
Camembert cheese captivates palates worldwide. This classic French cheese is famous for its distinctive flavor and creamy texture. People enjoy Camembert often. This article explores Camembert’s nutrition, taste profile, and health benefits. It also discusses its broader health implications. Understanding the nutrition of what we eat is important, especially for a beloved cheese like Camembert.
Key Takeaways
Camembert cheese offers good nutrition. It has protein, calcium, and helpful probiotics for your gut.
Camembert’s taste changes as it gets older. It goes from mild to a rich, earthy flavor.
You can enjoy Camembert in many ways. Serve it with bread, fruits, or bake it.
Store Camembert in the fridge. Wrap it in paper first, then loosely in plastic. This keeps it fresh.
Pregnant women should eat only pasteurized Camembert. Make sure it is cooked until very hot to be safe.
Understanding Camembert Cheese

Camembert Origin
Camembert cheese began in the 1790s. Marie Harel, a cheesemaker, created it in the village of Camembert, French Normandie. Legend says she received cheesemaking advice from a priest during the French Revolution. Napoleon or Napoleon III later tasted the cheese. He named it after the village. An engineer named Ridel invented the wooden box for safe transport. This box helped Camembert’s global reach. The rind of Camembert was once green. It changed to the white rind we see today in the 1920s and 1930s.
Production Process
Making Camembert cheese involves several steps.
Milk Collection and Preparation: Raw milk is collected. Workers heat it. Then, they add special bacteria to start fermentation.
Curdling and Molding Process: Rennet is added. This makes the milk curdle. The curds are cut. Workers gently place them into molds to drain liquid.
Salting and Initial Aging: The molded cheese is salted. This improves flavor and controls bacteria. It then ages for a short time in a controlled place.
Ripening with Penicillium camemberti: A mold called Penicillium camemberti is introduced. This mold creates the white rind. It also gives the cheese its earthy flavor during the final aging.
Key Characteristics
Authentic Camembert has distinct features. It has a thin, white, felt-like rind. The inside of the cheese is ivory to light yellow when fully ripe. Its texture is smooth and soft. The flavor starts milky and mild. It also has a slightly salty taste. As Camembert ages, its flavor becomes stronger and more fruity. Scientific studies confirm this unique flavor profile.
Comparing Camembert and Other Cheese
People often compare Camembert to Brie. These two cheeses have similar nutritional values. However, Camembert is slightly healthier. It has fewer calories per serving. Brie contains more fat, protein, and cholesterol. Brie also has higher amounts of vitamins like B12 and iron. Both are delicious, but Camembert offers a slightly lighter option.
Camembert Nutrition Profile
This section details the nutrition facts of Camembert. It explores its nutritional composition, highlighting its richness in protein and essential nutrients. Understanding the nutritional profile of this cheese helps consumers make informed dietary choices.
Calorie Content
Camembert offers a moderate amount of calories for a cheese. The calories in Camembert can vary slightly depending on the specific brand and fat content. For example, a 100g serving of Camembert 30% contains 200 kcal. Other varieties, like Isigny Ste Mere Camembert, may have around 284 calories per serving. This makes Camembert a moderate-calorie cheese compared to some other richer varieties. Individuals often monitor calories for weight management. Knowing the calories in Camembert helps with portion control. These nutrition facts provide a clear picture of its energy contribution.
Macronutrient Breakdown
Camembert provides a balanced mix of macronutrients. It is particularly rich in protein, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. A 100g serving of camembert typically contains about 18-20 grams of protein. This makes it a good source of complete amino acids. The nutrition facts for camembert also show its fat and carbohydrate content.
Macronutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Fat | 9.22g |
Carbohydrates | 0.17g |
Protein | 7.52g |
Note: Protein content can vary, with some sources indicating higher amounts (18-20g) than others (7.52g) per 100g. Always check the specific product’s nutrition facts.
The fat content contributes to the cheese‘s creamy texture and flavor. The carbohydrate content is very low, making camembert suitable for low-carb diets. These nutrition facts are important for understanding the overall nutrition of camembert.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Camembert is a nutrient-rich profile food. It provides several essential vitamins and minerals crucial for good health. It is high in calcium, which supports strong bones and teeth. A 100g serving of camembert contains approximately 110mg of calcium and 98mg of phosphorus. Both nutrients are vital for bone health.
Nutrient | Amount (per 100g) |
|---|---|
Calcium | 110mg |
Phosphorus | 98mg |
Beyond minerals, camembert also offers a range of vitamins. These nutrition facts highlight its contribution to daily vitamin intake.
Vitamin | Amount in 100g Camembert |
|---|---|
Vitamin B12 | 1.3µg |
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2) | 0.488mg |
Vitamin A | 241µg |
Vitamin E | 0.21mg |
Vitamin B3 | 0.63mg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.227mg |
These nutrition facts show that camembert is a good source of B vitamins, which play roles in energy metabolism and nerve function. Vitamin A supports vision and immune health. Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant. This comprehensive nutrition makes camembert cheese a valuable addition to many diets.
Lactose Content
Many people worry about lactose when consuming cheese. The nutrition facts for camembert show it has a very low lactose content. This is because the cheesemaking process, especially fermentation and aging, breaks down most of the lactose.
Cheese Type | Lactose Content (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
Camembert | <2.4 |
Another analysis confirms this low level:
Cheese Type | Lactose Content (g) | Serving Size (g) | Lactose Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
Camembert Cheese | 0.04 | 40 | Low |
This low lactose level means many individuals with lactose intolerance can often enjoy camembert without discomfort. These nutrition facts are beneficial for those managing dietary restrictions. The overall nutrition of camembert makes it a versatile food.
Camembert Health Benefits
Camembert offers several positive health benefits. This delicious cheese contributes to overall well-being. People can enjoy Camembert as part of a balanced diet. Its unique nutrition profile supports various bodily functions.
Bone Health Support
Camembert cheese provides excellent support for bone health. It contains significant amounts of calcium and phosphorus. These minerals are crucial for building and maintaining strong bones and teeth. The nutrition facts show that a 100g serving of Camembert contains approximately 110mg of calcium and 98mg of phosphorus. These nutrition facts highlight its role in preventing bone density loss. Regular intake of calcium and phosphorus helps keep bones healthy throughout life. This makes Camembert a beneficial food for skeletal strength.
Gut Health and Probiotics
Camembert is a fermented food. It contains probiotics and bioactive compounds. These elements can improve gut health. The cheesemaking process introduces beneficial bacteria. Studies show that consuming Camembert can increase good bacteria in the gut. For example, Enterococcus faecalis populations significantly increased in stool samples after Camembert ingestion. Researchers also detected L. lactis and Ln. mesenteroides from the cheese in faeces during the trial. These specific probiotic strains contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. The nutrition facts of fermented foods often include these beneficial microorganisms. Bioactive peptides in fermented dairy products, including aged cheeses, may also contribute to health benefits. These include potential anti-inflammatory effects. Specific peptide sequences released during cheese ripening demonstrate anti-inflammatory properties. Certain lactic acid bacteria (LAB) produce functional lipids, such as conjugated linoleic acid. This also exhibits anti-inflammatory activity. These nutrition facts show Camembert’s potential to reduce inflammation and support digestive health.
Muscle Growth and Repair
Camembert is a good source of protein. Protein is essential for the repair and growth of muscles. The nutrition facts confirm Camembert is rich in protein. This nutrient is crucial for muscle growth, repair, and overall bodily functions. A study involved 20 healthy young males. They compared the effects of ingesting 30g of protein from cheese versus milk protein concentrate. Participants underwent resistance exercise. Muscle protein synthesis rates increased significantly after consuming both cheese and milk protein. This happened both at rest and during recovery from exercise. There was no significant difference in the muscle protein synthetic response between cheese and milk protein ingestion. This indicates that the protein in cheese, such as Camembert, effectively contributes to muscle protein synthesis. This is vital for muscle growth and repair. These nutrition facts make Camembert a valuable food for active individuals.
Cognitive Function and Memory
Some research suggests Camembert may support cognitive function and memory. These health benefits are still under investigation. A study published in Nutrients suggests that Camembert cheese intake may help prevent mild cognitive decline in older women in Japan. The research indicated an association between Camembert consumption and a reduced risk of mild cognitive impairment. Another study published in Neuroscience Research found that fatty acid amides improved memory and learning in mice. These compounds generate during Camembert’s fermentation. Myristamide, a fatty acid amide, enhanced recognition and spatial memory in mice. It also increased the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hippocampus. This region is crucial for memory. This suggests Camembert cheese may offer cognitive benefits. It promotes neurogenesis and synaptic plasticity. These findings highlight potential health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
Health Risks of Camembert
Camembert, like many rich foods, carries potential downsides. People should consider these for overall health.
Saturated Fat and Cholesterol
This cheese contains saturated fat and cholesterol. People should consider these amounts for a balanced diet. A 100g serving of camembert has specific levels of these nutrients.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Saturated Fat | 15.45g |
Cholesterol | 71.95mg |
These values are important for individuals monitoring their fat intake.
Calorie Density Concerns
Camembert also has calorie density. This is a factor in weight management. Reducing energy density helps prevent obesity. It does not just focus on calorie intake. Camembert has a medium energy density of 3.0. Its protein-to-energy ratio is 2.7. This classifies it as a low P:E food. It may be less satiating than foods with a higher ratio. The satiety score for camembert is 50%. This indicates a medium level of satiety. Camembert contains 299 calories per 100g. Among low-carb cheese options, camembert is the least calorie-dense. Other options include goat, gruyere, and brie. People should consider these calories when managing their diet. Too many calories can lead to weight gain. Understanding the calories in camembert helps with portion control. These calories contribute to daily energy intake.
Sodium Levels
This soft cheese contains sodium. High sodium intake can affect blood pressure. People should consume camembert in moderation. This helps manage overall sodium levels in their diet.
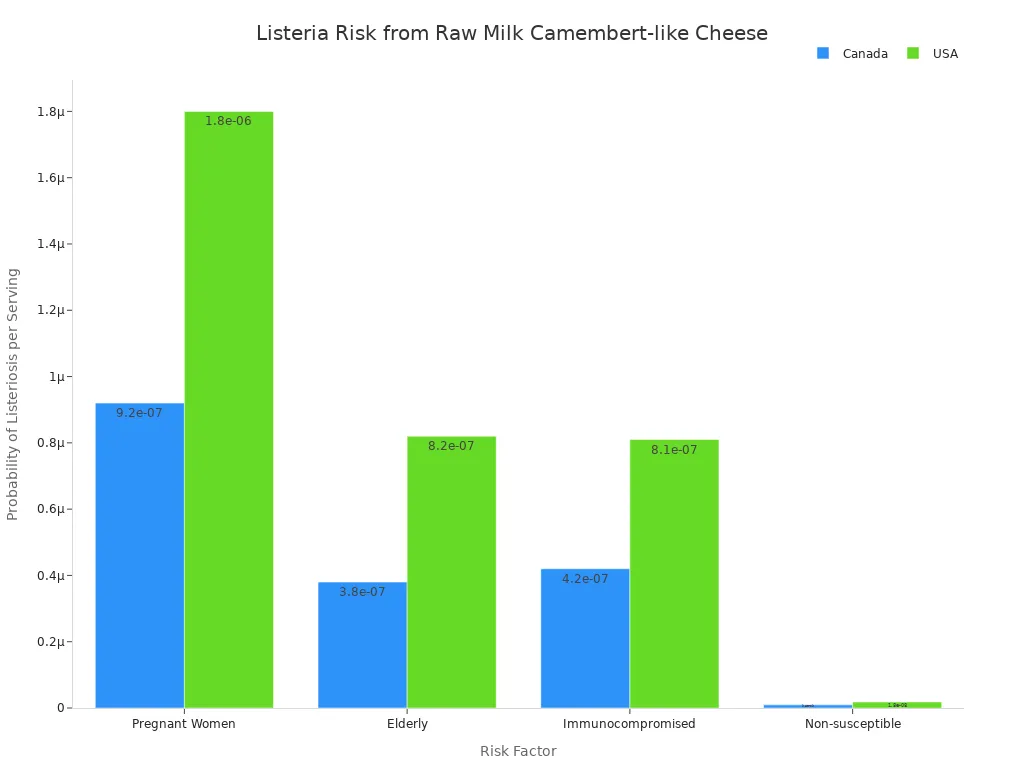
Listeria Risk
A significant concern with soft cheese, including camembert, is Listeria risk. Listeria monocytogenes is a bacterium. It can cause a serious infection called Listeriosis. This risk is higher with unpasteurized versions of camembert cheese.
Risk Factor | Probability of Listeriosis per Serving (Canada) | Probability of Listeriosis per Serving (USA) |
|---|---|---|
Pregnant Women (Raw Milk Camembert-like cheese) | 9.2 x 10^-7 | 1.8 x 10^-6 |
Elderly (Raw Milk Camembert-like cheese) | 3.8 x 10^-7 | 8.2 x 10^-7 |
Immunocompromised (Raw Milk Camembert-like cheese) | 4.2 x 10^-7 | 8.1 x 10^-7 |
Non-susceptible (Raw Milk Camembert-like cheese) | 9.5 x 10^-9 | 1.8 x 10^-8 |
Soft cheese made with unpasteurized milk is 50 to 160 times more likely to have L. monocytogenes infection. This is compared to those made with pasteurized milk.
Certain groups face a higher risk from raw milk soft cheese. These include:
Queso fresco
Blue-veined
Feta
Brie
Camembert
Lower risk cheeses are typically made from pasteurized milk. These include:
Processed cheese
Cream cheese
Mozzarella cheese
Hard cheese
Pregnant individuals need to be especially careful for their health.
Pasteurized camembert is safe to eat during pregnancy. It must be stored at a sufficiently low temperature.
Unpasteurized camembert can be consumed if thoroughly fried or baked. High temperatures kill Listeria monocytogenes bacteria.
It is generally safer to choose blue cheese made from pasteurized milk.
Consume camembert in moderation due to its high saturated fatty acid content. Limit fried and baked versions to occasional consumption.
Camembert is safe to eat during pregnancy only when it is piping hot and bubbling. Heat kills Listeria bacteria.
Avoid camembert that has been heated and then left to cool.
Mould-ripened soft cheeses like Brie and camembert are only safe to eat in pregnancy if they have been cooked.
Soft blue-veined cheeses such as Danish blue, Gorgonzola, and Roquefort should be avoided unless they have also been cooked.
Camembert Taste Profile
Camembert offers a complex sensory experience. Its taste profile changes significantly as it ripens. Understanding these changes helps appreciate this classic French cheese.
Aroma and Flavor Evolution
The aroma and flavor of camembert evolve during its ripening. Initially, it has a milky, fresh scent. As it ages, the aroma becomes more earthy and pungent. Fungi like Penicillium camemberti and Geotrichum candidum play a big role. They break down proteins and fats, creating typical sensory properties. Debaryomyces hansenii, a yeast, also speeds up surface changes and enhances the cheese’s flavor.
Specific bacteria and yeasts contribute to the rich flavor. L. lactis CCFM 12 increases fruity aromas by boosting ethyl acetate. Y. lipolytica produces sulfides, furans, and short-chain ketones, adding to the overall flavor. D. hansenii significantly increases branched-chain aldehydes and alcohols, which are crucial for flavor formation.
The chemical composition also changes. Lactic acid decreases during ripening. Glutamic acid, which gives an umami flavor, increases. Sensory tests show higher sourness in traditional camembert at day one. Umami flavor becomes more noticeable at days 19 and 28. Traditional methods create a higher overall flavor intensity. This is due to more taste-related compounds. So, what does camembert cheese taste like? It offers a journey from mild to a complex, earthy, and sometimes fruity flavor.
Texture and Mouthfeel
Camembert’s texture and mouthfeel are key to its appeal. It starts firm but softens considerably as it ripens. This change happens because of proteolysis. Proteolysis breaks down the protein network into smaller parts. This process makes the cheese less hard. A fully ripened camembert, around day 28, has a creamy interior. Its texture is smooth and almost liquid near the rind. Instrumental analysis shows that hardness values for properly ripened camembert range from 1 to 14 N. Lower values mean better ripening. This creamy texture is a hallmark of good camembert.
Ripening Stages
Camembert goes through distinct ripening stages. Each stage brings changes in its flavor, aroma, and texture. Young camembert is firm and mild. It has a fresh, milky flavor. As it ripens, the white rind develops. The interior softens, becoming more elastic and then creamy. The flavor deepens, becoming more complex and earthy. It develops notes of mushroom, butter, and sometimes fruit. The aroma also intensifies, becoming more pungent. This evolution makes camembert a dynamic cheese. Its rich flavour develops over time.
Enjoying Camembert

People enjoy Camembert in many ways. Proper preparation and pairing enhance its unique flavors. Knowing how to choose camembert cheese for ripeness ensures the best experience.
Serving Suggestions
Serve Camembert at room temperature. Allow it to sit out for about thirty minutes before eating. The rind is edible and contributes to its flavor. People often pair it with various types of bread, such as baguettes or crackers. Fruit preserves or honey also complement it well.
Add Camembert to salads with apples, pears, and nuts. A simple oil and vinegar dressing works best.
Bake Camembert (Camembert chaud). Enhance it with fruits, nuts, and herbs. This is a popular way to enjoy the soft cheese.
Cook Camembert on a barbecue. Wrap it in its box with aluminum foil. Place it on hot coals. This shows how to cook camembert cheese.
Wrap it in layers of sliced meat, like ham or prosciutto. Cook it on a stovetop skillet.
Melt Camembert into mac ‘n’ cheese with Gruyere.
For fondue, cut off the top and bake it. Then dip with crusty bread.
Deep-fried Camembert wedges are a treat. Serve them warm with cranberry sauce.
Make grilled cheese sandwiches with Camembert, cranberry sauce, and balsamic. Use ciabatta or baguettes.
Food Pairings
Many foods and beverages complement Camembert. This helps answer what goes with camembert cheese.
Fresh baguette: Its crusty exterior and soft interior highlight the creamy texture.
Apples and pears: Their crispness and sweetness contrast with the earthy taste.
Honey and nuts (walnuts, pecans, almonds): Honey adds sweetness, and nuts provide crunch.
Chutney and jam (fig, apple, apricot): These offer sweet and tangy contrasts.
Prosciutto or salami: Cured meats add saltiness, perfect for a charcuterie board.
Roasted vegetables: Carrots, sweet potatoes, and butternut squash develop sweetness. This complements the cheese‘s earthy flavors.
Cranberries and dried fruit: These provide a sweet and tangy contrast.
Crackers or biscuits: They offer a crunchy texture for spreading the soft, creamy cheese.
Storage Tips
Proper storage maintains Camembert’s quality and freshness. This addresses how to store camembert cheese.
Store Camembert in the refrigerator. Wrap it in wax or parchment paper. Then loosely cover it with plastic wrap. This allows airflow and prevents drying.
Avoid airtight containers. They can make it too soft and lead to spoilage.
Limit prolonged contact with plastic. It can negatively affect the taste.
Regularly inspect for mold. This ensures the cheese remains safe.
Consume Camembert within 1-2 weeks when stored correctly in the refrigerator. Once opened, consume it within 5-7 days. This answers how long does it last.
Camembert can be frozen for up to 6 months. However, its texture may change upon thawing.
Storage Location | Duration (Unopened/Opened) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Refrigerator | 1-2 weeks | Keep refrigerated at all times. Wrap first in wax or parchment paper, then plastic wrap. |
Freezer | 3-6 months | Best quality. |
Camembert offers rich nutrition, unique taste, and potential health benefits. This delicious cheese fits into a balanced diet when consumed in moderation. People appreciate camembert not just for its flavor but also for its valuable nutrition. Understanding the nutrition of this cheese helps make informed food choices. This cheese provides good nutrition. Enjoying camembert cheese thoughtfully enhances culinary experiences and supports well-being.
FAQ
Is Camembert cheese healthy?
Camembert offers protein, calcium, and beneficial probiotics. It supports bone health and gut function. People should consume it in moderation. It contains saturated fat and sodium.
Can pregnant women eat Camembert cheese?
Pregnant women can eat pasteurized Camembert. They must ensure it is piping hot if cooked. Avoid unpasteurized Camembert. It carries a risk of Listeria bacteria.
What is the best way to store Camembert cheese?
Store Camembert in the refrigerator. Wrap it first in wax or parchment paper. Then, loosely cover it with plastic wrap. This method allows the cheese to breathe and prevents it from drying out.
Does Camembert cheese contain lactose?
Camembert cheese has very low lactose content. The cheesemaking process breaks down most of the lactose. Many individuals with lactose intolerance can often enjoy it without discomfort.

