
You see plant-forward eating everywhere now. The global plant-based alternatives market is growing fast, projected to reach about USD 75.64 billion by 2034. This growth means more people choose options like coconut milk. Coconut milk is a creamy liquid from the grated flesh of mature coconuts. It is not the clear liquid found inside a young coconut, which is coconut water. Traditional cultures have used this plant-based drink for centuries. People now recognize the many uses of coconut milk and its potential health benefits. Understanding its nutritional profile helps you make smart food choices. You need to know the facts about coconut milk nutrition. This knowledge guides your dietary choices for coconut milk.
Key Takeaways
Coconut milk is a plant-based drink. It has good fats, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients help your body stay healthy.
Coconut milk can help you manage your weight. It makes you feel full. This helps you eat less food.
Coconut milk has properties that boost your immune system. It also fights bad germs. This helps your body stay strong.
You can use coconut milk in many ways. It makes food creamy. You can add it to drinks and meals.
Always check the type of coconut milk you buy. Some have more fat or added ingredients. Choose the best one for your health needs.
Coconut Milk Nutrition Facts

Understanding the coconut milk nutrition profile helps you make informed choices. This section breaks down the key components of this popular plant-based drink. You will learn about its macronutrients, vitamins, minerals, and calorie content. This nutritional information gives you a clear picture of what you consume.
Macronutrient Breakdown
Coconut milk contains carbohydrates, fats, and a small amount of protein. The carbohydrate content can vary. For example, some types of coconut milk have very few carbs. Other types, especially those with added sugars, contain more.
Nutrient | Amount per 100ml |
|---|---|
Carbohydrates | 2-4 grams |
You typically find a low amount of protein in coconut milk. This means it is not a significant source of protein for your diet.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
Coconut milk offers various essential vitamins and minerals. These nutrients contribute to your overall health. You get some Vitamin C and B vitamins from coconut milk.
Vitamin | Quantity per serving |
|---|---|
Vitamin B6 | 0.1mg |
Vitamin C | 2mg |
Vitamin B12 | 1.54 mcg |
Vitamin D | 2.44 mcg |
You also find important minerals in coconut milk. These include iron, magnesium, selenium, and manganese. These minerals play vital roles in many body functions.
Nutrient | % of Daily Value |
|---|---|
Iron | 22% |
Magnesium | 22% |
Selenium | 21% |
Copper | 32% |
Manganese | 110% |
Potassium | 18% |
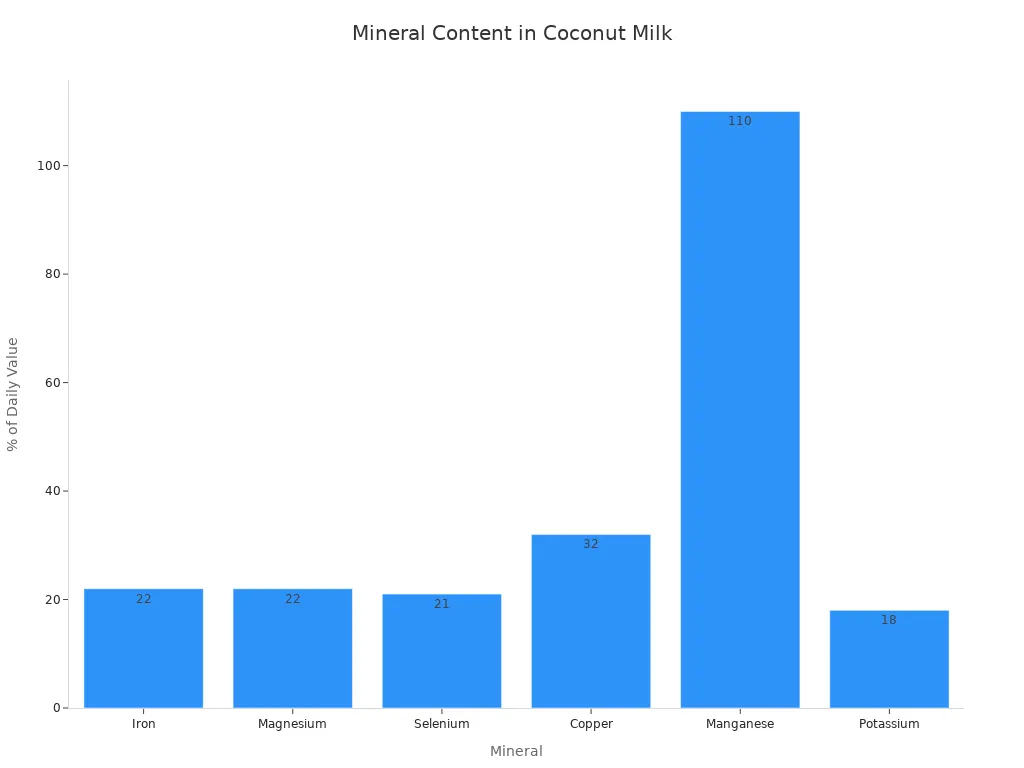
This chart shows you the significant nutritional value coconut milk provides in terms of minerals.
Electrolytes and Hydration
Coconut milk contains electrolytes. These are minerals that help your body maintain proper fluid balance. Potassium, magnesium, and sodium are key electrolytes found in coconut milk. They help with nerve and muscle function. Including coconut milk in your diet can support hydration, especially after physical activity.
Calorie and Fat Content
The calorie and fat content of coconut milk varies greatly. It depends on whether you choose full-fat or light versions. Full-fat canned coconut milk typically contains between 190 and 230 calories per 100ml.
Light coconut milk has fewer calories.
Brand | Calories | Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
Thai Kitchen Lite Coconut Milk | 45 | 1/7 can (2 fl. oz) |
Geisha Brand Lite Coconut Milk | 45 | 1/3 cup (80ml) |
Full-fat coconut milk is high in fat, especially saturated fat. A typical cup (approximately 240ml) of full-fat canned coconut milk contains 43-51g of saturated fat. This converts to approximately 17.9-21.25g of saturated fat per 100ml.
Light coconut milk has a much lower fat content.
Type of Coconut Milk | Saturated Fat (per cup) | Total Fat (per cup) |
|---|---|---|
Full-fat | Over 40 grams | 48 grams |
Light | 14 grams | 15 grams |
You can see a clear difference in the fat content. Super rich coconut milk contains approximately 14 grams of fat per ⅓-cup (80ml) serving. This detailed nutritional information helps you choose the right type of coconut milk for your dietary needs.
Health Benefits of Coconut Milk
Coconut milk offers many positive impacts on your health. Its nutritional components support various body functions. You can gain several health benefits of coconut milk by including it in your diet.
Weight Management and Satiety
Coconut milk can help you manage your weight. It promotes a feeling of fullness, which can reduce your overall food intake. This feeling of being full comes from several components. Fats in coconut milk make you feel satisfied. This helps prevent overeating, snacking, and cravings. Fiber also aids digestion and makes you feel full. Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) in coconut milk also promote fullness. These MCTs can boost your energy use, which helps with weight loss.
Studies show that consuming coconut milk can lead to a reduction in body weight. For example, research on Wistar rats found that coconut milk decreased body weight and visceral fat. When combined with a high-protein diet, it also lowered food intake in these rats. This suggests coconut milk plays a role in satiety for weight loss. MCTs in coconut milk prolong your feeling of fullness. This effect contributes to weight loss by potentially reducing how much food you eat.
Heart Health Support
The role of coconut milk in heart health is a topic of ongoing discussion. Some research suggests it can have beneficial effects on your lipid profile. A randomized controlled trial found that coconut milk supplementation could lower LDL (bad cholesterol) levels in people with high baseline LDL. It also showed positive effects on HDL (good cholesterol) in both low and high HDL groups. This study suggested coconut milk might not need exclusion from a heart-healthy diet. The differing amounts of protein, fat, and fiber in various coconut products might explain these varied effects.
However, other research presents a more cautious view. Coconut milk contains saturated fat. Some studies indicate that certain fatty acids in coconut milk tend to raise cholesterol. The American Heart Association (AHA) advises caution due to its saturated fat content. Rodent research suggests combining a high-protein diet with coconut milk might help manage cholesterol. Still, more human studies are needed to confirm these health benefits.
You might wonder about saturated fat. A meta-analysis of studies found no significant link between dietary saturated fat and increased risk of cardiovascular disease. The PURE study, involving over 135,000 people, found that higher total fat and saturated fat intake linked to a lower mortality rate. Other analyses also reported no association between higher saturated fatty acid intake and all-cause mortality or coronary heart disease. However, replacing saturated fatty acids with monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), or whole-grain carbohydrates can lower cardiovascular disease risk.
Immune System Boost
Coconut milk can help boost your immune system. It contains antioxidants like vitamins C and E. These vitamins neutralize harmful free radicals. Free radicals can damage cells and contribute to aging. Lauric acid, found in coconut milk, has antiseptic properties. It helps your body combat infections from bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Phenols in coconut also act as antioxidants. They help your body fight or remove reactive oxygen species.
Modern research shows that medium-chain fatty acids and monoglycerides in coconut act as natural antibiotics. They help modulate immunity. Studies evaluate the antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal benefits of coconut oil. Its metabolites, like lauric acid and monolaurin, have antimicrobial activity. They also activate the anti-inflammatory nature of your immune response. These compounds help you fight viruses and bacteria.
Antimicrobial Properties
Coconut milk possesses strong antimicrobial properties. Monolaurin, a compound in coconut milk, disrupts fungal cell membranes. This works particularly against Candida albicans. Monolaurin also disrupts bacterial cell membranes. It acts against certain bacterial strains like Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and E. coli.
Lauric acid, naturally present in coconut milk, shows antibacterial properties against harmful microorganisms. Monolaurin, formed from lauric acid during fermentation, has even stronger antibacterial and antifungal activities. Fermented coconut milk contains organic acids. These acids inactivate acid-resistant pathogens. Peptides produced during fermentation also contribute to antimicrobial effects. Other compounds in fermented coconut milk show antibacterial activity. These include ethanol, GABA, and various amino acids. This helps you fight viruses and bacteria.
A study noted that coconut milk fermented with S. salivarius K12 showed a greater antibacterial effect against Streptococcus pyogenes than penicillin. Coconut milk kefir is also known for its anti-microbial, anti-fungal, and anti-carcinogenic properties.
Digestive Wellness
Coconut milk supports healthy digestion. It contains fiber, which aids your digestion and promotes a healthy gut microbiome. Regular consumption can help prevent constipation. It also promotes regular bowel movements. This helps you improve digestion. The nutrients in coconut milk contribute to a balanced gut environment.
Metabolism and Energy
Coconut milk can boost your metabolism and provide a source of energy. It contains capric acid and caprylic acid. These are true medium-chain fatty acids (MCTs). Lauric acid, also present, has properties between medium- and long-chain fatty acids. Unlike longer-chain fats, your body transports MCTs directly to the liver. There, they are used for energy or ketone production. This makes them less likely to be stored as fat.
MCTs can help reduce your appetite. They can also decrease your calorie intake. They temporarily boost calorie expenditure and fat burning. This makes coconut milk a good source of energy.
Brain Health and Cognition
Coconut milk may support your brain health and cognition. MCTs in coconut milk convert into ketones. Ketones serve as an alternative source of energy for your brain. This can enhance cognitive function, memory, and attention. MCTs may improve neuronal metabolism and synaptic plasticity. These are crucial for learning and memory. They also offer neuroprotective effects. They reduce oxidative stress and inflammation in your brain.
Studies show that elderly individuals with mild cognitive impairment who consumed MCTs had improved memory and attention. MCT supplementation may enhance cognitive performance in people with Alzheimer’s disease. Lauric acid supports gut health. A healthy gut microbiome links to improved mood and cognitive function through the gut-brain axis. Antioxidants in coconut milk protect brain cells from damage. Vitamins and minerals contribute to neurotransmitter synthesis and overall brain health. These benefits make coconut milk a valuable addition for brain support.
Reducing Joint Inflammation
Coconut milk contains compounds that can help reduce inflammation. It has several phenolic compounds with anti-inflammatory properties. These include gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, and caffeic acid. Coconut milk also contains monolaurin. This compound, derived from lauric acid, has anti-inflammatory properties. Studies suggest that compounds in coconut milk can suppress inflammation. This can help reduce inflammation in your joints and throughout your body. These nutrients offer significant benefits for overall well-being.
Potential Downsides and Considerations
While coconut milk offers many benefits, you should also know its potential downsides. Understanding these helps you make informed choices.
Saturated Fat Content
Coconut milk contains saturated fat. You need to consider this when you add it to your diet. Health organizations recommend limiting saturated fat. For example, the American Heart Association suggests aiming for less than 6% of your total daily calories from saturated fat. This means about 13 grams or less for a 2,000-calorie diet. Other guidelines suggest keeping saturated fat under 10% of your daily calories, which is about 22 grams for a 2,000-calorie diet. You should moderate your intake of full-fat coconut milk to stay within these limits.
Allergic Reactions
Some people worry about allergies to coconut milk. Coconuts are botanically fruits, not tree nuts. However, the FDA classifies them as tree nuts. This can cause confusion. True coconut allergies are rare. Still, you might experience an allergic reaction. Symptoms can include hives, swelling, or digestive issues. If you have a tree nut allergy, consult your doctor before trying coconut milk. Always check labels carefully if you have any food sensitivities.
Additives and Preservatives
Commercial coconut milk products often contain additives. Manufacturers use these to improve texture, stability, and shelf life. You might find stabilizers like carboxymethyl cellulose (E466) or guar gum (E412). Emulsifiers such as polyoxethylene sorbitan monostearate (E435) or polysorbate 60 are also common. Some brands use thickeners like xanthan gum (E415). Preservatives like sodium benzoate or sodium metabisulfite can also appear. Bleaching agents and citric acid (an antioxidant) are sometimes present. You should read the ingredient list on your chosen coconut milk to avoid unwanted additives.
Packaging Concerns
The packaging of coconut milk can also be a concern. Many canned coconut milk products use cans lined with Bisphenol A (BPA). BPA is a chemical that can leach into food. Some studies link BPA to potential health issues. You can choose brands that offer BPA-free cans. Also, consider the environmental impact of packaging. Cartons or glass bottles might be more sustainable options for your coconut milk choices.
Essential Uses of Coconut Milk

Coconut milk is a versatile ingredient. You can find many uses for it in your kitchen. It adds a rich, creamy texture to countless dishes and drinks. Knowing how to use coconut milk helps you explore its full potential.
Culinary Applications
You can transform your cooking with coconut milk for cooking. It is a staple in many global cuisines. Think of creamy curries from Southeast Asia. You can also make rich soups and stews. Coconut milk thickens sauces and adds a subtle sweetness. Use it in marinades for tender meats or vegetables. It also works well in baked goods. You can create moist cakes and flavorful breads.
Beverages and Smoothies
Coconut milk shines in drinks. You can make delicious coconut milk beverages. Blend it into your morning smoothie for extra creaminess. It pairs well with fruits like mango, pineapple, and banana. You can also use it to make dairy-free lattes or hot chocolate. Many people enjoy coconut milk drinks as a refreshing alternative to dairy. These potential uses make it a favorite for many.
Selecting the Right Type
Choosing the right coconut milk is important. You will find coconut milk in a can for cooking. This type is usually thicker and richer. It works best for curries and desserts. For lighter coconut milk beverages, look for coconut milk in a carton. This version is often thinner and fortified with vitamins. It is perfect for smoothies or cereal. Always check the label for added sugars or thickeners in coconut milk products.
Storage Tips
Proper storage keeps your coconut milk fresh. Unopened coconut milk in a can or coconut milk in a carton lasts a long time in your pantry. Once you open it, refrigerate the unused portion. Transfer it to an airtight container. It usually stays good for 3-5 days. You can also freeze leftover coconut milk in ice cube trays. This extends its potential uses for future recipes.
Coconut Milk vs. Other Milks
You have many choices when selecting a beverage. Understanding the differences between coconut milk and other milk alternatives helps you choose wisely. Each type offers unique nutritional benefits and uses.
Dairy Milk Comparison
Dairy milk comes from animals. It provides protein, calcium, and vitamin D. Coconut milk, a plant-based option, offers different nutrients. It has less protein than dairy milk. However, coconut milk can be a good source of healthy fats and certain minerals. If you seek a dairy alternative, coconut milk as a dairy alternative works well in many recipes. You avoid lactose and animal products with coconut milk.
Almond Milk Comparison
Almond milk is another popular choice. It usually has fewer calories than coconut milk. Almond milk often contains less fat and protein. You might find it thinner in consistency. Coconut milk provides a richer, creamier texture. Both are good milk alternatives for those avoiding dairy. You choose based on your calorie goals and desired texture.
Oat Milk Comparison
Oat milk has gained popularity. It often has a creamy texture, similar to dairy milk. Oat milk typically contains more carbohydrates and fiber than coconut milk. Coconut milk offers more fat, especially saturated fat. You might prefer oat milk for its fiber content. You might choose coconut milk for its unique flavor and fat profile.
Choosing Your Best Option
You decide which milk is best for you. Consider your dietary needs and taste preferences. If you want a rich, creamy, plant-based option, coconut milk is excellent. If you need more protein, dairy milk might be better. For lower calories, almond milk could be your choice. For fiber, oat milk stands out. You have many options to fit your lifestyle.
You now understand the key coconut milk nutrition facts and its many health benefits. This versatile ingredient has diverse uses in your kitchen. You can experiment with coconut milk in various dishes and beverages. Remember to use coconut milk in moderation. Consider your personal dietary needs and any potential downsides of coconut milk. This helps you make informed choices. Thoughtfully add coconut milk to your balanced diet. Enjoy its unique flavor and nutritional value.
FAQ
Is coconut milk good for daily consumption?
You can enjoy coconut milk daily in moderation. It offers healthy fats and minerals. Choose light versions if you watch your calorie intake. Full-fat coconut milk is rich, so use it sparingly.
Can coconut milk help with weight loss?
Yes, coconut milk can support weight management. Its healthy fats promote fullness. This helps you eat less. Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) in coconut milk also boost your metabolism.
What is the difference between canned and carton coconut milk?
Canned coconut milk is usually thicker. You use it for cooking and rich dishes. Carton coconut milk is thinner. It works well in beverages and smoothies. Always check labels on coconut milk products for added ingredients.
Does coconut milk improve digestion?
Coconut milk contains fiber. This fiber aids your digestion. It helps maintain a healthy gut. Regular consumption can support smooth bowel movements. This contributes to overall digestive wellness.
Is coconut milk suitable for people with nut allergies?
Coconuts are botanically fruits. They are not true tree nuts. However, the FDA classifies them as tree nuts. If you have a tree nut allergy, consult your doctor before trying coconut milk.

