
Heavy cream is a luxurious dairy product. Many people consider heavy cream an indulgent ingredient. It brings a rich, velvety texture to countless dishes. You find heavy cream in diverse cuisines worldwide. Its reputation for richness is well-deserved. You might ask about heavy cream nutrition. Is this ingredient a dietary villain? Or can you enjoy heavy cream as a beneficial part of your diet in moderation? Let’s find out.
Key Takeaways
Heavy cream has a lot of fat. It must have at least 36% milkfat. This makes it thick and rich.
Heavy cream gives you energy. It has vitamins like A and K. These help your bones stay strong.
Heavy cream is good for low-carb diets. It has high fat and low carbs. This helps your body burn fat for fuel.
Eat heavy cream in small amounts. It has many calories and saturated fat. Too much can be bad for your health.
You can use heavy cream in many foods. It makes desserts creamy. It also makes sauces and soups rich.
Heavy Cream Nutrition: Essential Facts
Defining Heavy Cream and Fat Content
Heavy cream is a dairy product with a specific composition. You might wonder what makes it “heavy.” The answer lies in its fat content. To be legally classified as heavy cream in the United States, the product must contain at least 36% milkfat. This high percentage of milkfat gives heavy cream its thick texture and rich flavor. This is a key factor in its nutritional content.
Calorie and Macronutrient Breakdown
Understanding the heavy cream nutrition profile means looking at its calories and macronutrients. Heavy cream is calorie-dense due to its high fat content. Here is a breakdown of what you find in a cup of heavy cream:
Nutrient | Value per 1 cup |
|---|---|
Calories | 821 |
Total Carbs | 6.6g |
Fat | 88.1g |
For a smaller serving, like one tablespoon, you consume about 52 calories, 5.5g of fat, and 0.3g of carbohydrates. The primary macronutrient in heavy cream is fat. It contains very few carbohydrates and a small amount of protein.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
Beyond fats and calories, heavy cream also provides important nutrients. It contains several vitamins and minerals that contribute to your overall health.
💡 Tip: Heavy cream is a good source of fat-soluble vitamins.
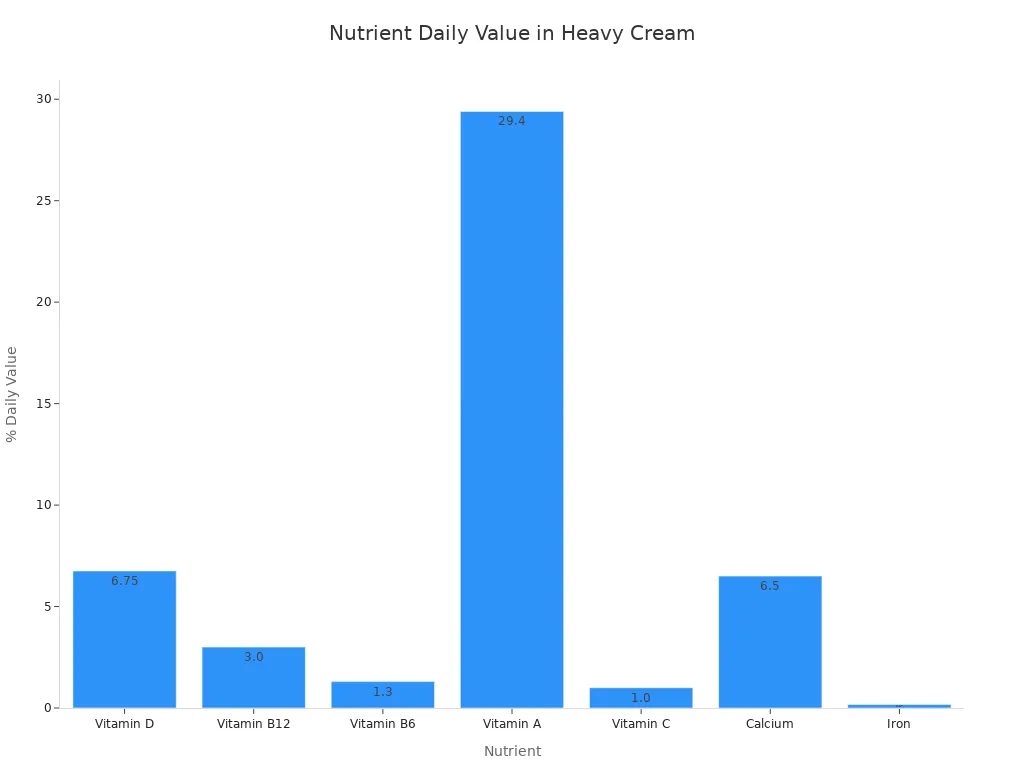
You get essential vitamins like Vitamin A. A cup of heavy cream can provide a significant portion of your daily Vitamin A needs. It also offers other vitamins and minerals. These include choline, calcium, and phosphorus. Here is a look at some of the nutrients found in heavy cream:
Nutrient | Amount | % Daily Value |
|---|---|---|
Vitamin D | 27 IU | 6.75% |
Vitamin B12 | 0.18 mcg | 3% |
Vitamin B6 | 0.03 mg | 1.3% |
Vitamin A | – | 29.4% |
Vitamin C | – | 1% |
Calcium | 65 mg | 6.5% |
Iron | 0.03 mg | 0.17% |
Folic Acid | 4 mcg | – |
Phosphorus | 62 mg | – |
Copper | 0.01 mg | – |
Magnesium | 7 mg | – |
Niacin | 0.04 mg | – |
Pantothenic Acid | 0.3 mg | – |
Potassium | 75 mg | – |
Riboflavin | 0.11 mg | – |
Thiamin | 0.02 mg | – |
Vitamin E | 1.06 | – |
Zinc | 0.23 mg | – |
Heavy Cream vs. Similar Dairy Products
You might see different types of heavy cream and other dairy products in the store. It helps to understand the difference between heavy cream and whipping cream and other options. These products vary mainly in their fat content.
Heavy cream, also known as heavy whipping cream, has a higher fat content. It must contain no less than 36% milk fat. Whipping cream, or light whipping cream, has a slightly lower milk fat content. Its range is typically 30–36%. This higher fat content in heavy cream gives it more body and stability when whipped.
Here is a comparison of some dairy products:
Product | Serving Size | Calories | Fat (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
Heavy Whipping Cream | 1 fl oz | 101 | 10.8 |
Half And Half Cream | 1 fl oz | 40 | 3.5 |
This table clearly shows the difference between heavy cream and whipping cream (represented by heavy whipping cream) and half-and-half. Half-and-half has a much lower fat content and fewer calories. When you consider heavy cream nutrition, its richness sets it apart from these lighter dairy options.
Heavy Cream Benefits
Heavy cream is more than just a tasty addition to your food. It offers several benefits that can support your overall health. You might find these health benefits surprising.
Healthy Fats for Energy and Cell Function
Heavy cream contains healthy fats. These fats are important for your body. They give you a lot of energy. Your body uses this energy for daily activities. These fats also help your cells work correctly. Every cell in your body needs fat to build its walls and function well. When you consume heavy cream, you provide your body with a concentrated source of these essential fats.
Nutrient Density and Satiety
Heavy cream offers a lot of energy in a small amount. This energy density can help you feel full. However, some studies show that heavy cream has a low nutrient density score of 10 out of 100. This means it does not have many essential minerals, vitamins, amino acids, or fatty acids per calorie. Its satiety score is also low, at 39%. This score predicts how full a food makes you feel. A study looked at how different fats, including heavy cream, affected feeling full. It found no big differences in hunger or fullness between heavy cream and other fat sources. This suggests that heavy cream might not make you feel full more than other fats.
Supporting Bone Health
You might not think of heavy cream for bone health, but it contains nutrients that help.
Vitamin K (K1 and K2): This vitamin is very important for strong bones. It helps your body use calcium. Because Vitamin K is fat-soluble, your body absorbs it well when you eat it with the natural fat in cream.
Calcium and Phosphorus: These minerals work together. They build and maintain strong bones and teeth. The fat in cream can help your body absorb these minerals better, especially if Vitamin D is also present.
Role in Low-Carb Diets
Heavy cream is a popular ingredient if you follow a low-carb or ketogenic diet. It fits well because it is high in fat and very low in carbohydrates. This helps your body stay in a state called ketosis, where it burns fat for fuel.
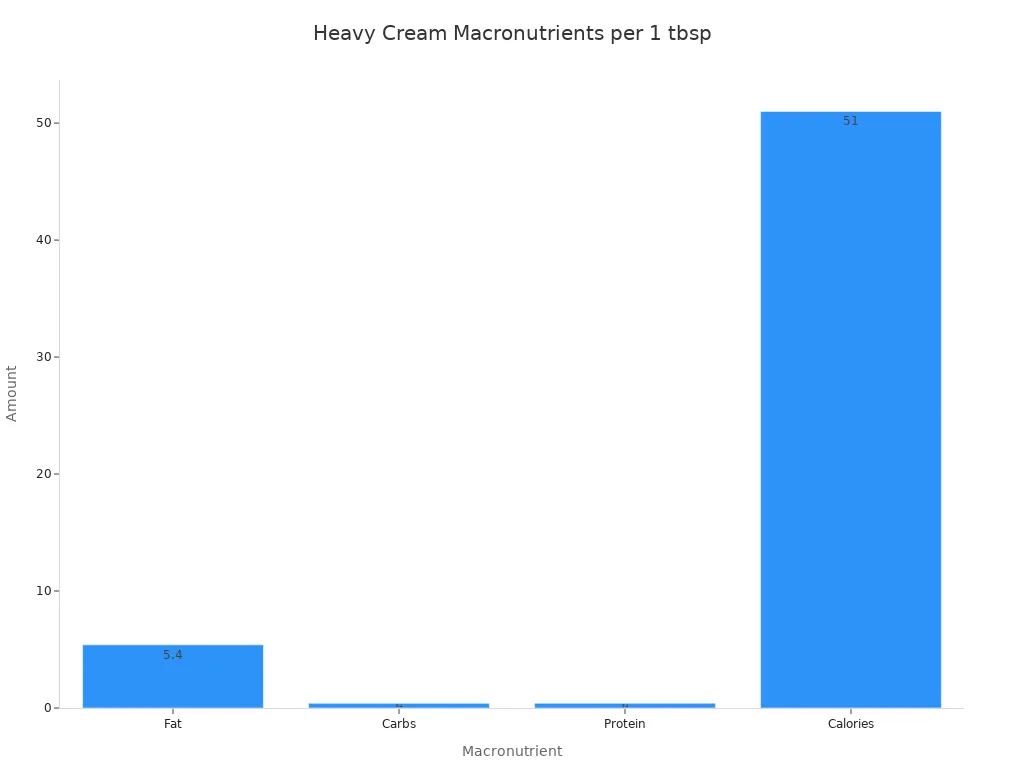
Here is a look at the macronutrients in one tablespoon of heavy cream:
Macronutrient | Amount per 1 tbsp |
|---|---|
Calories | 51 |
Fat | 5.4g |
Carbs | 0.4g |
Protein | 0.4g |
Heavy cream offers several advantages for low-carb eating:
It is high in fat and low in carbs. This makes it good for keeping ketosis.
It helps your body digest fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K.
You can use it in many ways. Add it to keto dinners, baked goods, desserts, coffee, soups, sauces, and smoothies.
It helps your body burn fat as its main fuel source.
Heavy Cream: Risks and Considerations
You now understand the nutritional profile of heavy cream. It is also important to consider potential risks. You should make informed choices about including it in your diet.
High Calorie and Saturated Fat Content
Heavy cream has a high calorie content. It also contains a significant amount of saturated fat. For example, one serving of heavy cream can contain 3.5g of saturated fat. This represents 17% of your daily value. Another serving size might contain 7g of saturated fat, which is 35% of your daily value. The American Heart Association suggests limiting saturated fat intake.
You should aim for 5% to 6% of your daily calories from saturated fat. If you consume about 2,000 calories daily, you should get no more than 120 calories from saturated fat. This equals about 13 grams of saturated fat per day. The high fat content of heavy cream contributes to its richness. However, you must be mindful of these amounts.
Importance of Moderation
Because of its higher fat content and high calorie content, you must consume heavy cream in moderation. You can enjoy its flavor and texture without overdoing it. Small amounts can enhance your meals. Large amounts can quickly add up. You should balance your intake with other healthy foods. This helps you maintain a balanced diet.
Lactose Intolerance and Sensitivities
Many people experience lactose intolerance. This means their bodies struggle to digest lactose, a sugar in dairy products. Approximately 65% of the adult human population experiences this. Experts estimate about 68 percent of the world’s population has lactose malabsorption. If you are lactose intolerant, you might experience symptoms.
These include bloating, gas, abdominal cramps, and diarrhea. You might also feel nauseous. Some people experience an urgent need for a bowel movement, vomiting, or lower stomach pain. Diarrhea is common. Undigested lactose draws water into your digestive tract. This leads to loose stool and sudden urges. If you have these symptoms, you should limit or avoid heavy cream.
Impact on Weight and Cardiovascular Health
You might worry about heavy cream’s impact on your weight and heart health. Research offers a nuanced view. Studies have not found a clear link between full-fat dairy products and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. This includes heart disease and stroke. These studies also did not find that full-fat dairy lowered the risk.
Interestingly, some research suggests potential benefits. A 2014 study found that people with the highest intake of full-fat dairy were less likely to be obese. They also had less belly fat. Another study showed that higher fat content from dairy consumption was linked to a reduced likelihood of developing diabetes later in life. You should consider these findings. They suggest that heavy cream, in moderation, might not be as detrimental as once thought.
Using and Storing Heavy Cream

Selecting Quality Heavy Cream
When you choose heavy cream, look for reputable brands. Always check the expiration date. Fresh heavy cream has a smooth, consistent texture. Avoid any cream that looks lumpy or has an off smell.
Proper Storage and Shelf Life
Proper storage keeps your heavy cream fresh. You should store heavy cream in the refrigerator. Keep it in its original container. This is the best way to store heavy cream. Unopened heavy cream typically lasts for 2-3 weeks. Once you open it, heavy cream remains fresh for about 1-2 weeks. Always seal the container tightly. This prevents spoilage. Following these steps is the best way to store heavy cream for maximum freshness.
Freezing Heavy Cream
You can freeze heavy cream to extend its life. This helps you avoid waste.
Pour heavy cream into an airtight container. Leave space for expansion. You can also use ice cube trays for smaller portions.
Seal and label with the date.
Freeze until solid, up to 3 months.
Thaw overnight in the refrigerator.
Shake or whisk the thawed cream well to re-emulsify. Thawed liquid cream works best for cooking or baking, not whipping. Add thawed cream directly to sauces and soups while cooking. Heavy cream tends to separate when thawed; shake well. Do not re-freeze heavy cream once thawed.
Finding the Best Substitute for Heavy Cream
Sometimes you need a substitute for heavy cream. Many options exist, both dairy and non-dairy. The best substitute for heavy cream depends on your recipe and dietary needs.
Here are some common substitutes:
Substitute | Key Properties & Uses |
|---|---|
Almond Milk | Light, subtly nutty base; can be thickened with cornstarch; good for desserts, sauces. |
Coconut Cream | Dense, rich; closest texture to heavy cream among non-dairy options; ideal for curries, vegan whipped cream. |
Soy Milk | Versatile, neutral flavor; high protein; use full-fat for heavier texture; good for creamy pastas. |
Cashew Cream | Soft, thick, smooth paste when soaked and blended; rich; good for dipping sauces, vegan Alfredo. |
Oat Cream | Mild flavor, seamless blendability; consistency mirrors light cream; good for fruit compotes, risottos. |
Silken Tofu | Light, mildly flavored when blended; low in calories, high in protein; ideal for creamy sauces, cheesecakes. |
You can see how different substitutes compare nutritionally:
Mastering the technique helps when you replace dairy cream. Pay attention to fat content and liquid ratios. Traditional heavy cream has about 36% fat. Alternatives like full-fat coconut milk can mimic this. Non-dairy creams often have more water. Reduce liquids or cook longer. You can add heart-healthy fats like olive oil to replicate richness. Thicken thin substitutes with starches. The best substitute for heavy cream depends on your specific recipe needs.
Rich Recipes: What Heavy Cream is Used For

Heavy cream is a versatile ingredient. You can use it in many culinary applications. It adds richness and a creamy texture to both sweet and savory dishes. Let’s explore some popular recipes where heavy cream shines.
Decadent Desserts and Sweet Treats
Heavy cream is essential for creating creamy desserts. Its high fat content, up to 40% butterfat, allows it to incorporate air. This creates a light, airy texture. You can whip heavy cream into a versatile topping for many desserts, like oatmeal. In no-churn ice cream, you whip heavy cream to provide a rich base. This creates a delicious homemade ice cream. Heavy cream also contributes to a decadently smooth filling for cream puffs. It enhances the richness of puddings and custards. You will find heavy cream crucial for the rich texture and layered flavors of tiramisu cake. These recipes truly showcase what heavy cream is used for in sweets.
Creamy Sauces and Savory Dishes
Heavy cream transforms savory dishes. It forms the base for many rich dishes. You often see it in classic Italian restaurant-style Fettuccini Alfredo. This cream sauce is typically enriched with Parmesan cheese. You can also use heavy cream to enhance chicken or white fish served with rice and vegetables. It makes creamy garlic sauces for noodles. You can drizzle it over meat and vegetables. Heavy cream even works as an alternative pizza sauce with chicken. These culinary applications demonstrate its power in savory cooking.
Enhancing Soups and Beverages
Heavy cream adds a velvety texture to soups. It balances and distributes flavors. Cream makes bitter notes less bitter and salty notes less salty. It smooths out acidity. For example, in cream of celery soup, you can add cream to balance the celery’s bitterness. You add a small amount, taste, and then add more until you reach your desired level. Heavy cream helps neutralize strong flavors. This creates a more balanced and complex rich taste.
Homemade Dairy Creations
You can make your own dairy products with heavy cream. Homemade ice cream is a popular choice. For brown butter ice cream, you combine heavy cream with whole milk, egg yolks, and sugar. You heat this mixture to create a custard base. After chilling, you churn it in an ice cream maker. This process turns simple ingredients into a delightful frozen treat. These recipes highlight the transformative power of heavy cream.
You now understand heavy cream nutrition, including its fat content and key vitamins. You learned about its benefits for energy and bone health, as well as considerations like its calorie and saturated fat content. Remember, moderation is key when you incorporate heavy cream into your diet. Explore the culinary versatility of heavy cream in your kitchen. Make informed choices and enjoy your food responsibly.
FAQ
Is heavy cream healthy?
Heavy cream provides healthy fats and important vitamins. You should enjoy it in moderation. It is calorie-dense. Balance it with other nutritious foods in your diet.
What is the difference between heavy cream and whipping cream?
Heavy cream has at least 36% milkfat. Whipping cream has slightly less, usually 30-36%. This higher fat content makes heavy cream thicker and more stable when you whip it.
Can I use heavy cream on a low-carb diet?
Yes, you can. Heavy cream is high in fat and very low in carbohydrates. This makes it suitable for low-carb and ketogenic diets. It helps you stay in ketosis.
How long does heavy cream last in the fridge?
Unopened heavy cream lasts 2-3 weeks in the refrigerator. Once you open it, use it within 1-2 weeks. Always keep it tightly sealed for freshness.

