This process gradually releases glucose into your bloodstream. This slow release gives you a steady supply of energy. You avoid quick energy spikes and crashes. This makes chestnuts an excellent food for sustained energy throughout your day.
Dietary Fiber Content
You will find chestnuts are a good source of fiber. Dietary fiber is important for your health. Fresh chestnuts contain about 6.3 grams of dietary fiber. This amount helps you meet your daily fiber needs. Fiber aids your digestion. It also helps you feel full longer. This can be helpful if you manage your weight.
Low Fat Profile
One of the most striking nutritional benefits of chestnuts is their low fat content. Unlike most nuts, chestnuts are naturally low in fat. A serving of chestnuts contains only about 0.2 grams of total fats. They have no cholesterol. This makes them a great choice if you follow a low-fat diet.
Look at how chestnuts compare to other common nuts:
Nutritional Component | Chestnuts (Raw, Peeled) | Walnuts | Almonds | Pistachios | Cashews |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Calories (per 1-ounce) | 56 | 185 | 164 | 159 | 160 |
Fat (grams) | 0.35 | 18.5 | 14.2 | 12.7 | 12.9 |
Carbohydrate (grams) | 12.52 | 3.9 | 5.6 | 7.7 | 8.6 |
Dietary Fiber (grams) | 0.9 | 1.9 | 3.5 | 3 | 0.9 |
Chestnuts have a much lower fat content compared to nuts like walnuts, almonds, and pistachios. Their fat content typically ranges from 1.6% to 7.4%. Other nuts often have fat content exceeding 40%. This low fat content makes chestnuts a unique and healthy option.
Vitamins and Minerals
Chestnuts offer a variety of essential vitamins and minerals. You get important nutrients when you eat them.
Vitamin C: Chestnuts are the only nuts that contain a significant amount of Vitamin C. A serving can provide as much as 49 mg of this vital vitamin. Vitamin C boosts your immune system. It also acts as an antioxidant, protecting your cells. This high in vitamin C content is a major advantage.
B Vitamins: You also find B vitamins in chestnuts. These include B6 and folate. B vitamins are crucial for energy production. They also support red blood cell formation and brain health.
Vitamin E: Chestnuts contain Vitamin E, another important antioxidant.
Here is a look at some of the vitamins found in chestnuts:
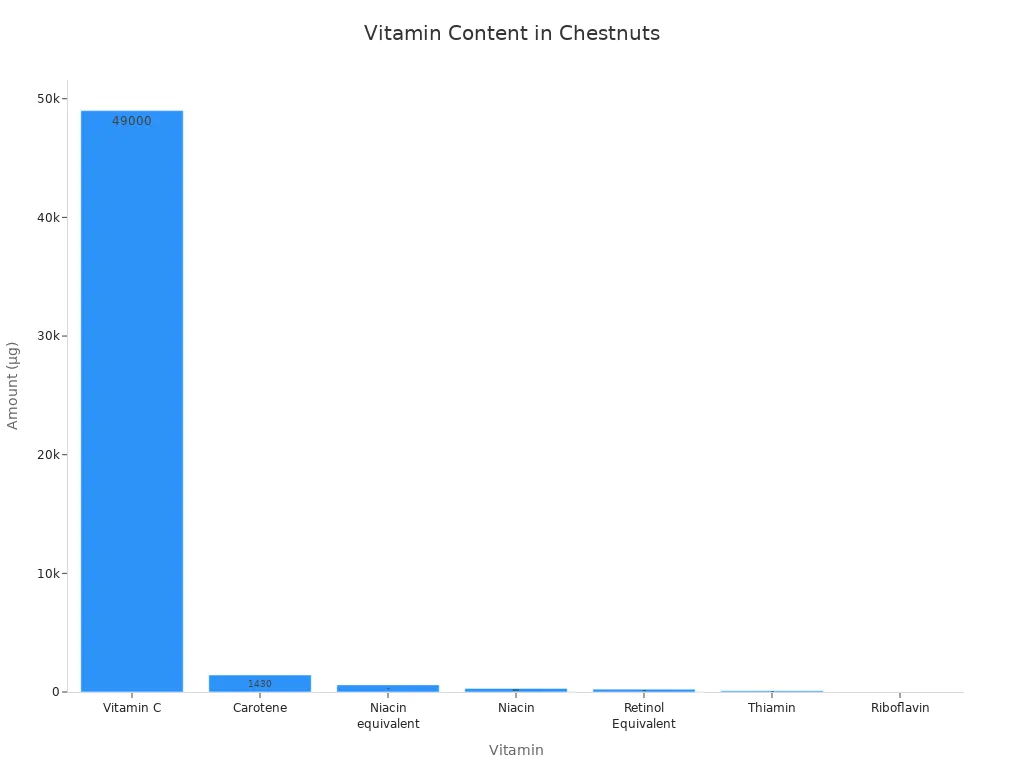
Chestnuts are also rich in essential minerals. You will find:
Potassium: Important for blood pressure regulation.
Manganese: Plays a role in bone health and metabolism.
Copper: Essential for iron absorption and energy production.
Magnesium: Supports muscle and nerve function.
Phosphorus: Important for strong bones and teeth.
Iron: Crucial for carrying oxygen in your blood.
These vitamins and minerals contribute to the overall nutritional benefits of chestnuts. They make chestnuts a truly wholesome food choice.
Chestnuts: A Nutritional Comparison
You might wonder how chestnuts stack up against other nuts. Chestnuts offer a distinct nutritional profile. They stand out in several key areas. You will see they provide energy similar to brown rice.
Fat Content Comparison
Chestnuts are notably low in fat. This sets them apart from many other popular nuts. You can see the difference clearly when you compare them.
Nut Type | Fat (g) per 1 oz serving |
|---|---|
Chestnuts (Peeled) | 0.36 |
Almonds | 14.2 |
Cashews | 12.5 |
Walnuts | 18.5 |
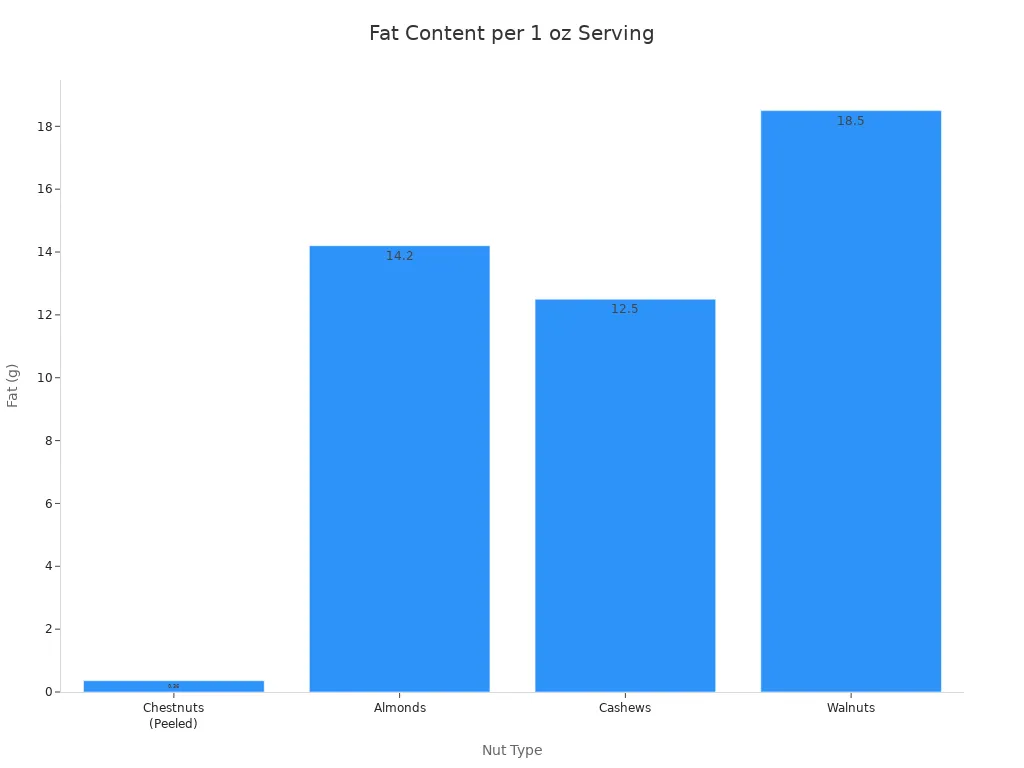
You can see chestnuts have significantly less fat. This makes them a great choice if you watch your fat intake.
Carbohydrate Comparison
Chestnuts are unique among nuts for their high carbohydrate content. This provides you with sustained energy.
Nut Type | Total Carbs (g/100g) | Net Carbs (g/100g) |
|---|---|---|
Chestnuts | 27.76 | 27.76 |
Pecans | 13.86 | 4.26 |
Chestnuts contain 27.76g of net carbs per 100g. Pecans have 13.86g of total carbs. Pecans also include starch, sugars, and a good amount of fiber. Specifically, 100g of pecans contains 9.6g of dietary fiber. This includes both soluble and insoluble types. Chestnuts give you more carbohydrates for energy.
Fiber Comparison
Chestnuts provide good fiber. Fiber is important for your digestion. However, some other nuts and seeds offer even more fiber per serving.
Nut/Seed | Fiber per 100g |
|---|---|
Macadamia Nuts | 9g |
Sunflower Seeds | 9g |
Peanuts (Dry Roasted) | 8g |
Brazil Nuts | 8g |
Chestnuts | 5g |
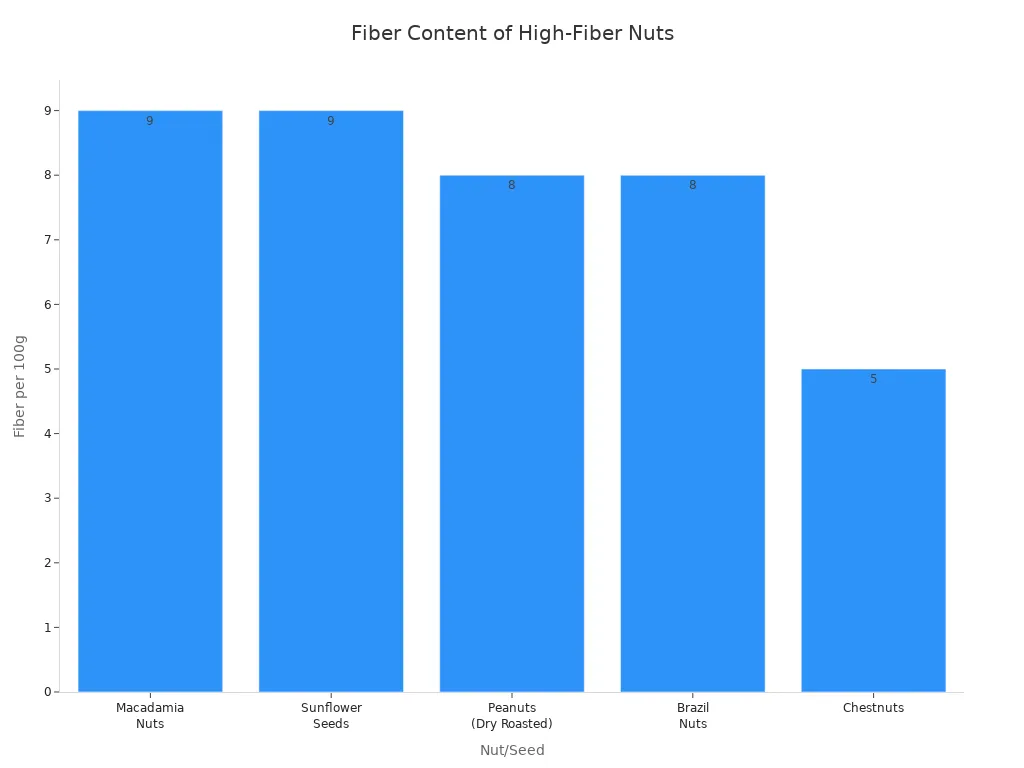
You still get a healthy dose of fiber from chestnuts.
Calorie Comparison
Chestnuts are also lower in calories compared to many other nuts. This makes them a lighter snack option.
Hazelnuts contain about 178 calories per 1 ounce (28 grams). Peanuts contain approximately 161 calories per 1 ounce (28 grams).
Nut/Seed | Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|---|
Chestnut | 100 g | 84 Cal |
Spanish Peanut | 100 g | 162 Cal |
You can enjoy more chestnuts for fewer calories. This is a great benefit for your nutrition goals.
Health Benefits of Chestnuts
Chestnuts offer many health benefits. You gain specific advantages from their unique nutritional makeup. These advantages support your overall well-being.
Digestive Health Support
Chestnuts are good for your digestive system. They contain a lot of fiber. This fiber helps you have regular bowel movements. It is especially helpful if you experience constipation. The dietary fiber in chestnuts also improves your body’s digestive function. It helps balance the good bacteria in your gut. This strengthens your gut microbiome.
Early studies show that chestnut extract can act as a prebiotic. Prebiotics feed beneficial bacteria like lactobacilli. This suggests a positive effect on your gut microbes. One study found that modified chestnut starch could help reduce diet-induced obesity. It did this by changing gut microbes. It also affected genes related to short-chain fatty acid receptors. This shows a positive influence on adjusting gut microbes. A review also highlighted chestnut shells as good sources of prebiotics. This means they could be useful functional ingredients.
Blood Sugar Regulation
You can use chestnuts to help manage your blood sugar. Their fiber content plays a key role. This fiber slows down how your body absorbs starches. This prevents quick spikes in your blood sugar. Chestnuts have a low glycemic index (GI) of 54. This classifies them as a low GI food. It means they will not cause a significant blood sugar spike. Some sources list the GI as 60, which is still considered a medium GI food. This means they cause a gradual rise in blood sugar levels.
A study suggests that chestnuts may help you manage blood sugar levels. They can also improve insulin sensitivity. This makes your cells more responsive to insulin. The fiber in chestnuts helps stabilize blood sugar levels after meals.
Type of Fiber | Function | Benefits for Diabetics |
|---|---|---|
Soluble Fiber | Dissolves in water, forming a gel-like substance that slows digestion. | Helps reduce blood sugar spikes after meals. |
Insoluble Fiber | Adds bulk to stool and helps food pass through the digestive tract. | Aids in digestion and overall gut health, contributing to better metabolic control. |
Heart Health Advantages
Chestnuts support a healthy heart. They contain antioxidants and important minerals. These include magnesium and potassium. These nutrients help lower your risk of cardiovascular problems. This includes heart disease or stroke.
You will find several components in chestnuts that benefit your heart:
Potassium: This mineral helps relax your blood vessels. It also works against sodium. This prevents high blood pressure. It reduces your risk of hypertension and stroke.
Fiber: Fiber lowers bad cholesterol (LDL). It increases good cholesterol (HDL). It also reduces plaque buildup in your arteries. This improves blood circulation.
Antioxidants (Vitamin C, Polyphenols): These reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in your blood vessels. They protect against damage from free radicals. This lowers your risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Magnesium: This supports a proper heart rhythm. It also helps muscle function and blood circulation.
Copper: Copper helps form healthy blood vessels.
Low Fat Content: Chestnuts provide nutrients without adding unhealthy fats. They do not increase cholesterol.
Complex Carbohydrates: Your body digests these slowly. This prevents sudden blood sugar spikes. It reduces stress on your cardiovascular system.
Low Calories: This helps you manage your weight. Weight management is important for reducing heart disease risk.
Dietary studies show that chestnuts can help reduce cholesterol levels. One study on mice showed a trend towards lower total blood cholesterol. Extracts from chestnut spiny burrs also decreased cholesterol levels in diabetic rats. Chestnuts contain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs). These include linoleic acid and γ-tocotrienol. They also have phytosterols like β-sitosterol and stigmasterol. These compounds link to cholesterol reduction. Chestnuts have the highest levels of phytosterols compared to other nuts.
Antioxidant Power
Chestnuts are rich in antioxidants. These compounds protect your body’s cells. You will find phenolics and flavonoids in chestnuts. They also contain ellagic acid. This phenolic compound is especially high in chestnut shells.
Antioxidants like ferulic acid help reduce oxidative stress. This stress can damage your cells. Ferulic acid neutralizes free radicals. These free radicals can contribute to cancer growth. By neutralizing them, chestnuts help protect your cells. Test-tube studies show that ferulic acid can suppress tumor growth. It also fights cancer cells and inflammation.
Chestnut inner shell extract (CISE) protects your body cells. It significantly blocks oxidative stress. It also keeps important antioxidant enzymes active. These include catalase, superoxide dismutase, and glutathione peroxidase. CISE also prevented the reduction of antioxidant enzyme activities. This happened even with CCl4 and high-fat diets in the liver. It greatly lowered hepatic lipid peroxidation. Scoparone and scopoletin are main compounds in CISE. They inhibit reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. They also maintain antioxidant enzyme activity in lab tests.
Weight Management Aid
Chestnuts can help you manage your weight. They are low in calories. You get only 131 kcal per 100g. This is much less than other nuts. They are also low in fat, with only 1.38g per 100g. This makes them suitable for low-fat diets.
The high fiber content in chestnuts helps you feel full. This feeling of fullness comes without adding too many calories. This makes them an excellent choice if you are trying to lose weight.
Chestnuts’ high fiber content makes you feel full. This can help you eat fewer calories overall. It prevents overeating.
Fiber intake can boost hormones that make you feel full. These include peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1).
Fiber can also reduce ghrelin production. Ghrelin is a hormone that makes you feel hungry.
Chestnuts give you a prolonged feeling of fullness. This is due to their substantial fiber content. Nuts can enhance satiety. This leads to eating less food later. They can decrease ghrelin concentrations. This reduces hunger. Dietary fiber from nuts delays how quickly your stomach empties. It also slows absorption. This suppresses hunger. These health effects make chestnuts a valuable part of a weight management plan.
Enjoying Chestnuts in Your Diet

You can easily add chestnuts to your meals. They offer a unique flavor and texture. Knowing how to prepare and use them helps you get the most benefits.
Preparation Methods
You must cook fresh chestnuts before eating them. They contain tannic acid. This makes them inedible raw. Two popular ways to prepare chestnuts are roasting and boiling.
Roasting Chestnuts: First, score an ‘X’ on the flat side of each nut. Cut through the shell but only slightly into the nut’s meat. This stops them from exploding. It also helps with peeling. Arrange the nuts cut-side up on a baking sheet. Roast them at 425°F for about 20 minutes. The shells will open and peel back. Peel the nuts while they are still warm. Remove both the hard outer shell and the papery inner skin.
Boiling Chestnuts: Score an ‘X’ on each nut. Add them to boiling water. Boil for 10-15 minutes. The shells will start to peel back and open.
You can also candy chestnuts. This process involves soaking boiled chestnuts in syrup for several days. Then you slowly dry them.
Culinary Versatility
Chestnuts are very versatile in the kitchen. You can use them in many dishes, both savory and sweet. They pair well with fruits, vegetables, chocolate, and meats. For example, you can make chestnut gnocchi with mushrooms. You can also enjoy a rich chocolate and chestnut cake.
Chestnuts can be used in various forms:
Whole or Pureed: Use them in soups, stuffings, or as a side dish.
Flour: Chestnut flour makes gluten-free pasta, cakes, and breads.
Candied: Enjoy them as a sweet treat.
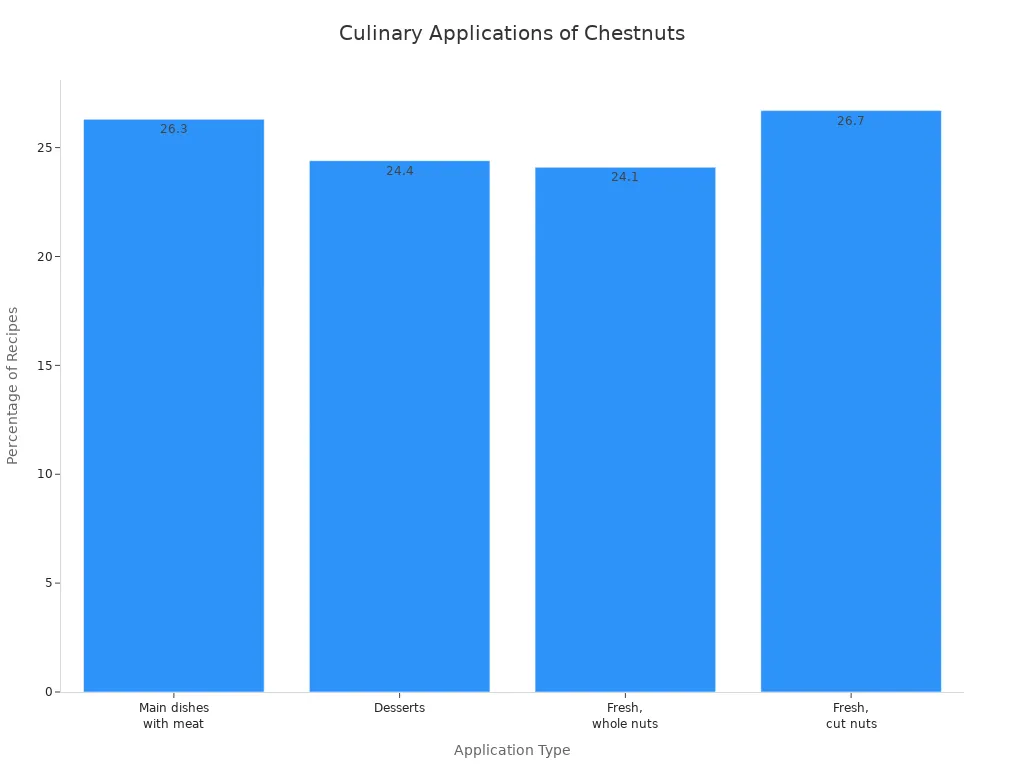
Here is how chestnuts are often used in recipes:
Application Type | Percentage of Recipes |
|---|---|
Main dishes with meat | 26.3% |
Desserts | 24.4% |
Fresh, whole nuts | 24.1% |
Fresh, cut nuts | 26.7% |
You can find chestnuts in many forms beyond fresh. They come canned, vacuum-packed, dried, pureed, or as powder. This extends their use past their fresh season.
Storage Guidelines
Store fresh chestnuts properly to keep them good. Keep them in a cool, dry place. You can also refrigerate them in a perforated bag. This helps them last longer. Cooked chestnuts should be stored in the refrigerator. Use them within a few days.
Seasonal Availability
You typically find fresh chestnuts in the fall and early winter. Their season usually runs from September through December. This is the best time to enjoy them at their peak.
You now understand the unique nutritional profile of chestnuts. They offer high carbohydrates, rich fiber, and a notably low-fat content. These features provide significant health benefits. You gain digestive health support, heart health advantages, and better blood sugar control. The health benefits of chestnuts make them a smart choice. Chestnuts are versatile in your kitchen. You can easily add them to your healthy diet. Explore the many chestnuts nutrition benefits. Embrace this delicious, wholesome food.
FAQ
What makes chestnuts unique among nuts?
Chestnuts stand out because they are low in fat. You find them high in carbohydrates and fiber. They also contain Vitamin C, which is rare for nuts. This combination gives you sustained energy and many health benefits.
Can you eat chestnuts raw?
No, you should not eat chestnuts raw. They contain tannic acid. This makes them taste bitter and can upset your stomach. You must cook them first. Roasting or boiling makes them safe and delicious to eat.
Are chestnuts good for managing blood sugar?
Yes, chestnuts can help manage your blood sugar. They have a low glycemic index. Their high fiber content slows sugar absorption. This prevents quick spikes in your blood sugar levels. You get a more stable energy release.
Do chestnuts contain gluten?
No, chestnuts are naturally gluten-free. You can safely include them in a gluten-free diet. This makes them a great option for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
What are the main health benefits of chestnuts?
You gain several health benefits from chestnuts. They support your digestive health with fiber. They help regulate blood sugar. Chestnuts also boost heart health and provide powerful antioxidants. They can even aid in weight management.

