Brown rice stands out as a true whole grain powerhouse. Its comprehensive nutritional profile offers many advantages over refined grains. Understanding the powerful health benefits of brown rice can transform your dietary choices. More than half of the global population relies on rice as their primary staple food. Do you know if your current rice consumption, especially brown rice, supports your health goals? Simple dietary swaps, like choosing brown rice, can significantly improve your diet. Health organizations globally recommend regular whole grain intake for better brown rice nutrition. This whole-grain rice provides numerous benefits for a healthier diet.
Key Takeaways
Brown rice is a whole grain. It has more fiber, vitamins, and minerals than white rice. This makes it a healthier choice.
Eating brown rice helps manage weight. Its fiber keeps you full longer. This can reduce how much you eat.
Brown rice helps control blood sugar. It has a lower glycemic index than white rice. This is good for people with diabetes.
Brown rice is good for your heart and digestion. It has compounds that lower cholesterol. Its fiber also helps your gut work better.
You can reduce arsenic in brown rice. Cook it with extra water and drain it. This makes it safer to eat.
Understanding Brown Rice Nutrition Facts

Brown rice offers an impressive nutritional profile. It provides essential nutrients that support overall health. Understanding these brown rice nutrition facts helps people make informed dietary choices.
Macronutrients and Calorie Profile
Brown rice is a good source of energy. One cup of cooked brown rice typically contains around 215 calories. This data comes from the USDA’s official FoodData Central database. It refers to standard long-grain rice prepared with water only. Another reference shows a 1-cup (195g) serving of cooked brown rice contains approximately 218 calories. Of these calories, 86% come from carbohydrates, 8% from protein, and 6% from fat.
Brown rice provides complex carbohydrates. These carbohydrates release energy slowly, helping to maintain steady blood sugar levels. Here is a look at its carbohydrate content:
Nutrient | Amount (g) |
|---|---|
Carbs | 44.42 |
Another source indicates one cup of cooked brown rice contains 50 grams of carbohydrates. A different reference within the same source shows 52 grams of total carbs for one cup of cooked brown rice. Brown rice also offers a moderate amount of protein, typically ranging from 4.5 to 5.5 grams per cooked cup.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
Brown rice is rich in important vitamins and minerals. It contains several B vitamins. These vitamins are crucial for energy production and nerve function.
Vitamin B1 (thiamine)
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
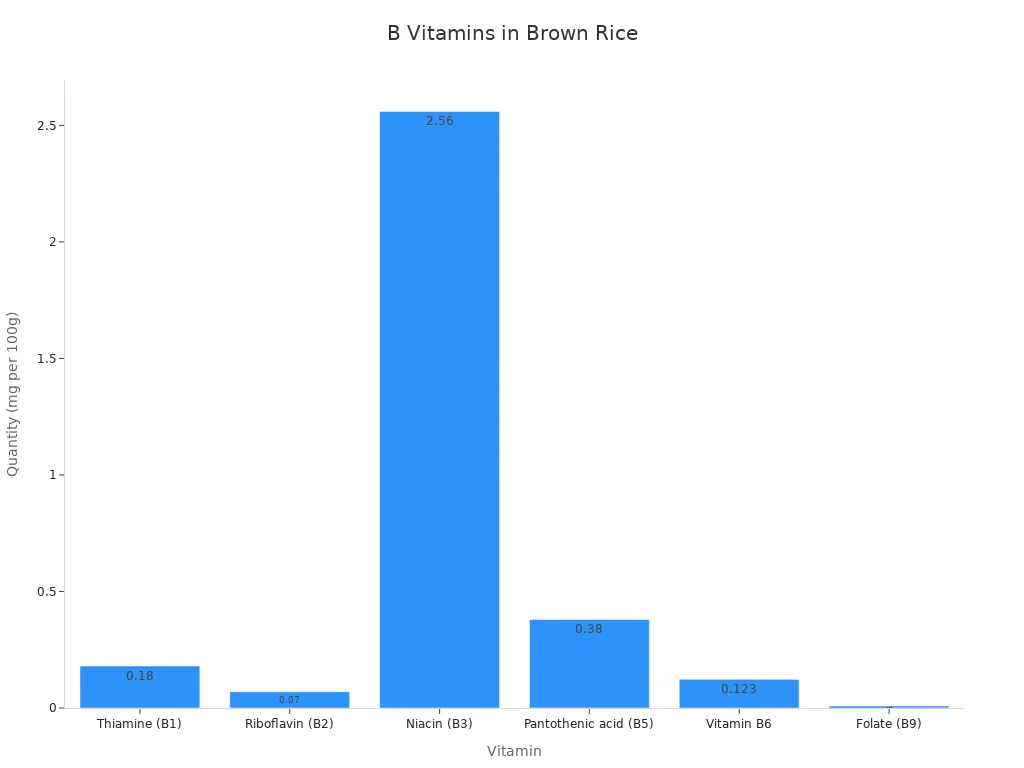
Here is a detailed breakdown of some B vitamins found in brown rice per 100g:
Vitamin | Quantity (per 100g) |
|---|---|
Thiamine (B1) | 0.18 mg |
Riboflavin (B2) | 0.07 mg |
Niacin (B3) | 2.56 mg |
Pantothenic acid (B5) | 0.38 mg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.123 mg |
Folate (B9) | 9 μg |
Beyond B vitamins, brown rice also supplies vital minerals. These minerals play many roles in the body.
Magnesium: 68mg
Potassium: 127mg
Iron: 0.9mg
Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function. Potassium helps maintain fluid balance. Iron is essential for carrying oxygen in the blood.
Fiber and Antioxidant Power
Brown rice stands out for its higher amounts of fiber. A single cooked cup typically provides 3 to 4.5 grams of dietary fiber. This fiber content is significantly higher than that found in white rice. Fiber aids digestion and promotes a feeling of fullness. This can help with weight management.
Brown rice also contains powerful antioxidants. These compounds protect the body’s cells from damage caused by free radicals. Antioxidants contribute to overall wellness and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases. The presence of these beneficial compounds further enhances the value of brown rice in a healthy diet.
Powerful Health Benefits of Brown Rice
Brown rice offers many health benefits. These advantages come from its rich nutritional content. People can improve their health by including brown rice in their diet.
Supporting Weight Management
Brown rice can help with weight management. Its high fiber content plays a key role. Fiber helps people feel full longer.
This feeling of fullness can reduce overall food intake. Studies on obese rats showed that brown rice, rich in fiber, helped moderate energy intake. It also improved metabolic health. The fiber in brown rice ferments into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs). These SCFAs offer metabolic benefits. They improve gut bacteria and energy use. Germinated brown rice (GBR) also reduced body weight gains and food intake in obese rats. Its high fiber content increases satiety. It also suppresses appetite. Chewing fiber-rich foods longer also helps people feel full. This reduces how much they eat.
Brown rice fiber, along with its complex carbohydrates, slows digestion. This leads to a slow rise in blood sugar. It also creates a lasting feeling of fullness. This sustained satiety can prevent cravings for unhealthy snacks. It helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. A study found that brown rice significantly reduced weight. It also lowered waist and hip circumference and BMI in overweight women.
This shows a direct benefit of brown rice for weight control. Brown rice has four times more dietary fiber than white rice. Its components, like arabinoxylan and β-glucan, feed good gut bacteria. These include Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus. Research links gut bacteria to obesity. Brown rice increases SCFAs in the large bowel. It also positively changes gut bacteria in humans.
These effects contribute to brown rice’s anti-obesity properties. Leptin regulates food intake. GABA, found in rice bran, may prevent obesity by working with leptin. Animal studies suggest brown rice has anti-obesity effects. It can reduce fat-making genes. Gamma-oryzanol (γ-ORZ) in brown rice bran can also help. It may reduce stress in the brain. This can improve leptin resistance. It can also reduce a preference for fatty foods. These mechanisms show brown rice’s potential to help with weight loss.
Regulating Blood Sugar and Diabetes Risk
Brown rice helps regulate blood sugar levels. This can lower the risk of diabetes. White rice has a higher glycemic index (GI) than brown rice. This is because white rice lacks its outer bran layer. The bran contains fiber and other protective factors.
Rice Type | Mean Glycemic Index |
|---|---|
White Rice | 64 |
Brown Rice | 55 |
Brown rice has a lower glycemic index. It causes a smaller and slower rise in blood sugar after eating. This helps to improve blood sugar levels. Some studies show brown rice can improve blood glucose management in diabetic patients. It also helps with lipid-related markers. Other studies report lower blood glucose and insulin reactions with brown rice compared to white rice.
Consuming white rice seems to increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. However, eating brown rice appears to decrease that risk. Researchers looked at data from large studies. They found that more brown rice consumption linked to a lower risk of diabetes. This link remained strong even after adjusting for other risk factors. People who ate two or more servings of brown rice per week had a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Dr. Qi Sun from the Harvard School of Public Health suggests replacing refined grains like white rice with whole grains, including brown rice. This helps prevent type 2 diabetes. Replacing 50 grams of white rice with brown rice can reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by 16%.
Boosting Digestive Health
Brown rice is excellent for boosting digestive health. Its high fiber content promotes better digestion. Brown rice-based diets improved bowel function. They reduced total colon transit time. They also increased bowel movements compared to white rice diets. The brown rice diet group saw an increase in bowel movements from 3.4 to 5.0 per week. This brought their bowel function into a normal range. The mixed dietary fiber in brown rice, including insoluble fiber, helps soften bowel movements. This reduces constipation.
The fiber in brown rice supports the growth of good bacteria in the gut. These bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids like butyrate. Butyrate has anti-inflammatory effects. It helps keep the gut barrier strong. Brown rice also contains gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA has anti-inflammatory properties. It has reduced colon inflammation in mice.
Brown rice is a good source of insoluble fiber. This fiber helps waste move through the digestive system. Fiber in brown rice acts as a prebiotic. It boosts healthy bacteria in the gut. Resistant starch-enriched brown rice (RBR) significantly helped four probiotic strains grow. It did better than white and regular brown rice. RBR also suppressed colon shortening in obese mice. It increased Bifidobacteria growth. It improved intestinal permeability. These benefits show how brown rice supports a healthy gut.
Promoting Heart Health
Brown rice contributes to heart health. It contains compounds that help reduce cholesterol. These include Oryzanol, Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA), and Phytosterol glycosides (ASG). Tocopherols, monounsaturated fatty acids, and phenolic compounds also help. These compounds work together to lower cholesterol. They may regulate how the body absorbs cholesterol.
A study looked at whole grain foods and coronary heart disease (CHD). It followed US men and women for over 25 years. Higher consumption of most whole grain foods, including brown rice, linked to a significantly lower risk of CHD. People who ate two or more servings of brown rice per week had a 21% lower risk of CHD. This was compared to those who ate less than one serving per month. The study concluded that more whole grain intake helps prevent CHD. This highlights the health benefits of brown rice for the heart.
Antioxidant Properties and Overall Wellness
Brown rice has strong antioxidant properties. These protect the body’s cells from damage. Brown rice antioxidants, especially from germinated brown rice (GBR) extracts, protect cells in two main ways. They boost the body’s antioxidant defenses.
They also control genes that protect cells. GBR extracts fight oxidative damage. They improve the ability to remove harmful radicals. They also reduce levels of damaging substances. This protection happens by increasing antioxidant genes like Catalase and Superoxide Dismutase (SOD). It also boosts genes that help cells survive. GBR extracts increase SOD 2. This prevents cell death. It also promotes cell survival. These actions help cells reduce oxidative stress. They prevent cell destruction. This contributes to overall wellness and can lower risk of chronic diseases.
Brown Rice Versus White Rice: A Nutritional Comparison
People often wonder about the differences between brown rice and white rice. Their processing methods create significant nutritional variations. Understanding these differences helps make better food choices for a healthy diet.
Key Nutritional Differences
Brown rice is a whole grain. It keeps its bran and germ layers. White rice undergoes milling and polishing. This process removes the bran and germ. This refining strips away many important nutrients.
Consider the fiber content:
Rice Type | Fiber (per 1 cup cooked) |
|---|---|
Brown Rice | 3.5g |
White Rice | 0.6g |
Brown rice contains more dietary fiber than white rice. The bran and germ in brown rice hold most of this fiber. White rice loses this fiber when processors remove the bran. This makes brown rice more nutrient-dense.
Brown rice also contains higher amounts of specific B vitamins. These include B1, B3, B6, and B9. It also has more magnesium, potassium, and iron. The removal of bran in white rice leads to a significant loss of nutrients. This includes about 85% of fat and 70% of B vitamins. The bran layer is rich in fiber, B vitamins, and antioxidants. The germ contains healthy fats and vitamin E.
Why Choose Brown Rice
Choosing brown rice offers clear advantages. It is a whole grain. It digests more slowly because of its fiber content. This leads to a more gradual rise in blood sugar. It also creates a steadier insulin response. The insoluble fiber from the bran helps promote regular bowel movements. This makes brown rice a more nutritious choice for many people.
Impact on Health Outcomes
The choice between brown rice and white rice impacts long-term health. Brown rice is associated with an 11% reduction in the risk of type 2 diabetes. This comes from studies in Western populations. White rice, however, has a higher glycemic index.
This links to an elevated risk of chronic disease. It increases insulin demand and resistance. White rice also has lower beneficial nutrients due to milling. High intake of white rice shows a positive association with the risk of overall chronic disease in women. More research is needed, especially in Asian populations, to fully understand the effects of substituting brown rice for white rice on chronic disease and mortality risk.
Incorporating Brown Rice into Your Diet

People can easily add brown rice to their daily meals. It offers many health benefits. Knowing how to cook it and address concerns helps people make good choices.
Simple Cooking Methods and Preparation
Cooking brown rice is straightforward. Different methods work well. For pressure steaming, use about 1 1/3 cups of liquid per grain. Pressure steam it for 15-20 minutes. Then, let it release naturally. A rice cooker is also simple. Use 1 cup of brown rice to 2 cups of water. Cook until the cycle finishes, then let it rest for 5 minutes. An Instant Pot needs 1 cup of brown rice to 1 cup of water. Cook for 22-24 minutes on high pressure. Then, allow a 10-minute natural release.
Different types of brown rice have different boiling times:
Rice Type | Boiling Time |
|---|---|
Medium grain brown rice | 30 minutes |
Long grain brown rice | 30 minutes |
Brown basmati rice | 12-14 minutes |
Baking is a hands-off way to cook brown rice. It works for short, medium, and long grain types. This method takes 75 minutes. It cooks the tough outer layer perfectly. It also avoids scorching the bottom.
Versatile Recipe Ideas
Brown rice is very versatile. People can use it in many dishes. It makes a great side dish for chicken or fish. You can add it to stir-fries with vegetables and soy sauce. Brown rice also works well in salads. Mix it with chopped veggies, herbs, and a light dressing. For breakfast, make a warm brown rice porridge with fruit and nuts. It can also be the base for hearty grain bowls. These bowls include roasted vegetables, protein, and a flavorful sauce. This helps people stick to a healthy diet.
Addressing Arsenic Concerns
Brown rice can have higher arsenic levels than white rice. This is because milling removes the outer layers of white rice. These layers contain inorganic arsenic. Brown rice keeps these layers. Studies show brown rice has about twice the inorganic arsenic of white rice. Arsenic levels vary by region and rice type. Weather patterns also affect these levels. One company’s tests showed their brown rice averaged 90 ppb for inorganic arsenic. The range was 0.01 – 0.29 ppm.
People can reduce arsenic in brown rice during cooking.
Boil water first.
Add rice and boil for 5 more minutes.
Remove the arsenic-laden water.
Add fresh water to cook at a low temperature until the water absorbs.
The ‘parboiled and absorbed (PBA)’ method is very effective. It removes 54% of inorganic arsenic. It also keeps most nutrients. Cooking rice in a coffee percolator also works. It can reduce arsenic by about 50%. One sample even showed an 85% reduction. For this method, add rice to the percolator where coffee grounds usually go. Let water filter through the brown rice three times. Then, test for doneness.
Brown rice is a nutritional powerhouse. It offers many health benefits. This versatile whole grain is better for your diet than white rice. Brown rice supports heart health, aids digestion, and manages blood sugar. Readers should choose brown rice. Gradually add brown rice to your meals. This helps improve health long-term. Take control of your health with mindful diet changes.
FAQ
Is brown rice truly healthier than white rice?
Yes, brown rice is a whole grain. It keeps its bran and germ layers. These layers provide more fiber, B vitamins, and minerals. White rice loses these nutrients during processing. This makes brown rice a more nutritious choice.
How does brown rice help manage weight?
Brown rice contains high fiber. Fiber helps people feel full longer. This reduces overall food intake. It also slows digestion, leading to stable blood sugar and fewer cravings. These factors support effective weight management.
Can people with diabetes eat brown rice?
Yes, people with diabetes can eat brown rice. It has a lower glycemic index than white rice. This causes a slower rise in blood sugar. Eating brown rice helps manage blood glucose levels. It can also lower the risk of type 2 diabetes.
What is the best way to cook brown rice?
Many methods work well. A rice cooker or Instant Pot simplifies cooking. Use about 1 cup of brown rice to 1-2 cups of water, depending on the method. Baking also provides a hands-off approach for perfect results.
How can people reduce arsenic in brown rice?
People can reduce arsenic by cooking brown rice with excess water, then draining it. The ‘parboiled and absorbed’ (PBA) method removes a significant amount of arsenic. Cooking in a coffee percolator can also reduce arsenic levels.

