
Ground turkey has become a popular choice in many kitchens. People often choose it as a healthy option. This versatile ground turkey is a fantastic lean protein alternative. This article will examine ground turkey nutrition. It highlights its many health benefits. We will uncover the true advantages and practical uses of ground turkey.
Key Takeaways
Ground turkey is a good source of protein. It has important vitamins and minerals. These help your body stay healthy.
Eating ground turkey can help your heart. It has less bad fat than some other meats. It also helps you manage your weight.
Ground turkey is easy to use in many meals. You can swap it for other meats in recipes. This makes your meals healthier.
Cook ground turkey until it reaches 165 degrees Fahrenheit. Do not overcook it. This keeps it juicy and tasty.
Ground Turkey Nutrition Facts

Understanding the nutritional content of ground turkey helps people make informed dietary choices. This section details the specific components that make ground turkey a valuable addition to many diets. It explores its macronutrient breakdown, its rich micronutrient profile, and how its calorie count compares to other meats.
Macronutrient Breakdown
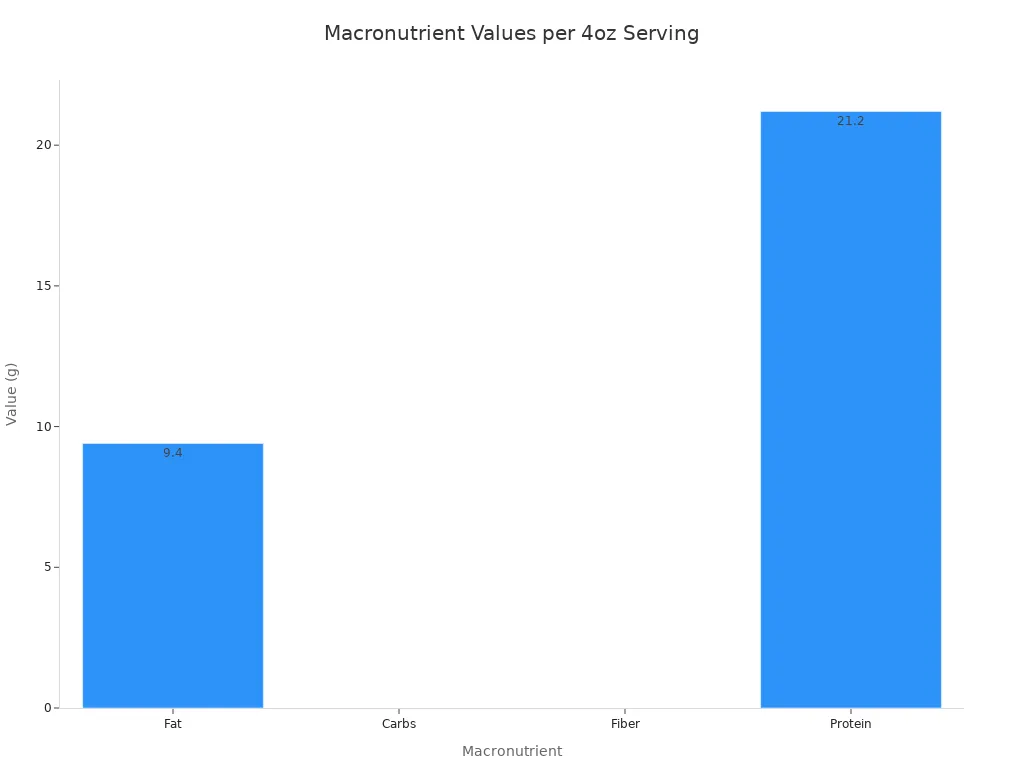
Ground turkey offers an excellent source of protein with varying fat levels depending on the lean-to-fat ratio. A standard 4-ounce serving of 93% lean ground turkey, when raw, contains approximately 160 calories and 22 grams of protein. When cooked, a 3-ounce portion of 93% lean ground turkey provides about 180 calories, 10 grams of fat, 2.5 grams of saturated fat, 90 milligrams of cholesterol, and 23 grams of protein.
Here is a closer look at the macronutrients in a 4-ounce serving of 93% lean ground turkey:
Macronutrient | Value (4 oz serving) |
|---|---|
Total Fat | 8 g |
Saturated Fat | 3 g |
Trans Fat | 0 g |
Total Carbohydrate | 0 g |
Dietary Fiber | 0 g |
Total Sugars | 0 g |
Protein | 21 g |
This data shows ground turkey provides a high-quality protein source. It contains minimal carbohydrates and sugars.
Micronutrient Powerhouse
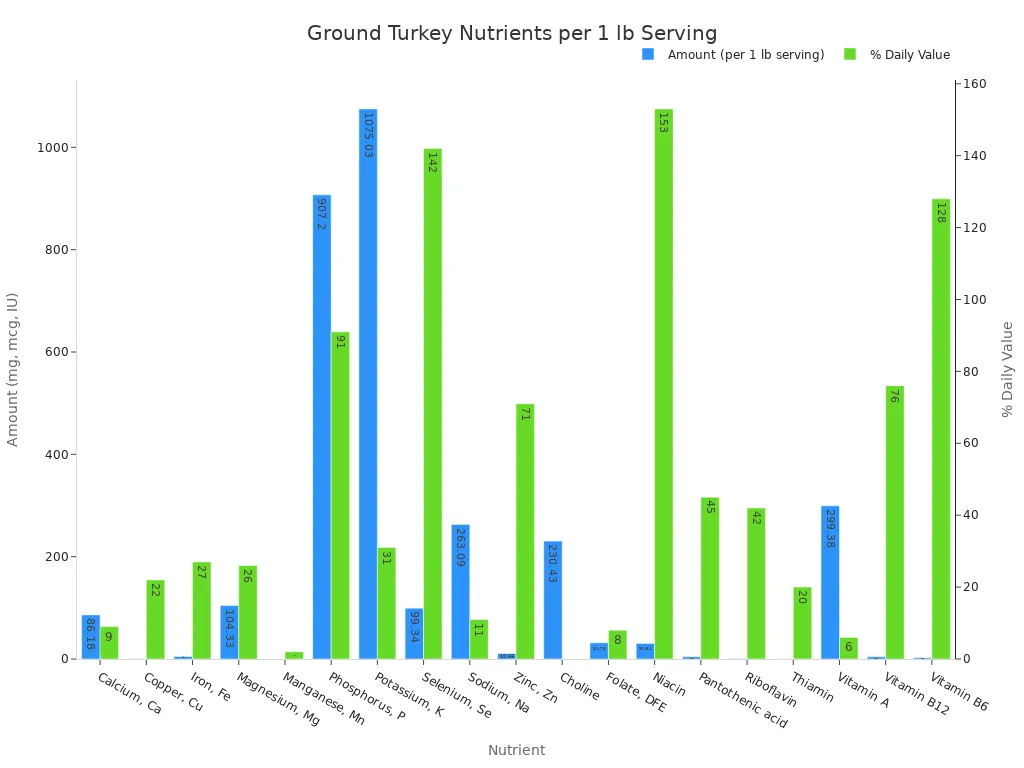
Beyond its macronutrients, ground turkey is a nutritional powerhouse. It offers a rich micronutrient profile, making it one of the truly nutrient-dense foods available. It supplies essential vitamins and minerals vital for overall health.
A 1-pound serving of ground turkey provides a significant amount of various micronutrients:
Nutrient | Amount (per 1 lb serving) | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
Minerals | ||
Calcium, Ca | 86.18 mg | 9 % |
Copper, Cu | 0.44 mg | 22 % |
Iron, Fe | 4.94 mg | 27 % |
Magnesium, Mg | 104.33 mg | 26 % |
Manganese, Mn | 0.04 mg | 2 % |
Phosphorus, P | 907.2 mg | 91 % |
Potassium, K | 1075.03 mg | 31 % |
Selenium, Se | 99.34 mcg | 142 % |
Sodium, Na | 263.09 mg | 11 % |
Zinc, Zn | 10.66 mg | 71 % |
Vitamins | ||
Choline | 230.43 mg | – |
Folate, DFE | 31.75 mcg | 8 % |
Niacin | 30.54 mg | 153 % |
Pantothenic acid | 4.5 mg | 45 % |
Riboflavin | 0.71 mg | 42 % |
Thiamin | 0.3 mg | 20 % |
Vitamin A | 299.38 IU | 6 % |
Vitamin B12 | 4.54 mcg | 76 % |
Vitamin B6 | 2.56 mg | 128 % |
This high-protein meat is particularly rich in B vitamins, such as Niacin and Vitamin B12, which support energy metabolism and nerve function. It also provides important minerals like Selenium, Zinc, and Phosphorus, which play roles in immune health, cell growth, and bone strength.
Calorie Count Comparison
When comparing different types of ground meats, ground turkey often stands out for its lower calorie and fat content. Fat-free ground turkey, for example, contains over 45 fewer calories per serving compared to 95% lean ground beef. It also has significantly less total fat and saturated fat. This makes ground turkey nutrition a favorable choice for those managing their calorie intake or looking to reduce dietary fat. The leaner varieties of ground turkey offer a substantial amount of protein without excessive calories.
Superb Health Benefits of Ground Turkey
Ground turkey offers numerous superb health benefits. Understanding ground turkey nutrition reveals why it is a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Lean Protein Source
Ground turkey stands out as an excellent lean protein source. This makes it ideal for muscle building and repair. A typical serving provides about 17 grams of protein and 153 calories. Ground turkey is a protein powerhouse. It contains essential amino acids. These amino acids are crucial for individuals aiming to build muscle. Its lean profile and rich nutrient content boost protein intake. This supports fitness goals. The protein content in broad-breasted Bronze turkey muscles ranges from 19.69% to 25.31% per 100g.
Muscle Type | Protein Content (g/100g) |
|---|---|
Pectoral (male) | 25.31 |
Pectoral (female) | 24.33 |
Thigh (female) | 20.24 |
Thigh (male) | 19.69 |
The pectoral muscle in both male and female turkeys has significantly higher protein and amino acid content. This is true compared to the thigh muscle. These essential amino acids are vital for muscle growth and repair. The pectoral muscle shows a higher ratio of essential to other amino acids.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Ground turkey is a nutritional powerhouse. It provides many essential vitamins and minerals. These support overall bodily functions. It contains B vitamins. These include B12 and B6. B12 supports brain function and energy production.
B vitamins also play a role in energy metabolism, red blood cell production, and nerve function. Ground turkey also offers important minerals. These include Selenium, Zinc, and Iron. Selenium supports immune health. Zinc is vital for cell growth and immune function. Iron helps transport oxygen in the blood. These make ground turkey a truly nutrient-dense food.
Heart-Healthy Choice
Choosing ground turkey can benefit heart health. It offers a favorable unsaturated fat content. The fat in turkey meat is largely of the beneficial unsaturated variety. Only one-third of its fat is saturated. Turkey meat is nearly fat and cholesterol-free, especially when people remove the skin. This makes it a better choice for individuals with high blood cholesterol or cardiovascular atherosclerosis. Ground turkey also contains abundant Vitamin B3 (Niacin).
Niacin helps lower cholesterol. It provides great Vitamin B12 and Folate. These vitamins work together. They convert homocysteine to methionine. This prevents high homocysteine levels. High homocysteine levels are toxic to the heart. Ground turkey is also bountiful in Selenium. Selenium is a powerful antioxidant. It combats oxidative stress. This helps protect against heart disease. These factors make ground turkey a healthy option for cardiovascular well-being.
Supports Weight Management
Ground turkey strongly supports weight management efforts. Its nutritional profile promotes satiety. A 3.5-ounce serving contains 30 grams of protein. This makes it one of the most protein-dense natural foods. This high protein content promotes satiety more effectively than most other food groups. It also supports muscle repair. Protein maximizes the thermic effect of food. This means the body expends more calories during digestion.
For protein, this is 20-30% of its calories. For carbs, it is 5-10%. For fats, it is 0-3%. Protein is also less likely to convert into stored body fat. The body prioritizes its use for muscle repair, enzymes, and energy. Leaner varieties of ground turkey contribute to weight management. They offer a lower caloric content compared to fattier meats.
Replacing high-saturated-fat meats with lean turkey helps lower LDL cholesterol. It also reduces inflammatory arachidonic acid. This acid links to difficulties in weight loss. Ground turkey’s high protein and low-calorie profile make it an excellent choice. It helps create a calorie deficit without hunger. Protein is the most satiating macronutrient. It triggers the release of satiety hormones. It suppresses ghrelin, the hunger hormone. This helps prevent overeating. These aspects highlight the significant health benefits of incorporating ground turkey into a healthy diet for weight management.
Ground Turkey vs. Other Meats
People often compare ground turkey to other popular ground meats. Understanding these differences helps consumers make the best choices for their diet. This section explores how ground turkey stacks up against ground beef and ground chicken. It also highlights situations where ground turkey is the optimal choice.
Ground Turkey vs. Ground Beef
Ground turkey often serves as a leaner alternative to ground beef. When comparing similar lean percentages, ground turkey typically has fewer calories and less saturated fat. For example, 99% lean ground turkey is less calorie-dense than 95% lean ground beef. This makes ground turkey a favorable option for those watching their calorie and fat intake. Both meats provide excellent protein. However, the fat profile often differs significantly, with ground turkey offering a healthier fat composition in leaner varieties.
Ground Turkey vs. Ground Chicken
Ground turkey and ground chicken are both poultry options. They offer distinct nutritional profiles. Here is a comparison per 100g:
Nutrient | Chicken Breast (per 100g) | Ground Turkey (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
Protein | 33.4g | 27.4g |
Fat | 4.7g | 10.4g |
This table shows chicken breast has more protein. Ground turkey contains more than double the fat of chicken breast.
Chicken breast offers 18% more protein than ground turkey.
Ground turkey contains more fat.
Chicken breast has less saturated fat (1.29g) compared to ground turkey (2.67g).
Ground turkey is richer in monounsaturated fats (3.46g vs 1.72g) and polyunsaturated fats (2.92g vs 1.07g).
Optimal Choice Scenarios
Ground turkey is an excellent choice for various dietary goals. It is valuable for weight management. It allows for greater food volume with fewer calories. This makes dieting less restrictive. Its versatility in healthy cooking helps people transform their relationship with food. It fits well into calorie-controlled approaches.
Ground turkey adapts to many dietary needs. These include high-protein diets, ketogenic lifestyles, and specialized protocols. In personalized dietary plans for chronic illness, nutrient-dense proteins like ground turkey support the body’s natural healing processes. Ground turkey lowers calories and saturated fat in high-frequency meals. It supports long-term weight and heart goals. It allows for a healthier nutritional profile without changing familiar recipes. This makes ground turkey a smart choice for many.
Versatile Ground Turkey Uses

Ground turkey offers many practical ways to enhance daily meals. Its mild flavor and adaptable texture make it a favorite for home cooks. People can easily incorporate it into various dishes, making meals both delicious and healthy.
Everyday Meal Ideas
Ground turkey fits into many popular recipes. For example, a healthy turkey chili provides a comforting meal for cold evenings or meal prep. It includes ground turkey, beans, vegetables, and warm spices. Many people enjoy a juicy and flavorful turkey burger, perfect for cookouts or weeknight dinners. Other popular options include turkey meatballs with maple mustard sauce, Indian-style meatballs, or ground turkey and sweet potato skillet. People also make ground turkey Korean rice bowls, Thai turkey meatballs, and cheesy ground turkey quesadillas. Its versatility allows for dishes like ground turkey pizza, tacos, and spaghetti.
Healthy Swaps and Substitutions
Ground turkey serves as an excellent substitute for other meats in many recipes. People often use it instead of ground beef. This swap works well in dishes like chili, meatballs, and tacos. The spices and sauces in these recipes enhance the turkey’s flavor. Specific examples include Korean ground turkey and rice bowls, ground turkey gluten-free meatloaf, and meat sauce with ground turkey. One can also make high-protein spicy garlic noodles or lemon ricotta ground turkey pasta with broccoli. These substitutions help reduce fat and calories while maintaining flavor.
Cooking Tips for Ground Turkey
Cooking ground turkey properly prevents it from becoming dry. People should avoid overcooking it. Cook ground turkey until it reaches an internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit. Using an instant-read thermometer helps ensure accuracy. To add moisture, grate water-heavy vegetables like onion or mushrooms into the meat. This releases liquid and flavor. Incorporating sauces such as ketchup, barbecue sauce, or mayonnaise also keeps the meat tender. Adding olive oil or grated butter introduces richness and moisture. Minimizing handling of the raw meat prevents a dense texture. Choosing ground turkey with a slightly higher fat percentage, like 93% lean, works well for burgers or meatballs. For dishes cooked in sauces, leaner options are fine as the turkey absorbs moisture. Using a panade, which is breadcrumbs soaked in liquid, also helps keep the meat moist. These techniques ensure ground turkey remains a delicious and nutrient-dense foods option.
Ground turkey offers significant nutritional benefits. It provides lean protein, essential vitamins, and minerals. It supports heart health and aids in weight management. This versatile meat easily fits into many healthy diets. Readers should consider making it a regular part of their healthy eating plan. Make informed food choices for a better lifestyle.
FAQ
Is ground turkey always healthier than ground beef?
Not always. Lean ground turkey often has fewer calories and less saturated fat than ground beef. However, some ground turkey varieties can have similar fat content to leaner ground beef. Always check the nutrition label for specific fat percentages.
Can you freeze ground turkey?
Yes, people can freeze ground turkey. Store it in an airtight container or freezer bag. It stays good in the freezer for three to four months. Thaw it in the refrigerator before cooking.
What is the best way to cook ground turkey without drying it out?
Avoid overcooking ground turkey. Cook it until it reaches an internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit. Adding moisture, like grated vegetables or a panade (breadcrumbs soaked in liquid), helps keep it juicy.
What is the difference between white and dark ground turkey meat?
White meat comes from the breast. It is leaner and has fewer calories. Dark meat comes from the thighs and legs. It contains more fat and a richer flavor. Both offer good protein.

