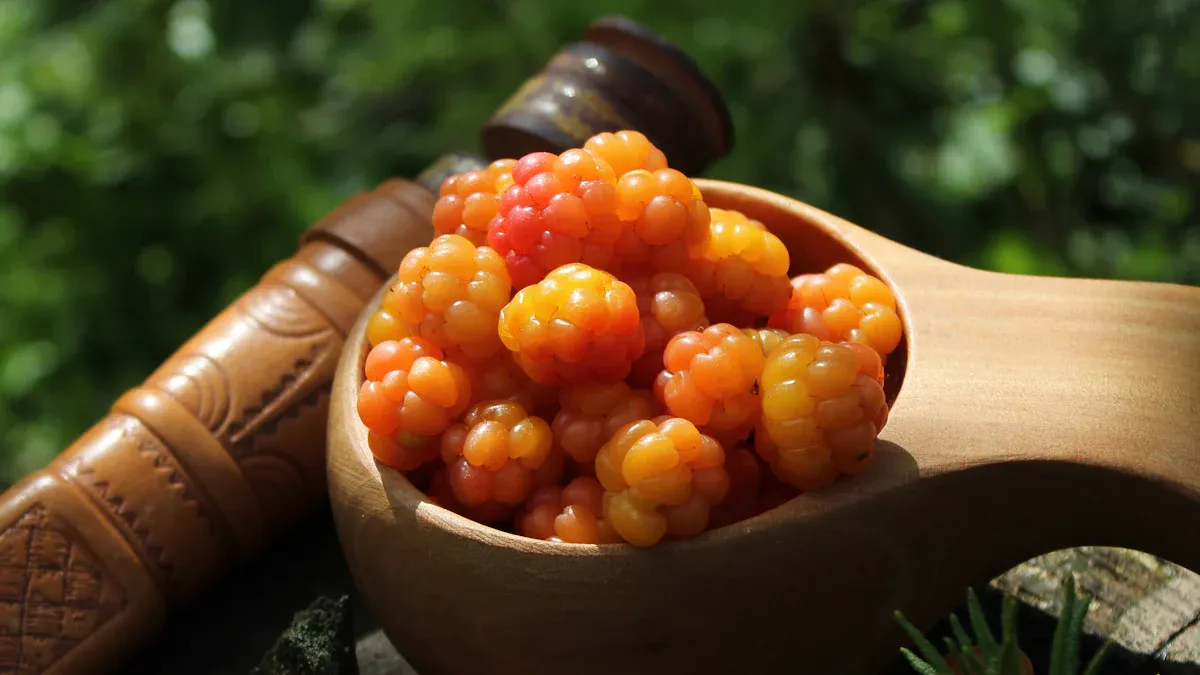

Cloudberries are a rare and prized “gold of the forest.” These amber-colored fruits thrive in arctic and subarctic regions. A single cloudberry offers a unique tart-sweet flavor. This berry provides exceptional nutritional value. It is truly an arctic super-fruit, packed with essential vitamins. Each cloudberry offers powerful benefits.
Key Takeaways
Cloudberries are rare arctic fruits. They grow in cold places. They have a unique tart-sweet taste.
These berries are very healthy. They have lots of Vitamin C, A, and E. They also have important minerals and antioxidants.
People use cloudberries in many ways. They make jams and desserts. They also use them in skincare products.
Fresh cloudberries are hard to find. This is because they grow in remote areas. Their harvest season is very short.
Understanding Cloudberries: The Arctic Berry
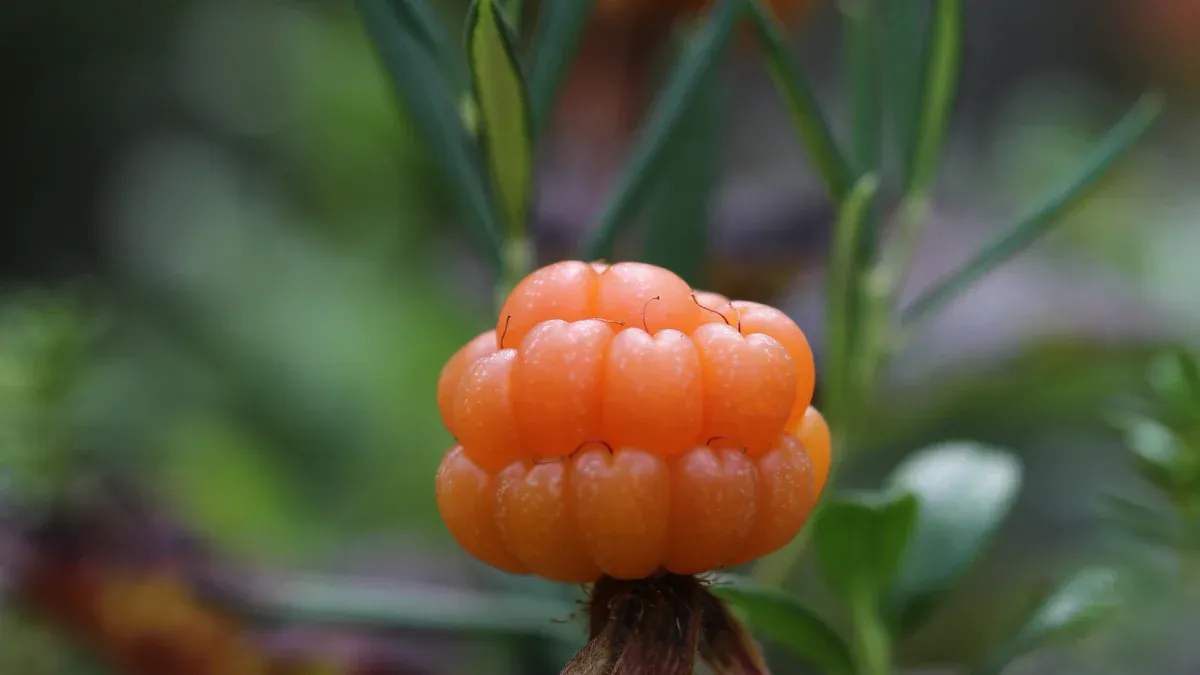

Defining This Unique Fruit
Cloudberries are a unique fruit. They thrive in cold climates where other fruits struggle. This plant tolerates frost and extreme weather conditions. It requires acidic soil, with a pH between 3.5 and 5.0. Cloudberry plants grow best in moist, well-drained, and peat-rich soil. These conditions are similar to wetlands or boggy areas. The plant needs consistent moisture but avoids waterlogging. It grows best in cool, northern climates with mild summers and cold winters. Cloudberries do not tolerate extreme heat or drought. This resilience makes them a true “gold of the forest” in their harsh environments.
Appearance and Characteristics
Cloudberries are small, edible fruits. They resemble raspberries but have a vibrant amber hue. These plants belong to the Rosaceae family. This family also includes apples, cherries, and blackberries. Cloudberry plants are dioecious. This means each plant is either female or male. They have a slow reproduction cycle. It takes seven years for a plant to bear fruit. Cloudberries are native to peat-rich moors and mountainous bogs. These areas are within or near the arctic Circle. They thrive in acidic, low-nutrient soil. This allows their cultivation in harsh polar regions. The fruits ripen from a bright red to their signature amber shade. This happens between July and mid-August. This distinctive berry offers a unique taste and appearance.
The Arctic Habitat of Cloudberries
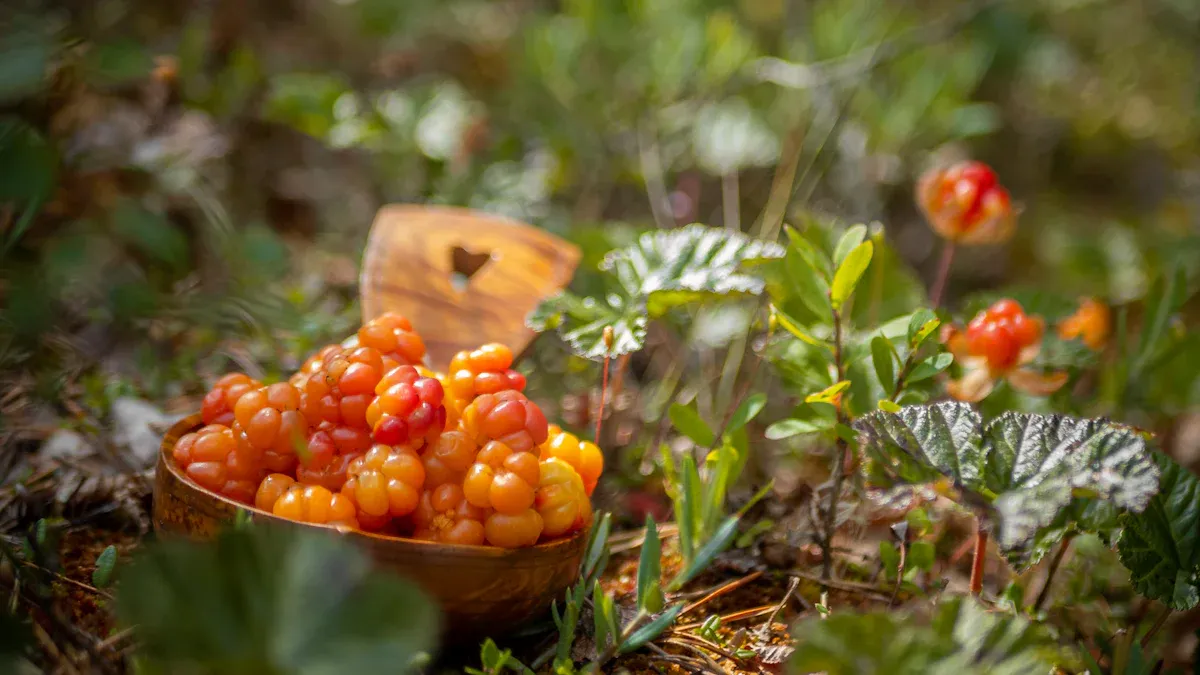

Native Regions and Climate Preferences
Cloudberries have a wide distribution. They grow naturally across the Northern Hemisphere. Key regions include Northern Europe, such as Scandinavia and Baltic countries like Latvia. Canada also has many of these berries. Sometimes, they appear in northern Germany and Poland. People also find them in mountain ranges in Poland and the Czech Republic. These plants prefer cooler climates. They need acidic, peat-rich soils. The best soil pH for cloudberry growth is between 3.5 and 5.0. They require plenty of sunlight. However, they thrive in cooler temperatures. This mimics their natural boggy homes in Northern Europe and North American tundras. The arctic environment suits them well.
Harvesting Season and Challenges
The cloudberry harvest season is short. In Lapland, the fruit usually ripens from mid-July through early August. This window lasts about two to three weeks. The exact timing changes each year based on the weather. Northern areas ripen later than southern parts. In Norway, lowland cloudberries ripen in mid-July. Mountain cloudberries ripen two to three weeks later. This is because mountain areas are cooler. Gathering this fruit generally happens in mid-to-late summer.
However, harvesting presents significant challenges. Weather conditions greatly affect the crop. Strong winds (40-60 km/h) or heavy rain in spring can destroy delicate blossoms. Extreme warm temperatures (above 25° Celsius) in summer can burn the fruit. Conversely, cold and damp conditions hinder growth. This results in small or sparse berries. These weather variations make the yield unpredictable.
Accessibility also poses problems for the harvest. Many communities have moved away from traditional picking grounds. This makes it harder to reach the berries. People face financial and time constraints. Rigid work schedules further limit picking time. Harvesters often need multiple day trips. Sometimes, they can only pick for short periods. These factors make gathering the prized cloudberry a difficult task.
Cloudberry: An Arctic Super-Fruit’s Vitamins
Cloudberry is truly an arctic super-fruit. It offers an impressive nutritional profile. These berries pack essential vitamins and nutrients. They provide significant health benefits.
High Vitamin C Content
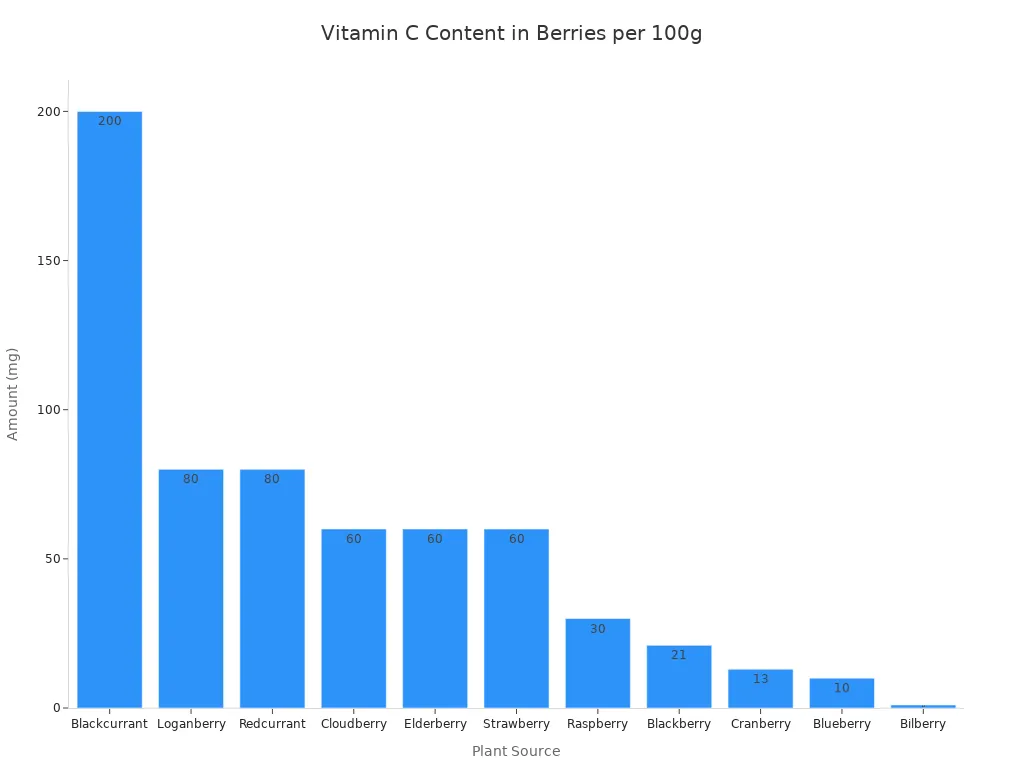
Cloudberries contain exceptionally high levels of vitamin C. This makes them a powerful source of this vital vitamin. A 100-gram serving of cloudberry provides 176% of your daily vitamin C needs. This amount is more than twice that of orange juice. Cloudberries also surpass many other berries in vitamin C content.
Here is a comparison of vitamin C in various berries:
Plant source | Amount (mg / 100g) |
|---|---|
Blackcurrant | 200 |
Cloudberry | 60 |
Loganberry | 80 |
Redcurrant | 80 |
Elderberry | 60 |
Strawberry | 60 |
Raspberry | 30 |
Blackberry | 21 |
Cranberry | 13 |
Blueberry | 10 |
Bilberry | 1 |
The high levels of vitamin C in cloudberries act as a potent antioxidant. This vitamin neutralizes free radicals. This antioxidant activity helps prevent oxidative damage. Oxidative damage contributes to wrinkles, fine lines, and dull skin. Vitamin C also boosts collagen production. Collagen is essential for maintaining firm and smooth skin. Furthermore, vitamin C, abundant in cloudberries, plays a crucial role in supporting immune function.
Key Vitamins A and E
Cloudberries also contain other important vitamins. They are rich in beta-carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. Vitamin A supports vision, immune function, and skin health. These berries also provide vitamin E. This vitamin is another powerful antioxidant. It protects cells from damage. Alpha-tocopherol (α-tocopherol) is a form of vitamin E found in cloudberries. Both vitamin A and vitamin E contribute to overall health and well-being.
Potent Antioxidants and Phenolics
Beyond vitamins C, A, and E, cloudberries offer a wealth of other potent antioxidants. These include ellagic acid, citric acid, malic acid, and anthocyanins. Modern scientific interest highlights their rich profile of antioxidants. This profile also includes ellagitannins and flavonoids. Ellagic acid was identified as the main phenolic compound in cloudberry. These compounds work together. They provide comprehensive protection against cellular damage. They support immune health. Cloudberries also contain benzoic acid. This compound acts as a natural preservative. It helps the berries stay fresh longer.
Essential Minerals and Fiber
Cloudberries provide essential minerals. These minerals are vital for many bodily functions.
Mineral | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Potassium | 162 mg |
Magnesium | Present |
Calcium | Present |
Other minerals present include:
Mineral | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Calcium | 18.0 mg |
Phosphorus | 35.0 mg |
Iron | 0.7 mg |
Trace minerals are also found in cloudberries:
Mineral | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Zinc | 0.33-0.35 mg |
Copper | 0.05-0.07 mg |
Chromium | 0.011-0.012 mg |
Iron | 0.25-0.28 mg |
These minerals support bone health, nerve function, and energy production. Cloudberries are also a good source of dietary fiber. The fiber content of cloudberries contributes to their reputation as a wholesome addition to a balanced diet. This fiber promotes digestive health. It also assists in weight management. Historically, cloudberry leaves were used in folk medicine to improve digestion.
Culinary and Traditional Cloudberry Uses
Historical and Indigenous Applications
Cloudberries hold a significant place in the history and traditions of northern communities. Indigenous Arctic communities historically used cloudberries as a remedy for scurvy. They leveraged the berries’ rich content of vitamin C, vitamin A, and vitamin E. People also used the plant’s roots and leaves for their medicinal properties.
Historical records show the importance of this fruit. Vikings carried barrels of cloudberries on their voyages. This helped prevent scurvy during trips into the Mediterranean. Arabic literature mentions this practice. In 1596, German physician Henrik Høyer documented how Norwegians used cloudberries to treat scurvy. He described cooking the berries to a soft consistency without adding liquid. They often mixed the resulting jam with honey wine. Høyer noted the high regard for this remedy. He stated it was more effective than other known scurvy treatments. These included scurvy grass or chickweed. He also recounted the practice of isolating scurvy patients on islands rich with cloudberries. Patients would consume the berries until they recovered. Nineteenth-century Arctic explorers, like Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld and Fridtjof Nansen, carried cloudberries. They used them to supplement their diets and prevent vitamin C deficiency. Nansen, in his memoir, specifically mentioned consuming a cloudberry liquor. He described a New Year’s Eve celebration with a ‘cloudberry punch bowl’ during his expedition.
Modern Culinary Versatility
Today, cloudberry remains a prized ingredient. Its unique flavor makes it versatile in modern kitchens.
Cloudberry jam is a popular topping for homemade Quark Cake (Käsekuchen Mit Quark).
Many people in Newfoundland and Labrador use cloudberry jam as a cheesecake topping.
Cloudberries are a treasured ingredient in ‘Bakeapple Pie’.
The aboriginal ‘Arctic Yup’ik’ mix cloudberries with seal oil, reindeer or caribou fat, and sugar. This creates an ice cream-like treat called Akutaq.
Chefs also use cloudberry in various other dishes. They make sauces for game meats. They pair the berries with soft cheeses. People enjoy them in tarts, mousses, and other desserts. The distinct tart-sweet taste adds a special touch to many recipes.
Cloudberry Liqueurs and Beverages
Cloudberries also feature prominently in beverages. As Nansen’s account shows, cloudberry liquor has a long history. Many producers create cloudberry liqueurs. These spirits capture the fruit’s unique essence. People enjoy them as an after-dinner drink or in cocktails. Beyond liqueurs, people make cloudberry juices and cordials. They also use the berries to flavor ciders and beers. These beverages offer a refreshing way to experience the distinctive taste of this arctic fruit.
Beyond the Kitchen: Cloudberries in Skincare
Protecting Skin from Harsh Climates
Cloudberry extract is a popular ingredient in Nordic skincare. It helps protect skin from harsh arctic climates. Cloudberry plants naturally thrive in challenging Arctic conditions. Indigenous peoples historically used cloudberries to protect their skin against extreme cold and wind. This suggests the berries possess inherent properties adapted to these harsh environments. This fruit contains a high concentration of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. These essential fatty acids strengthen the skin’s natural barrier. A strengthened barrier prevents moisture loss and keeps the skin hydrated. This hydration and barrier support protect the skin from harsh elements. This is especially beneficial in colder climates. This extract deeply nourishes skin. It helps maintain the skin’s lipid barrier. This barrier locks in moisture and provides essential moisture. This protection prevents dryness and irritation.
Brightening and Anti-Aging Benefits
Cloudberry oil also offers significant anti-aging benefits. It helps brighten and give luminosity to the skin. This contributes to an anti-aging effect. Cloudberries are rich in ellagitannins. These phenolic compounds offer potent antioxidant benefits. They help protect against premature skin aging caused by lifestyle factors and UV exposure. Ellagic acid, a byproduct of ellagitannins, contributes to skin brightening. It alters melanin formation pathways. The unusually high amount of Vitamin C in this fruit is a well-known booster for skin radiance. Omega 3, 6, and Gamma-Linolenic Acid are essential fatty acids. They help minimize the signs of aging. Phytoceramides are botanical lipids. They plump and fortify the skin barrier. This smooths out the appearance of fine lines. It also imparts a healthy glow. This berry provides skin-loving nutrients. It supports skin cell regeneration. Its hydration-boosting properties improve the overall complexion. This contributes to its powerful anti-aging effects. It protects skin from free radicals.
The Distinctive Cloudberry Flavor Profile
A Complex Blend of Tastes
Cloudberries offer a truly unique taste experience. They present a delicate, tart-sweet flavor. This flavor profile includes a subtle floral note. Many describe it as a sophisticated blend of raspberry and red currant. Some detect a hint of citrus. The fruit provides a bright, refreshing tartness. This tartness is never overpowering. An underlying sweetness intensifies as the berries mature. A delicate musky undertone distinguishes cloudberries from other berries. Chef John Shields notes a distinct floral note. He also finds hints of raspberry, mango, apricot, and passionfruit. Extracting the nectar reveals flavors of yeast, citrus, and concentrated watermelon. This complex combination makes cloudberry a prized ingredient.
Comparisons to Other Berries
Cloudberries possess a flavor profile distinct from more common berries. People often describe their taste as similar to apricots. Cranberries, in contrast, have a tart and slightly bitter flavor. Raspberries, in contrast, are known for their sweet and juicy taste. They often have a slightly tart aftertaste. Cloudberries combine elements of both. They offer a unique balance of sweet and sour. Their texture resembles blackberries. This makes them stand out. The unique taste of cloudberry sets them apart in the berry world.
Availability and Preservation of Cloudberries
Limited Fresh Access
Finding fresh cloudberries is often difficult. Their short harvest season and remote growing locations make them rare. The berries ripen for only a few weeks each summer. This brief window means people must act quickly to gather them. Many cloudberry patches grow in hard-to-reach bogs and wetlands. These areas are far from towns and cities. The challenges of harvesting also limit the fresh supply. Weather conditions can easily destroy a crop. This makes fresh cloudberries a prized and expensive delicacy. Most people cannot buy them fresh in regular grocery stores.
Common Forms: Frozen and Preserved
Because fresh cloudberries are so rare, people often enjoy them in preserved forms. Freezing is a popular method to keep the berries fresh for longer. To freeze them, spread the cloudberries on a baking sheet. This allows them to freeze individually. Then, transfer them to an airtight container or freezer bag. This method prevents clumping. It also helps keep their texture and taste for up to 6-12 months.
Many products use cloudberry to extend its usability and flavor. People make jams or preserves from the berries. These products allow everyone to enjoy the unique taste year-round. Common preserved forms include:
Cloudberry Jam
Bakeapple sauce
Cloudberry teas
Cloudberry Jelly (seedless jam)
These preserved options make the arctic super-fruit accessible to more people. They capture the distinct flavor and nutritional benefits of the berry.
Cloudberries are a unique, nutrient-dense Arctic fruit. They boast a rich history and versatile uses. People enjoy them in culinary delights and skincare products. This cloudberry is truly an arctic super-fruit. It offers essential vitamins like C and E. It also provides powerful antioxidants. This prized delicacy from the northern wilderness contributes to health and well-being. It is a true gold of the forest.
FAQ
What regions are native to cloudberries?
Cloudberries grow in cold, northern regions. They thrive across the Arctic and subarctic. These areas include Scandinavia, Canada, and Russia. They prefer peat-rich bogs and wetlands.
What does a cloudberry taste like?
Cloudberries offer a unique tart-sweet flavor. Many describe it as a blend of raspberry and red currant. They also have subtle floral and musky notes. Some detect hints of apricot or citrus.
Are cloudberries healthy?
Yes, cloudberries are very healthy. They contain high levels of Vitamin C, Vitamin A, and Vitamin E. They also provide potent antioxidants and essential minerals. These nutrients support immune health and skin vitality.
Can people easily buy fresh cloudberries?
Fresh cloudberries are difficult to find. Their harvest season is short. They grow in remote locations. Most people buy them frozen or in preserved forms. These include jams, jellies, and liqueurs.
