
You love the creamy texture of avocados, right? Their popularity is undeniable; the global avocado market was estimated at USD 15,828.7 million in 2023. This delicious fruit is more than just a tasty addition to your meal; it is a true superfood. Avocados hold surprising health benefits, making them a nutritional powerhouse. This blog aims to uncover the incredible avocado nutrition and the diverse health benefits of avocados. You will discover what makes this fruit so healthy, its specific avocado benefits, and practical ways for eating avocados to support a healthy diet. You will learn about the superfood benefits that truly set it apart.
Key Takeaways
- Avocados are a superfood. They have many nutrients.
- Avocados offer many health benefits. They help your body.
- Eating avocados supports a healthy diet. They are good for you.
Nutritional Value of Avocados

Avocados are a true superfood, packed with essential nutrients. You get a nutritious powerhouse when you enjoy this nutrient-rich fruit. Let’s explore the specific components that make up the impressive avocado nutrition.
Healthy Monounsaturated Fats
You might hear that avocados are loaded with healthy fats. This is absolutely true! The majority of fat you find in avocados consists of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs). These fats are incredibly beneficial for your body. A standard serving, which is one-third of a medium avocado (about 50 grams), gives you 5 grams of these healthy monounsaturated fats.
One key monounsaturated fat in avocados is oleic acid. This compound is healthy for the heart. Studies show that consuming avocados can increase your “good” HDL cholesterol. They also help reduce total cholesterol, “bad” LDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. Avocado intake specifically reduces small, dense LDL particles, which are more prone to oxidation and linked to heart disease risk. You are actively protecting your heart when you include avocados in your diet.
Vitamins and Minerals
Avocados provide a wide array of vitamins and minerals essential for your health. You get important nutrients from even a small serving.
| Mineral/Vitamin | Amount per 1/3 medium avocado (50g) | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
| Iron | 0.3mg | 2% |
| Magnesium | 15mg | 4% |
| Potassium | 250mg | 6% |
| Folate/Folic Acid | 45mcg | 10% |
| Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.1mg | 8% |
| Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) | 0.7mg | 15% |
| Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) | 0.1mg | 6% |
| Thiamin (Vitamin B1) | 0.04mg | 4% |
| Vitamin E | 1mg | 6% |
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | 4mg | 4% |
| Vitamin K | 11mcg | 10% |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) | 1mg | 6% |
As you can see, avocados are a great source of potassium, a mineral vital for blood pressure regulation. They are also a great source of potassium for nerve function. You also get a good amount of Vitamin K, Vitamin E, Vitamin C, and several B vitamins like Pantothenic Acid (B5) and Folate. These vitamins play many roles, from supporting your immune system to helping with energy production. This chart further illustrates the daily value percentages for these important nutrients:
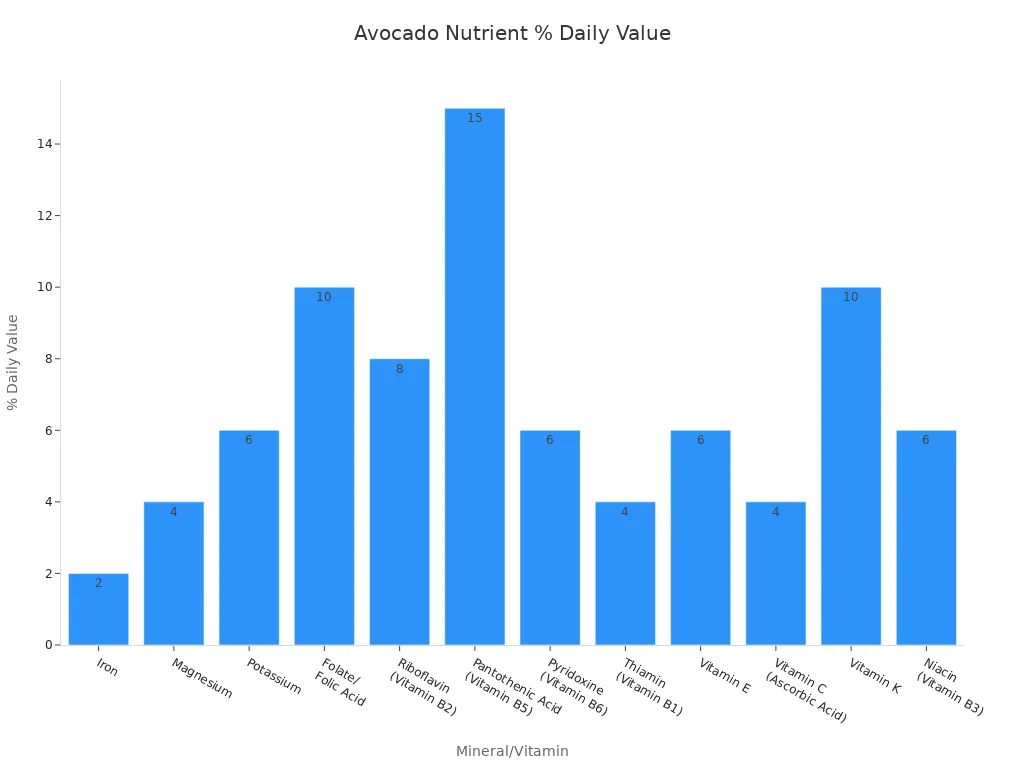
Avocados are a great source of potassium, which is often lacking in many diets.
Fiber Content
Fiber is crucial for your digestive system, and avocados deliver! A whole medium avocado provides an impressive 10 grams of fiber. If you eat a single serving (one-third of a medium avocado), you get 3 grams of fiber. This includes 1 gram of soluble fiber and 2 grams of insoluble fiber.
Fiber helps promote good gut health. It increases the diversity of your gut microbiome, which means you have more beneficial bacteria in your digestive tract. This fiber acts like a natural probiotic, feeding those good bacteria. The recommended daily fiber intake is 25 grams, based on a 2,000-calorie diet. Avocados help you reach that goal easily.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
Beyond vitamins and minerals, avocados contain special plant compounds called antioxidants and phytonutrients. These compounds protect your cells from damage.
- Avocados contain carotenoids. These phytonutrients act as powerful antioxidants in your body.
- The natural compounds in avocados share characteristics with resveratrol, found in grapes, and other beneficial phytonutrients present in many fruits and vegetables.
These components contribute to the overall nutritional value of avocados, making them a truly remarkable superfood.
Health Benefits of Avocados
Avocados offer a wide range of health benefits of avocados, making them a truly remarkable superfood. You gain many advantages from their rich avocado nutrition. Let’s explore the specific ways this nutritious powerhouse supports your well-being.
Heart Health
You can significantly support your heart health by including avocados in your diet. Avocados are rich in compounds that help regulate blood pressure and manage cholesterol.
Avocados contain monounsaturated fatty acids, potassium, magnesium, and bioactive phytochemicals. These components all support cardiovascular health and blood pressure regulation. Avocado oil can reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It also improves kidney function. This happens partly by reducing oxidative stress in the kidneys. Avocado oil’s effects on blood pressure and kidney health may decrease the actions of Ang-II on mitochondria. This suggests it could be a nutritional approach to lessen the harmful effects of high blood pressure on your kidneys.
Avocado leaf extract contains flavonoids and quercetin. These compounds inhibit the ACE enzyme, which is a key factor in blood pressure regulation. Avocado leaf decoction has consistently lowered blood pressure in humans. This is likely due to its diuretic properties, helping your body remove excess water and salt. Combining avocados with other potassium-rich foods, like coconut water, can enhance blood pressure-lowering effects. This is because of their high potassium content.
Regarding cholesterol, a 2015 meta-analysis showed that when people ate avocados instead of animal fats, their LDL cholesterol levels decreased by 18.80 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dl). However, some experts suggest that avocados themselves may not directly lower cholesterol. They believe any observed decrease might come from reducing animal fats in the diet. While avocados contain phytosterols that can lower LDL cholesterol, the amount in a single avocado is often not enough to have a significant impact. You need 600–3,300 mg of phytosterol daily for a successful reduction, which is more than one avocado provides. A 2018 review found no significant difference in serum LDL cholesterol levels between avocado intake and control groups. However, it did note an increase in HDL cholesterol levels.
Digestive Wellness
Avocados are excellent for improving digestion. Their high fiber content plays a crucial role in your gut health.
A whole medium avocado gives you 10 grams of fiber. This fiber promotes good gut health. It increases the diversity of your gut microbiome. This means you have more beneficial bacteria in your digestive tract. This fiber acts like a natural probiotic, feeding those good bacteria.
A study in The Journal of Nutrition found that eating avocados daily positively impacts microbial diversity in your gut.
- Daily avocado consumption leads to more gut microbes that break down fiber.
- These fiber-breaking microbes produce beneficial metabolites that support gut health.
- People eating avocado daily showed greater microbial diversity compared to those who did not.
This makes eating avocados a smart choice for improving digestion.
Eye Health
You can protect your vision with the help of avocados. They contain specific compounds that promote healthy eyes. This is one of the many health benefits of avocado.
- Lutein and Zeaxanthin: These carotenoids promote eye health. Higher intakes of lutein and zeaxanthin can reduce the risk of nuclear cataracts and improve visual performance.
- Monounsaturated fatty acids: These fats, found in avocados, protect against age-related eye dysfunction.
- Other Carotenoids: Avocados contain a diverse array of carotenoids. These include Alpha-carotene, Beta-carotene, Beta-cryptoxanthin, Chrysanthemaxanthin, Neochrome, Neoxanthin, and Violaxanthin. They scavenge free radicals and contribute to eye health.
- Oleic acid: This fatty acid enhances the absorption of carotenoids. It promotes the formation of chylomicrons, which transport carotenoids in your body.
Lutein and Zeaxanthin, along with monounsaturated fatty acids, increase macular pigment density in older adults. Lutein specifically helps prevent macular degeneration, cataracts, and other age-related eye issues. This makes avocados great for vision.
Bone Health
Avocados contribute to strong bones. They provide important vitamins and minerals for bone density.
Avocados contain Vitamin K. This vitamin is crucial for bone health. It assists in calcium absorption and contributes to bone mineral density. Both are vital for preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
Avocados are also a good source of boron. Boron is a mineral that helps your body absorb magnesium. It also enhances the function of vitamin D. A half-cup serving of avocado provides 1.07 mg of boron. This makes it a significant plant-based source of this nutrient for bone health.
Maternal and Fetal Health
Avocados offer significant health benefits for expectant mothers and developing babies. They provide crucial nutrients for fetal development.
- Folate: This is essential for the normal growth and development of the baby’s brain and spinal cord. It helps produce and maintain new cells. It can also reduce the risk of premature births and congenital disabilities.
- Unsaturated Fats: These are crucial for the normal growth and development of the brain and central nervous system.
- Fiber: Low fiber intake links to an increased risk of gestational diabetes. This can harm a developing baby.
- Potassium: This helps balance sodium intake. It can prevent preeclampsia, a condition associated with high blood pressure.
- Lutein: This is the most abundant carotenoid in avocados. Avocados aid in its absorption. Lutein is also found in breast milk, and its levels increase over time.
Avocados contain high amounts of folate and potassium. These are often under-consumed in maternal diets. They also provide fiber, monounsaturated fats, and lipid-soluble antioxidants. These are all linked to improvements in maternal health, birth outcomes, and breast milk quality.
Nutrients in avocados, such as choline, lutein, and fatty acids, work together. They improve brain function and support cognitive development. Choline is integral to brain fatty acids. It mediates the export of fatty acids to the brain. Lutein co-localizes with DHA. It improves visual acuity and protects fatty acids from peroxidation. This research aims to establish avocados as a viable food for optimizing human milk with nutrients that support brain development. This ultimately sets children on a trajectory for school readiness.
Mood and Brain Health
Avocados can positively impact your mood and brain function. This is another one of the health benefits of avocados.
Avocados are a source of B vitamins, including thiamine, riboflavin, and niacin. Deficiencies in these B vitamins link to increased anxiety and stress. Incorporating avocados into your diet can help mitigate these issues.
Avocados contain significant amounts of folate (Vitamin B9). Folate is a crucial B vitamin. People with insufficient folate intake are more susceptible to depression. They may also respond less effectively to antidepressants. Folate acts as a key cofactor for enzymes involved in the metabolic recycling of common neurotransmitters. Healthy methylation metabolism, supported by folate, is vital for neurotransmitter metabolism and overall brain function. This indirectly supports mood regulation. Avocado consumption, due to its richness in folate, may contribute to an improved mood. Studies show a strong link between folate deficiency and an elevated risk of developing depression.
Avocados are rich in monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs). MUFAs protect glial cells in the brain, specifically astrocytes. These astrocytes are crucial for supporting information-carrying nerves. A 2012 animal study showed that MUFAs improved muscle control in animals with impaired astrocyte function. The neuroprotective properties of MUFAs in avocados are also used in diets for people with neurological disorders like epilepsy.
A study found that older adults who regularly consume avocados show improved cognitive abilities. This positive impact on cognition remained significant even after accounting for other variables. These variables include education, age, physical activity, and smoking. A 12-week study on adults with overweight and obesity showed that avocado intake enhanced performance in attentional inhibition. Daily avocado consumption also increased serum lutein concentrations.
Compounds in avocados act as unique antioxidants. They effectively suppress radical generation. This suggests their potential as neuropreventive agents. The diverse bioactive nutrients in avocados are vital for preventing and treating various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s. The healthy fats in avocados are essential for brain development. This is especially true during critical stages in adolescence. They contribute to a highly functioning and intelligent brain.
Cancer Risk Reduction
Avocados may play a role in reducing cancer risk. This is a promising area of avocado nutrition research.
Avocados contain nutrients and phytochemicals with potential anticarcinogenic effects. This is based on in vitro studies and limited human studies. In vitro studies show that Persea americana var drymifolia extract can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7). It does this by increasing specific protein expressions and decreasing mitochondrial membrane potential. Human studies also suggest that daily avocado consumption can lead to lower fecal bile acid concentrations. It also leads to a better abundance of fiber-fermenting bacteria, which are known pro-apoptotic agents.
Research indicates that avocado extracts possess antiproliferative properties. This means they can inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells. Studies on HT 116 (colon cancer) and HepG2 (liver cancer) cell lines found that Persea americana fruit and seed extracts exhibited antioxidant effects. Avocatin B, a lipid in avocado, shows potential as a cytotoxic agent and fatty acid oxidation inhibitor.
Human studies with overweight and obese adults showed that daily avocado consumption for 12 weeks led to significant differences in hs-CRP and VCAM-1 expression. This indicates anti-inflammatory effects. A pilot study also found that avocado consumption preserved IκBα. This reduces the activation of the NF-κB pathway, which is involved in inflammation. In vitro studies on murine macrophages treated with avocado seed extracts showed a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α). They also showed inhibition of prostaglandin E2 production. Avocado oil supplementation in mice also reduced pro-inflammatory cytokine levels.
A prospective study involving over 112,000 men and women investigated avocado consumption and cancer risk. In men, consuming one or more weekly servings of avocados linked to a decreased risk of total cancer, colorectal cancer, lung cancer, and bladder cancer. In women, avocado consumption associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in one cohort. However, a younger cohort showed no association.
Immune Support
You can strengthen your immune system with the help of avocados. This is another one of the surprising health benefits of this superfood.
- Avocados contain Vitamin C, an antioxidant that may contribute to healthy immune function.
- Avocados provide Vitamin E, an antioxidant essential for keeping your immune system strong against bacteria and viruses.
- The healthy fats in avocados act as a ‘nutrient booster.’ They increase the absorption of fat-soluble nutrients like vitamins A, D, K, and E. These are crucial for immune health.
Carotenoids, fiber, and several vitamins (A, D, C, E, B6, B12, B9) and minerals (zinc, iron, copper, selenium, magnesium) are vital for immune health. These nutrients play specific roles in both innate and adaptive immune responses. They help resolve infections and inflammation. Multiple nutrients often work together to ensure proper immune function at each stage. For example, vitamins A, D, and C, along with minerals like zinc, iron, copper, and selenium, support the innate immune biochemical response. This mediates acute inflammation. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables containing these nutrients has been shown to reduce inflammation.
Chronic Disease Prevention
Eating avocados regularly can help prevent or manage several chronic diseases. This is a significant part of the health benefits of avocado.
Excess belly fat increases your risk of developing health conditions. These include type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. Research suggests that eating one avocado per day for 12 weeks can positively affect visceral adiposity (belly fat) in women.
Daily avocado intake for 26 weeks improved diet quality, sleep health, and blood lipids in US adults with abdominal obesity. These improvements are relevant for managing risk factors associated with cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and stroke. This highlights the broad health benefits of avocados.
Practical Guide to Avocados

You can easily enjoy the many benefits of avocados. Here is how you can select, store, and add this superfood to your meals.
Selecting and Storing
You want to pick the perfect avocado. A ripe avocado should yield to gentle palm pressure but remain firm. If it feels too soft or mushy, it is overripe. If it is too hard, it is not ready yet. Most ripe avocados have a dark, almost black skin, but this can vary by type. You can also check under the stem. If the stem easily detaches to show green flesh, your avocado is ripe. A brown color under the stem means it is overripe. Store ripe avocados in the refrigerator to keep them fresh longer.
Incorporating Avocados
You can add avocados to almost any meal. Eating avocados is simple and delicious. You can sprinkle avocado slices with salt and pepper. Try adding them to your morning toast instead of butter. You can also dice avocados and add them to scrambled eggs. For lunch, add avocado to salads. This makes them more filling. You can also make a creamy avocado sauce for pasta. For dinner, use avocado slices as a topping for sandwiches, burgers, or tacos. You can even blend avocado into smoothies for extra nutrients. This helps you maintain a healthy diet.
Avocado Recipes
Many delicious recipes feature avocados. You can try a Caprese Avocado Toast for a quick breakfast. For a sweet treat, make a Chocolate Coconut Avocado Smoothie. If you like savory options, try Huevos Rancheros Casserole. You can also make Vegan Avocado Fritters. These recipes show how versatile avocados are. Eating avocados can be a fun and tasty experience.
Common Questions and Considerations
You might have questions about how avocados fit into your daily life. Here, you will find answers to common concerns about this superfood.
Daily Avocado Intake
You might wonder how much avocado you should eat. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) updated the official serving size. Now, you should consider 1/3 of a medium avocado as one serving. This equals about 50 grams. This amount gives you 11% of your Daily Value for fiber. It also provides 10% of your Daily Value for folate. This serving size offers around 80 calories. It is rich in healthy fats, fiber, and nearly 20 essential vitamins and minerals. If you do not have a scale, you can estimate this as two to three tablespoons of mashed avocado.
Avocados and Weight Management
You may worry about avocados and weight gain because they contain fat. However, eating avocados does not negatively affect your body weight. Regular avocado intake links to a lower chance of being overweight. It can also slow adult weight gain in normal-weight people over time. Avocados have a unique nutrient profile. They have a low-to-medium energy density and low sugar content. They also contain high fiber, about 9.2g of total fiber per Hass avocado. This helps you feel full. However, studies have not confirmed that avocado intake directly causes weight loss in adults who are overweight.
Potential Allergies
You should know that some people can have an allergic reaction to avocados. While not common, avocado allergies do occur. You might experience symptoms like:
- Itchy lips, mouth, or throat
- Hives or a rash
- Vomiting or stomach discomfort
- Swelling in and around the mouth and throat
- Red and watery eyes or a runny nose
- Sneezing
- Anaphylaxis, which is a severe allergic reaction
The prevalence of avocado allergies varies by region. You can see the reported prevalence in different areas:
| Region | Reporting Method | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Australia | Parent-reported and Physician-diagnosed | 0.05% |
| Australia | Self-reported | 0.02% |
| Mexico (Guadalajara) | Self-reported | 1.0% |
| Mexico (Toluca) | Self-reported | 1.4% |
| United States | Self-reported | 2.7% |
| Brazil (Limoeiro) | Parent-reported | 0.24% |
| Brazil (Uberlandia) | Self-reported (part of overall fruit allergy) | 1.6% (overall fruit allergy) |
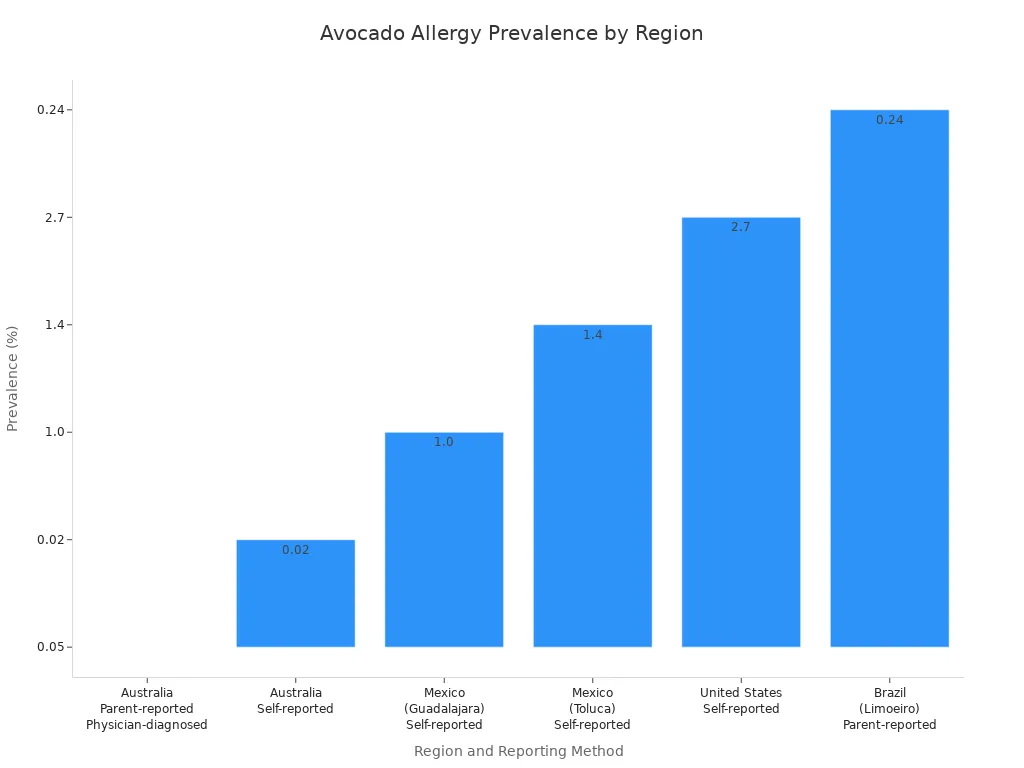
You can see the United States has the highest self-reported prevalence at 2.7%.
You now know avocados are a versatile and incredibly nutritious “creamy superfood.” This nutritious powerhouse offers many health benefits. You gain improved brain health, stronger bones, and better blood sugar regulation. Avocados also support skin care and may help prevent cancer. You can see their rich nutrient profile below.
Embrace eating avocados as a regular part of your healthy diet. Start experimenting with this superfood today and enjoy its amazing advantages for your overall well-being!
FAQ
Are the fats in avocados truly healthy?
Yes, avocados are loaded with healthy fats. They contain monounsaturated fats, like oleic acid. These fats are healthy for the heart. They help improve your cholesterol levels. This supports your overall heart health. This is a key part of avocado nutrition.
What makes avocados a superfood?
Avocados are a superfood because of their amazing avocado nutrition. They are a nutritious powerhouse, packed with vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants. This nutrient-rich fruit offers many health benefits. These superfood benefits support your well-being. The nutritional value of avocados is truly impressive.
How do avocados help my digestion?
Avocados are great for improving digestion. They contain a lot of fiber. This fiber feeds good bacteria in your gut. It helps keep your digestive system regular. Eating avocados supports a healthy gut microbiome. This is one of the many health benefits of avocados.
Can eating avocados help me manage my weight?
Yes, eating avocados can help with weight management. Their high fiber content makes you feel full longer. This can reduce overeating. Avocados are part of a healthy diet. They provide essential nutrients without excess sugar. These avocado benefits contribute to a healthy lifestyle.
Why is potassium in avocados important?
Avocados are a great source of potassium. This mineral helps regulate your blood pressure. It also supports proper nerve and muscle function. Getting enough potassium is vital for your overall health. This is one of the surprising health benefits of this superfood.

