
Can beets really lower blood pressure? Many people ask this important question. High blood pressure affects many adults; globally, an estimated 33% had hypertension in 2024. Beets are a vibrant superfood offering significant health benefits. You can discover how these remarkable vegetables impact your blood pressure. Studies show regular beetroot consumption can reduce systolic blood pressure by 4-5 mmHg. This blog explores the amazing health benefits beets provide, their unique nutrition, and how they help lower blood pressure. You will also learn practical ways to add beets into your daily diet.
Key Takeaways
Beets help lower blood pressure. They contain nitrates. These nitrates turn into nitric oxide in your body. Nitric oxide relaxes blood vessels.
Beets are full of good nutrients. They have vitamins, minerals, and fiber. These help your body stay healthy and aid digestion.
Beets fight inflammation. They also boost athletic performance. They can even help your brain work better.
You can eat beets in many ways. Try them raw, cooked, or as juice. Beet powder is also a good option for daily use.
Beets and Blood Pressure

Beets are a powerful food for maintaining healthy blood pressure. You can understand how these vibrant vegetables work their magic. The key lies in their unique compounds.
Dietary Nitrates and Nitric Oxide
Beets contain a high nitrate content. When you eat nitrate-rich foods like beets, a special process begins in your body. First, bacteria in your mouth, specifically on your tongue, convert the nitrate into nitrite. Humans do not have the enzyme to do this directly. These bacteria are crucial for this first step. Then, your body can further reduce this nitrite into nitric oxide (NO). This conversion happens more easily in areas of your body with lower oxygen levels. Nitric oxide is a vital molecule for your vascular health.
How Beets Lower Blood Pressure
Nitric oxide plays a big role in keeping your blood pressure healthy. It acts as a vasodilator. This means nitric oxide relaxes and widens your blood vessels. When nitric oxide enters the smooth muscle cells of your blood vessels, it activates a specific enzyme. This enzyme then produces a molecule called cGMP. cGMP signals your muscles to relax. This relaxation helps your blood vessels expand. Wider blood vessels allow for healthy blood flow. This reduces the pressure against your artery walls. Your heart does not have to work as hard to pump blood. This process effectively helps to lower blood pressure.
Scientific Evidence and Heart Health
Research strongly supports the health benefits beets offer for your heart. You can see noticeable blood pressure-lowering effects from beet juice within a few hours. Some studies show effects around 3 hours after you drink beet juice. A reduction in systolic blood pressure can be observed quickly. For sustained benefits and significant improvement in hypertension, you should consume beetroot daily for at least 60 days. After you drink beet juice, nitrates reach their highest level in your blood within three hours. They stay at helpful levels for about 10 hours. Consistent consumption of beetroot juice over several weeks can lead to further decreases in systolic blood pressure.
Regular consumption of beetroot can reduce your risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and stroke. Pre-clinical studies show that beetroot juice can protect your heart. It may reduce damage to your heart muscle after an injury. Clinical trials have also explored the impact of beetroot juice on heart health. For example, one study found improved blood flow in postmenopausal women who drank nitrate-rich beetroot juice. This suggests a potential reduction in the risk of heart problems. However, these positive effects can fade within 24 hours if you stop consuming it. It is also important to know that beetroot does not significantly change your cholesterol levels. So, it is not a supplement for adjusting lipid profiles, which are also risk factors for heart disease.
Beets also contain potassium. Potassium helps manage healthy blood pressure by counteracting the effects of sodium. It helps your body get rid of excess sodium through urine. Potassium also helps relax the walls of your blood vessels, which contributes to lower blood pressure. However, the nitrate content in beets is much more potent than potassium for resisting blood pressure increases caused by high salt intake. The primary reason beets help maintain healthy blood pressure is their high nitrate content.
Beet Nutrition Facts
Beets are a nutritional powerhouse. You get many nutrients from them with very few calories. This makes them an excellent addition to your diet. You can enjoy significant nutritional benefits from these vibrant vegetables.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
Beets are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. They provide a good source of Vitamin C, Folate, Potassium, Manganese, and Iron. You can see how much a 100-gram serving of raw beets offers:
Nutrient | Amount (per 100g raw beets) |
|---|---|
Iron | 0.8 mg |
Potassium | 325 mg |
Manganese | 0.33 mg |
A standard 1-cup serving of beetroot offers even more. It gives you 148 mcg of folic acid. This is 37% of the 400 mcg FDA daily value. The potassium content in 1 cup of beets is 442 mg. This represents 13% of the 3,500 mg the FDA recommends daily. You can see the daily recommended intake percentages for various nutrients from a standard serving of beets in this chart:
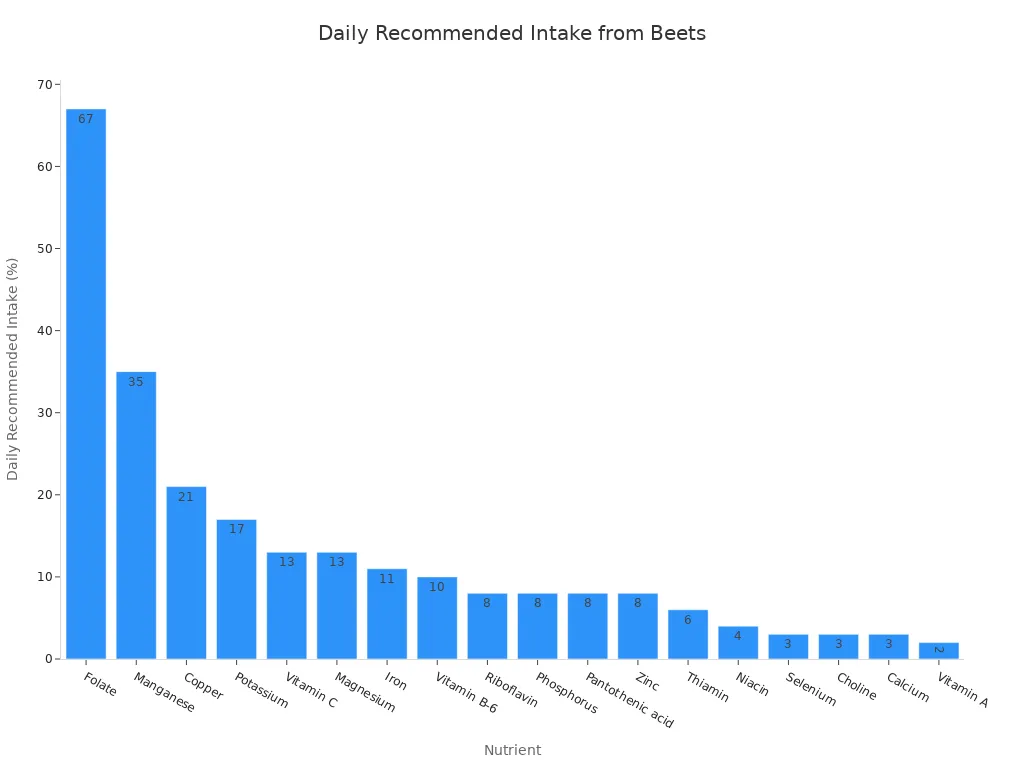
You gain a substantial amount of these vital nutrients from eating beets.
Fiber for Digestive Health
Beets are an excellent source of dietary fiber. Fiber is crucial for your digestive system. One cup of beetroot contains 3.8 grams of fiber. This amount is 16% of the FDA recommended 25 grams daily intake.
Fiber helps your body in several ways:
It helps control blood sugar levels.
It assists in maintaining a healthy weight.
It lowers cholesterol.
It promotes regularity.
Fiber bypasses digestion in your stomach and small intestine. It travels to your colon. In the colon, fiber feeds friendly gut bacteria. This process adds bulk to your stools. These actions promote digestive health and maintain regularity. Fiber helps prevent digestive conditions. These include constipation, inflammatory bowel disease (IBS), and diverticulitis. A balanced fiber diet may also reduce the risk of chronic diseases. These include colon cancer, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.
Women should aim for at least 25 grams of fiber daily. Men should aim for 38 grams of fiber daily. A cup of raw beetroot provides nearly 4 grams of fiber. A serving of cooked beets provides 2 grams of fiber. You can easily boost your daily fiber intake with beets.
Antioxidants and Phytonutrients
Beets are rich in health-promoting compounds. These include antioxidants, carotenoids, and nitrates. They are an excellent source of betalains. Betalains are a type of phytonutrient. They have powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Beet greens contain lutein and zeaxanthin. These two carotenoids are crucial for eye health. They reduce the risk of conditions like macular degeneration and cataracts.
Beetroots contain organic acids. These include citric, ascorbic, malic, fumaric, succinic, and oxalic acids. Malic acid and citric acid are the most abundant. Phosphoric acid, citric acid, oxalic acid, malic acid, and shikimic acid are also in beetroot juice. Shikimic acid is a precursor for aromatic amino acids and betalains.
Betalains are nitrogen-containing and water-soluble pigments. They divide into betaxanthins and betacyanins. Red beetroot is an excellent source of betanin (75–95%). It also has lower concentrations of isobetanin, betanidin, and betaxanthin. Betanin is the primary betalain in beetroot. Its antioxidant capacity is nearly twice as high as some anthocyanins. Its free radical scavenging ability links to phenolic hydroxy groups and rich unsaturated bonds in its structure.
Betalains demonstrate many health benefits. They reduce the risk of cancer, cardiovascular disease, and type 2 diabetes. Emerging evidence suggests benefits for neurodegenerative diseases. They improve lipid profiles. They reduce total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL cholesterol. They also increase HDL cholesterol. Betalains have antiviral, antifungal, antiprotozoal, and antibacterial activity. They inhibit a wide range of pathogens. They possess hepatoprotective effects. They enhance detoxification through increased phase II detoxifying enzymes. Animal models indicate neuroprotective properties. This suggests potential benefits for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Betalains consistently show antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, and cardioprotective properties. As powerful antioxidants, betalains scavenge free radicals. They inhibit lipid peroxidation and LDL cholesterol oxidation. They induce the endogenous antioxidant system by activating Nrf2. This activates the antioxidant response element (ARE) for transcribing antioxidant enzymes. Betalains exhibit anti-inflammatory effects. They interfere with pro-inflammatory signaling cascades. They suppress COX-2 expression. They repress ICAM-1. They inhibit pro-inflammatory LOX and COX enzymes. They reduce levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen/nitrogen species. You gain significant protection from these compounds.
Other Health Benefits of Beets
Beets offer many more health benefits beyond blood pressure control. You can gain significant advantages for your entire body. These vibrant vegetables support various bodily functions.
Fighting Inflammation
Beets are powerful inflammation fighters. They contain betalains, which are strong antioxidants. These compounds help reduce inflammation throughout your body. You can see reductions in key inflammatory markers. For example, studies show decreases in tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6). These markers can drop by significant percentages. Beetroot treatment also inhibits activities like regulated oncogene-alpha (GRO-alpha). You also benefit from reduced NF-κB DNA-binding activity. This indicates fewer pro-inflammatory signals. These health benefits beets provide help protect your cells.
Boosting Athletic Performance
You can improve athletic performance with beetroot. Dietary nitrate from beet juice helps your body use oxygen more efficiently. This means your muscles need less oxygen during exercise. This happens because nitric oxide enhances how your mitochondria produce energy. Supplementation with beet juice can lead to better performance. You may see improved oxygen uptake. Taekwondo athletes show better specific performance. Female endurance athletes can experience a nearly 5% increase in maximal oxygen consumption (VO2 max). Beet juice also boosts muscular endurance.
Metric Improved | Exercise Type | Specifics of Improvement |
|---|---|---|
Muscular Endurance (repetitions) | Back Squat (65% 1RM) | Increased number of repetitions |
Muscular Endurance (mean velocity) | Back Squat (65% 1RM) | Increased mean velocity |
Muscular Endurance (power production) | Back Squat (65% 1RM) | Increased power production |
Brain Health Support
Beets can support your brain health. The nitric oxide produced from beets increases blood flow to your brain. This improved circulation helps your brain function better. You can experience enhanced cognitive activity. This is especially true in areas like the frontal and prefrontal lobes. Nitric oxide also protects brain cells. It helps form new memories and improves learning. Beetroot consumption can improve memory capacity and frontal skills. Some studies even show beetroot extract has anti-anxiety and antidepressant properties. This means beets offer comprehensive health benefits for your mind.
Liver Function and Detoxification
Beets are excellent for your liver. They contain betalains and betaine. These compounds support your liver’s natural detoxification processes. Betalains act as antioxidants, protecting liver cells from damage. Betaine helps your body digest fats. This prevents fat buildup in the liver. Beetroot juice also boosts your liver’s detoxification enzymes. It increases bile production, which is vital for removing toxins. Pectin, a fiber in beets, further helps cleanse your system. These actions help your liver eliminate harmful substances. This contributes to overall health benefits and can indirectly help maintain lower blood sugar levels by supporting metabolic health.
Enjoying Beets: Tips and Recipes

Raw Beets and Beet Juice
You can enjoy beets in many forms. Eating them raw offers maximum fiber. Grate raw beetroot into your salads. You can also blend this vegetable into smoothies. Cold-press raw beetroot into beetroot juice. Light steaming is another option. It softens texture while keeping nutrients. When you make beetroot juice, remember a key difference. Juicing removes almost all fiber from the beetroot. This process extracts liquid, concentrating sugar. So, beetroot juice has higher sugar content than a whole beet. The juicing process separates liquid from fiber. This results in a loss of fiber-bound nutrients and the fiber itself. You can combine beet juice with other flavors. Try beet juice with orange, carrot, apple, lemon, mint, or ginger. This enhances taste and adds nutrients. You can also add beet powder to your beet juice for extra concentration. Many people use beet powder in morning routines. A scoop of beet powder offers quick benefits. You can even mix beet powder into water for a simple beet juice drink. Enjoy this beet juice for a health boost. You can also make a beet juice blend with other fruits. Try a beet juice smoothie.
Cooking Methods for Beets
You can cook beets in various ways. Roasting brings out their sweetness. You can boil or steam them until tender. Pickling beets creates a tangy side dish. You can make a delicious beetroot soup. Sauté onions and garlic, then add chopped beetroot. Cook and blend the mixture. You can serve this soup hot or cool. For a quick snack, try beetroot cutlets. Mash beetroot and potatoes. Add spices, shape them, and pan-fry. Serve them with mint chutney. You can also use beet powder as seasoning for roasted vegetables. Sprinkle beet powder on your cooked dishes.
Incorporating Beetroot into Meals
You can easily add beetroot to your daily meals. Grate raw beetroot into salads for crunch and color. Blend beetroot into your favorite smoothie recipes. You can make beetroot parantha. Incorporate grated beetroot into dough. This gives a colorful and tasty twist to traditional paranthas. Serve them with curd and pickle. Try beetroot raita. This is a refreshing mix of grated beets, curd, and spices. Serve it with rice or as a side dish. You can also make beetroot pickle. Soak chopped beetroot in vinegar with salt and spices. Marinate it for a week. This creates a tangy and sweet side dish. For a quick nutrient boost, add beet powder to your oatmeal. You can also use beet powder in homemade energy bars. Many find beet powder convenient for busy days.
You now understand the many health benefits beets offer. They significantly impact your blood pressure. Beets help maintain healthy blood pressure. You can easily add beetroot to your diet. Beetroot is versatile. Experiment with different beet preparations. Enjoy their great nutrition. These health benefits support your overall well-being. For maintaining healthy blood pressure, beets are a great choice. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice. This is especially true if you have existing health conditions or concerns about your blood pressure.
FAQ
How much beet juice should I drink to lower blood pressure?
You can start with 1 to 2 cups of beet juice daily. This amount provides enough nitrates. Consistent intake helps lower blood pressure. You can also use beet powder for convenience.
Can I use beet powder instead of fresh beets?
Yes, beet powder is a great alternative. It offers concentrated nutrients. You can mix beet powder into water or smoothies. Many people find beet powder convenient for daily use.
Are there any side effects of eating beets?
Beets are generally safe. You might notice red or pink urine or stool. This is harmless. Some people may experience digestive upset. Start with small amounts of beet juice or beet powder.
How quickly does beet juice work?
You may see blood pressure effects within a few hours of drinking beet juice. For long-term benefits, drink beet juice regularly. Consistent use of beet powder also helps maintain healthy blood pressure. You can easily add beet powder to your routine.

