
Cockles are a surprisingly nutrient-dense seafood. Their impressive cockles nutrition profile makes them a valuable addition to a healthy diet. This small cockle offers significant amounts of essential nutrients, particularly iron and protein. For instance, cockles are higher in iron content than 96% of foods. They also provide more protein than 64% of foods. This excellent nutrition comes with low calories and fat.
This post explores their nutritional profile, health benefits, and general facts about this shellfish.
Key Takeaways
Cockles are small shellfish. They have many nutrients. They give you a lot of iron and protein.
Eating cockles helps your body. They give you energy. They make your muscles strong. They also help your heart and bones.
Cockles have many vitamins and minerals. These include Vitamin B12, iodine, and selenium. These are good for your health.
You can cook cockles in many ways. Always clean them well first. This removes sand. Cook them until their shells open.
It is important to get cockles that are caught in a good way. This helps protect the ocean. It makes sure there are enough cockles for the future.
Cockles’ Nutritional Profile

Cockles offer an impressive nutritional profile. They pack essential vitamins and minerals into a small, low-calorie package. Understanding these nutrition facts helps people appreciate their value.
Iron Content: Essential for Energy
Cockles are an outstanding source of iron. Iron is vital for energy production and transporting oxygen in the blood. A 100-gram serving of cockles provides a significant amount of this crucial mineral.
Nutrient | Value (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
Total Iron (TI) | 17.6 ± 0.07 |
Heme Iron (HI) | 7.20 ± 2.69 |
Nonheme Iron (NHI) | 10.50 ± 2.55 |
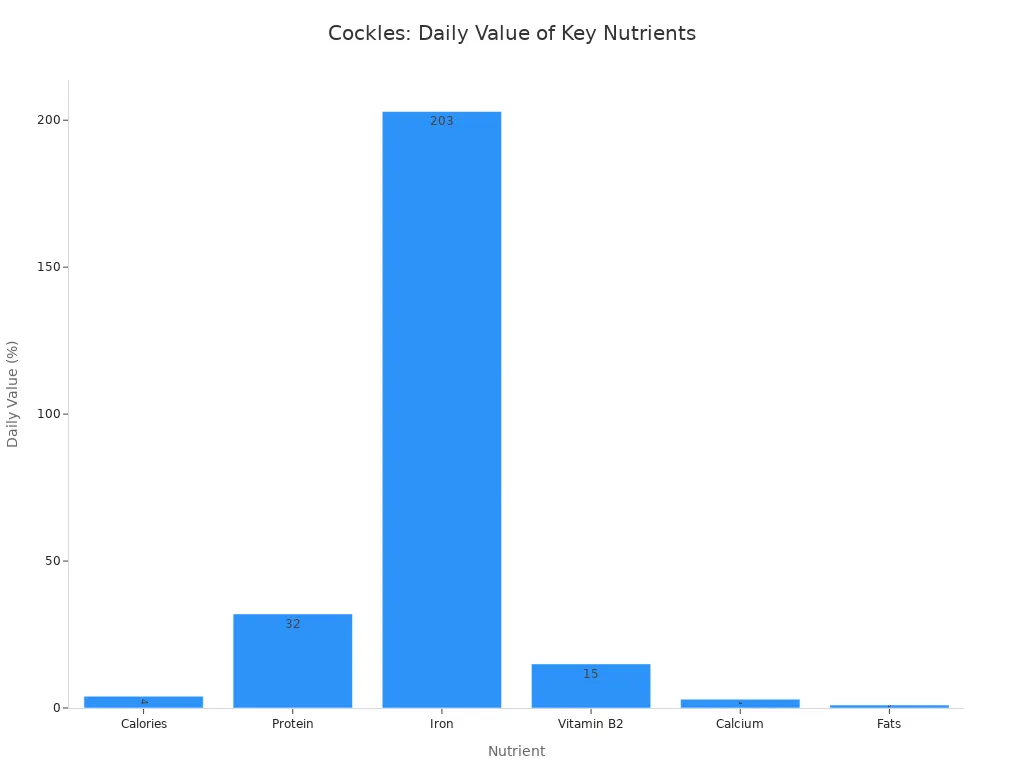
This 17.6 mg of iron per 100 grams far exceeds the daily recommended intake for most adults. It represents over 200% of the daily value. This makes cockles an excellent food choice for preventing iron deficiency.
Protein Power: Muscle and Satiety
Cockles are also a powerful source of protein. Protein is essential for building and repairing tissues. It also helps people feel full and satisfied after eating. A 100-gram serving of cockles delivers about 14 grams of protein. This amount provides 32% of the daily value for protein.
The overall macronutrient breakdown for 100 grams of cockles shows their lean nature. They contain approximately 52 Calories. This serving includes about 8.5 grams of protein, 1 gram of carbohydrate, and only 0.47 grams of lipids (fats). This nutritional information highlights that cockles are low in calories and fat. They are rich in protein, making them a great option for weight management and muscle support.
Vitamins and Minerals: Beyond Iron
Beyond their high iron and protein content, cockles offer a wide array of other essential vitamins and minerals. These nutrients contribute to overall health.
Vitamin B12: Cockles are exceptionally rich in Vitamin B12. A 4-ounce serving provides an astounding 541% of the daily value. This vitamin is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
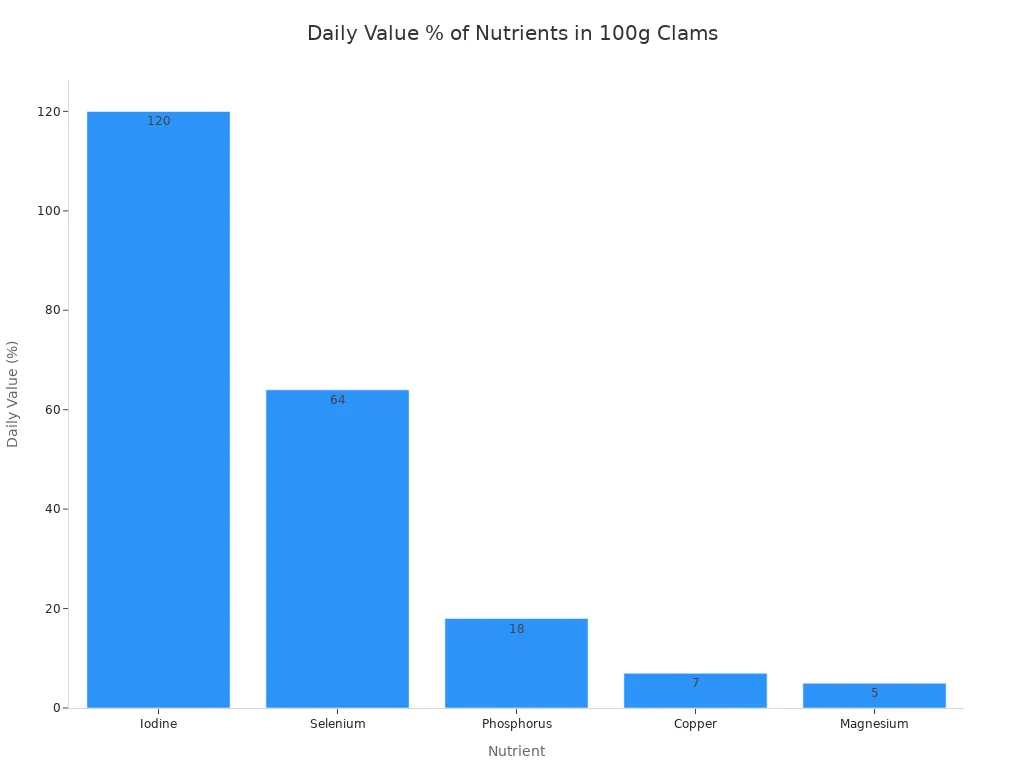
Iodine: They contain 180.6 µg of iodine per 100 grams, which is 120% of the daily value. Iodine is vital for thyroid hormone production.
Selenium: Cockles provide 35.2 µg of selenium per 100 grams, meeting 64% of the daily value. Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant. It also plays a key role in thyroid health.
Phosphorus: A 100-gram serving offers 227.7 mg of phosphorus, or 18% of the daily value. Phosphorus is important for bone health.
Copper: They supply 61.0 µg of copper, which is 7% of the daily value. Copper helps with iron absorption and energy production.
Magnesium: Cockles contain 21.9 mg of magnesium per 100 grams, providing 5% of the daily value. Magnesium supports muscle and nerve function.
This diverse range of nutrients makes the cockle a true superfood. The nutrition facts confirm their status as a valuable addition to any diet.
These nutritional values demonstrate the comprehensive benefits of including cockles in meals. Their rich nutritional information supports various bodily functions.
Health Benefits of a Cockle-Rich Diet
A diet that includes cockles offers many health advantages. These small shellfish provide essential nutrients. They support various bodily functions.
Boosting Energy and Immunity
Cockles are excellent for energy and immunity. Their high iron content plays a crucial role. Iron helps the body make red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen throughout the body. This process prevents fatigue and boosts overall energy levels.
Cockles contain iron. This iron is important for avoiding anemia.
Protein in cockles also aids energy. It helps repair and build tissues. This supports muscle growth and overall body function. Vitamin B12 is another key nutrient in cockles. It helps the body convert food into energy. It also supports healthy nerve function. This combination of nutrients keeps the body energized and strong.
Supporting Heart Health
Cockles contribute to a healthy heart. They contain omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids are beneficial for cardiovascular health. Studies show that eating fish can improve omega-3 levels. It also helps blood lipid profiles in people with heart conditions. Health experts advise adults to increase their intake of long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, including EPA and DHA.
Cockles are a healthy source of omega-3 fatty acids. These are great for heart health. They also contain important minerals. These minerals include iron, potassium, and calcium.
Nutrient | Amount |
|---|---|
Calcium | 158.3 mg |
Iron | 38.9 mg |
Potassium | 613.9 mg |
These minerals help regulate blood pressure. They also support proper heart rhythm. Including cockles in a regular diet can support a strong cardiovascular system.
Bone and Nerve Function
The nutrition in cockles supports strong bones and healthy nerves. Vitamin B12 is vital for nerve function. It helps maintain the myelin sheath. This sheath protects nerve fibers. This ensures proper communication throughout the nervous system.
Phosphorus is abundant in cockles. It works with calcium to build strong bones and teeth. Magnesium also contributes to bone health. It helps regulate calcium and vitamin D levels. Selenium acts as an antioxidant. It protects cells from damage. It also supports thyroid function. A healthy thyroid is important for metabolism and bone density. The comprehensive nutrition from this cockle supports overall well-being.
Cockle Facts and Sustainability
Understanding Cockle Species
Many types of cockle exist. They are a diverse group of marine bivalve mollusc species. True cockles live on sandy, sheltered beaches around the world. Their shells are rounded and bilaterally symmetrical. They appear heart-shaped when viewed from the end. Most cockle shells have many radial, evenly spaced ribs. Some genera, like Laevicardium, have smooth shells. Cockle shells can close completely. This differs from some other bivalves. People distinguish them from scallops by the absence of ‘auricles’ (ear-shaped protrusions) on their shells. They also have a pallial sinus. Cockles live buried in sediment. They use a foot to burrow and filter plankton for food. They possess three mantle apertures: inhalant, exhalant, and pedal. Cockles can ‘jump’ by bending and straightening their foot. Many bivalves, including the cockle, show gonochorism. This means their sex varies with conditions. Some species mature quickly. Over 205 living species of cockles exist. Many fossil forms also exist. The common cockle (Cerastoderma edule) lives along Northern European coastlines. Its range extends from Ireland to the Barents Sea, Norway, and as far south as Senegal. These are some key characteristics of the cockle.
Species | Distinguishing Characteristics | Size | Distribution |
|---|---|---|---|
Great Heart Cockle (Atlantic giant cockle) | Distinct heart shapes (hidden heart when turned on side); houses tiny crabs | Up to 6 inches across, 30-40 radial ribs | Atlantic coast |
Florida Prickly Cockle | Spiny appearance; brown or salmon color (rare albino shells) | Less than an inch (fingernail size) | Coastal shores of southwestern Florida |
Atlantic Strawberry Cockle | Narrower than other local species; reddish, rust-colored striping | N/A | Florida’s coastline |
Yellow Cockle | Yellow in color, almost circular shape; two equal valves; serrated, interlocking edges; 20-40 radiating ribs (some smooth, some spiny); yellowish-white outer shell with pale brownish-red markings; delicate yellow or white inner surface | Around 2 inches long | Atlantic coast |
Sustainable Sourcing Practices
Responsible harvesting of cockles is important. It protects marine environments. Cockle harvesting can impact target organisms. It also affects non-target species. It disrupts nursery functions. It alters trophic structure. It damages habitats. It can degrade water quality. A significant ecological concern is the potential reduction in densities of larger polychaete worms. These worms are a primary food source for shorebirds like black-tailed godwit and curlew. Disturbance from pump-scoop dredging for shellfish may cause these low densities. This highlights the need to monitor and regulate activities.
Sustainable practices help ensure future cockle populations.
Harvesters limit catches to specific months of the year.
They harvest only cockles of a minimum size. This allows them to reach maturity and reproduce.
They leave a portion of the cockles for estuary wildlife. This includes wading birds. They also leave some for stock health for the following season. For example, they catch a third, leave a third for seabirds, and a third for stock health.
Certifications help consumers choose sustainably sourced cockles.
Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) certification shows environmental sustainability of the fishery.
Seafish Responsible Fishing Scheme (RFS) certification demonstrates responsible operations on fishing vessels. It shows industry best practice and commitment to responsible sourcing.
Freshness and Storage Tips
Proper handling ensures the best taste and safety for cockles. To determine the freshness of cockles, discard any with broken shells. Also discard those that do not close when tapped on a hard surface. These indicate they are dead or compromised.
Follow these steps for storing fresh cockles:
Rinse cockles under cold water. Scrub off any dirt.
Store cleaned fresh cockles in an airtight container.
Line the container with damp paper towels.
Refrigerate them until ready to use.
Consume them within 24 hours for optimal taste and texture.
Culinary Uses and Preparation

Cockles offer versatility in the kitchen. People enjoy their unique flavor in many dishes. Preparing them properly ensures a delicious meal.
Simple Cockle Recipes
Many cuisines feature cockles. For example, Thai cuisine offers a spicy, herby, and briny cockle salad. This dish provides a vibrant taste. Portuguese cooking includes Ameijoas à Bulhão Pato. This recipe uses olive oil and coriander. It is similar to preparing cockles with white wine and garlic butter. This method creates tender and flavorful shellfish.
You can pair cockles with various ingredients. Crusty bread soaks up the cooking liquid. A simple green salad with lemon vinaigrette complements their taste. Linguine or spaghetti with garlic and olive oil also makes a great combination. For a tapas-style dish, chorizo and garlic work well.
Beginner cooks can try simple recipes. Cockles with Shallot Mignonette highlight their natural flavor. A mignonette sauce combines finely minced shallot, garlic, horseradish, and vinegars. Broiled Cockles with Garlic and Capers is another easy option. This recipe uses chopped capers, garlic, and olive oil. One-Pot Cockles with Green Cabbage and Coconut Curry combines ocean flavor with coconut and green curry. This dish cooks quickly.
Cleaning and Cooking Cockles
Proper cleaning removes grit from cockles. This step is crucial for enjoyment. Leave cockles in seawater overnight. This allows them to filter out sand. Seawater is essential. Fresh water can harm the cockle. If you do not have natural seawater, create it. Dissolve 35 grams of sea salt in 1 liter of non-chlorinated water. Submerge the cockles in 1.5 to 3 inches of this water. Cover the container. An overnight purge is usually enough.
After cleaning, cook cockles quickly. Place them in a large pan with about 150 ml of water and Noilly Prat. Cook them at high heat for 3-5 minutes. Shake the pan occasionally. All cockles should open. Discard any that remain closed. Decant the cooked cockles into a colander. Save the cooking juices. Once slightly cooled, remove the meat from the shells.
Cockles offer impressive cockles nutrition. They provide high amounts of iron and protein. These shellfish also contain many other valuable nutrients. This rich nutrition supports various health advantages. A diet including cockles boosts energy and aids muscle support. It also contributes to overall wellness. Readers should explore cockles. They are a delicious, nutritious, and sustainable seafood option. This small cockle provides significant health benefits.
FAQ
What are cockles?
Cockles are small, edible saltwater clams. They live buried in sandy beaches and mudflats. People recognize them by their distinctive ribbed, heart-shaped shells. They are a popular seafood choice in many parts of the world.
What makes cockles a healthy food choice?
Cockles offer excellent nutrition facts. They are rich in iron, which helps prevent anemia. They also provide high-quality protein for muscle health. Additionally, cockles contain essential vitamins like B12 and minerals such as selenium and iodine.
What do cockles taste like?
Cockles have a distinct, briny, and slightly sweet flavor. Their texture is tender and chewy. Many people describe their taste as a milder version of clams or mussels. They absorb flavors well from other ingredients.
What are sustainable ways to harvest cockles?
Sustainable cockle harvesting involves limiting catch sizes and specific seasons. Harvesters only take cockles above a minimum size. This allows smaller ones to grow and reproduce. They also leave enough cockles for wildlife and future stock.

