
You need proper nutrition for effective muscle recovery. After exercise, your body demands specific nutrients for muscle repair, rebuilding, and energy replenishment. This crucial post-workout recovery is fundamental for achieving your fitness goals and preventing overtraining. A fitness-focused diet supports overall muscle recovery. Protein supplementation, for example, significantly increases muscle protein synthesis and aids muscle repair. Carbohydrates also help with glycogen recovery, especially when you consume them within 30 minutes post-exercise. This blog highlights 7 essential foods that significantly aid in your muscle recovery.
Key Takeaways
Eat protein after exercise to help your muscles repair and grow stronger.
Consume carbohydrates to refill your body’s energy stores after a workout.
Include healthy fats and berries in your diet to reduce swelling and soreness in your muscles.
Drink plenty of water to help your body recover and move nutrients around.
Eat foods like salmon, eggs, Greek yogurt, sweet potatoes, berries, quinoa, and leafy greens for better muscle recovery.
Understanding Muscle Recovery: Key Nutrients

To truly optimize your muscle recovery, you must understand the specific roles key nutrients play. These nutrients are vital for repairing muscle, replenishing energy, and reducing post-exercise stress. Effective muscle recovery depends on these nutritional foundations. Prioritizing these nutrients significantly boosts your overall muscle recovery.
Protein: Building Blocks for Recovery
Protein is absolutely essential for muscle recovery. It provides the amino acids your body needs for protein synthesis and muscle repair. After a workout, your muscle fibers experience micro-tears. Protein helps rebuild these fibers, leading to stronger muscle. You should aim for high-quality protein intake. Athletes often need 1.6-2.2g of protein per kg of body weight daily. You can divide this into 20-40g per meal or snack. This consistent protein intake supports optimal muscle recovery. Specific amino acids, like leucine, isoleucine, and valine, are particularly crucial for muscle repair. Leucine, for example, acts as a “green light” for muscle growth, triggering pathways for protein muscle fiber repair. These amino acids support energy and muscle repair, making protein a cornerstone of your recovery strategy. Adequate protein intake is non-negotiable for muscle recovery.
Carbohydrates: Energy Replenishment
Carbohydrates are your body’s primary fuel source. After intense exercise, your body depletes its glycogen stores. Glycogen is stored energy in your muscles and liver. You need to replenish glycogen stores to restore energy levels and prepare for your next workout. Complex carbohydrates are best for sustained energy release. Foods like whole grains, legumes, and sweet potatoes provide a slower, steady release of glucose into your bloodstream. For optimal glycogen replenishment, aim for 1-1.5g of carbohydrates per kg of body weight every hour in the early stages of recovery, totaling 6-10g/kg over 24 hours. This ensures your body has the energy for continued muscle recovery.
Healthy Fats: Inflammation Reduction
Healthy fats play a significant role in cellular health and can reduce inflammation. Long-chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (LC-PUFA), specifically DHA and EPA, are particularly beneficial. You find these in fatty fish like salmon. These omega-3s help modulate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses to exercise. They can reduce inflammation and decrease delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS). Studies show that omega-3 supplementation can significantly reduce biological markers of exercise-induced muscle damage. This helps your muscle recovery by managing inflammation effectively.
Micronutrients: Electrolytes, Minerals, Antioxidants
Micronutrients are vital for overall cellular function and combating oxidative stress. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium are critical. You lose these minerals through sweat during exercise. They maintain proper nerve function, muscle contraction, and fluid balance, all essential for recovery. Antioxidants, such as Vitamin C, Vitamin E, selenium, and polyphenols, help neutralize free radicals produced during physical activity. This reduces oxidative stress and supports your body’s ability to recover. These micronutrients collectively enhance your muscle recovery, ensuring your body can handle the demands of exercise.
Top 7 Best Foods for Muscle Recovery

You need to incorporate specific foods into your diet to accelerate muscle recovery and enhance your fitness. These are the best foods for muscle recovery. They provide the nutrients your body needs to repair, rebuild, and refuel after exercise. Making these essential foods a regular part of your meals helps you achieve your fitness goals.
1. Salmon and Fatty Fish
Salmon and other fatty fish are excellent choices for muscle recovery. They are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and provide high-quality protein. Omega-3s, like EPA and DHA, help reduce inflammation in your body. This is crucial after intense workouts when your muscles experience micro-damage and inflammation.
A study in ‘Nutrients’ showed that omega-3 supplements significantly reduced inflammatory mediators by 27–41% in physically active men. This helps your body recover faster. Another review in ‘Advances in Nutrition’ confirmed that fish oil supplementation consistently reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are markers of inflammation.
You get a good amount of omega-3s from salmon. For example, Atlantic Salmon contains 0.9 to 1.4 grams of omega-3s per 100 grams. Chinook Salmon offers 0.6 to 1.5 grams per 100 grams.
Salmon Type | Omega-3 Content (grams per 100g) |
|---|---|
Atlantic Salmon | 0.9 – 1.4 |
Chinook Salmon | 0.6 – 1.5 |
You also get high-quality protein from salmon. This protein provides the building blocks for muscle repair. Aim for two to three servings of fatty fish per week. Other great options include mackerel, sardines, and trout. These foods are vital for reducing inflammation and supporting muscle repair.
2. Eggs: Complete Protein Source
Eggs are one of the best foods for muscle recovery. They are a complete protein source, meaning they contain all nine essential amino acids your body cannot produce on its own. These essential amino acids are crucial for muscle repair and growth.
You get about 6 grams of protein from one large egg. The protein in eggs is highly bioavailable, meaning your body can easily absorb and use it. Eggs are versatile. You can enjoy them scrambled, boiled, or as an omelet.
Here is a look at some amino acids found in eggs:
Amino Acid (mg/100 g) | Whole Eggs | Albumen | Yolk |
|---|---|---|---|
Arginine | 814.9 | 525.6 | 1142.8 |
Histidine | 312.3 | 209.5 | 399.8 |
Isoleucine | 668.3 | 551.1 | 785.1 |
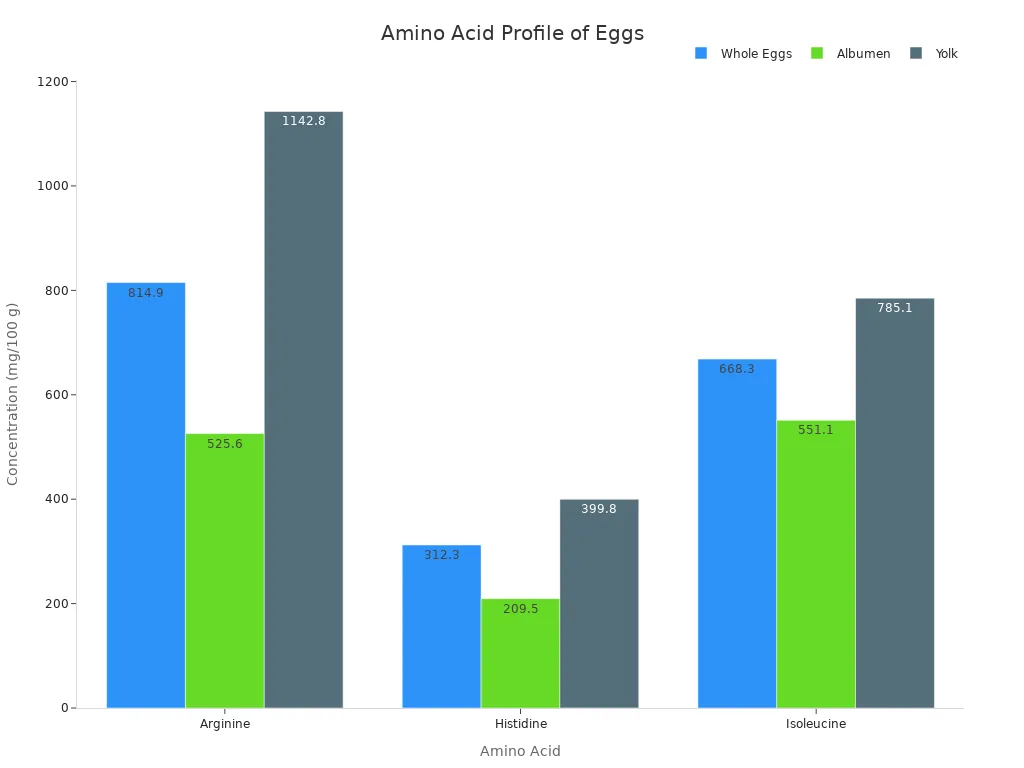
Lysine is also abundant in eggs. Fresh whole eggs contain 929 mg/100 g of lysine. Yolk has 1182 mg/100 g, and albumen has 760 mg/100 g. Methionine values are 400 mg/100 g in fresh whole eggs, 375 mg/100 g in yolk, and 396 mg/100 g in albumen. These amino acids support muscle repair and overall recovery.
3. Greek Yogurt
Greek yogurt is another excellent food for muscle recovery. It offers a high amount of protein, which is essential for muscle repair. Greek yogurt contains both casein and whey protein. Whey protein digests quickly, providing immediate amino acids to your muscles. Casein digests slowly, offering a sustained release of amino acids over several hours.
Greek yogurt has more protein than regular yogurt. A 200g serving of Greek yogurt provides 19.9 grams of protein. Regular yogurt only gives you 10.5 grams for the same serving size.
Type of Yogurt | Protein (per 200g serving) |
|---|---|
Regular yogurt | 10.5 g |
Greek yogurt | 19.9 g |
A 5.3-ounce container of plain, nonfat Greek yogurt contains 15.4 grams of protein. This is more than double the amount in regular yogurt. Greek yogurt also contains probiotics. These beneficial bacteria support gut health, which can indirectly aid your overall recovery. You can combine Greek yogurt with berries for a powerful recovery snack. Cottage cheese is a good alternative if you prefer it.
4. Sweet Potatoes
Sweet potatoes are fantastic for energy replenishment and muscle recovery. They are a complex carbohydrate. This means they provide a steady release of glucose into your bloodstream. This helps replenish glycogen stores in your muscles after exercise.
Sweet potatoes have a low glycemic index. This helps stabilize your blood sugar levels. Consuming 1-4 g/kg of body weight of carbohydrates, like sweet potatoes, before an event can increase your body’s glycogen stores. This enhances endurance. After exercise, sweet potatoes are crucial for glycogen restoration. They replace the carbohydrates your muscles used during training. Early carbohydrate intake after a workout is vital for maximizing refueling. The rate of glycogen re-synthesis is only 5% per hour.
Sweet potatoes also contain essential vitamins and minerals that support muscle function. They are rich in potassium, which stimulates muscles to contract and helps your heart pump blood. Magnesium helps regulate blood pressure and blood sugar. It is crucial for maintaining muscle and nerve function. Sweet potatoes also contain choline, a nutrient that assists with muscle movement. These essential foods help your body recover.
5. Berries
Berries are small but mighty foods for muscle recovery. They are packed with antioxidants. Antioxidants combat oxidative stress. Oxidative stress occurs when your body produces free radicals during exercise. These free radicals can damage cells and contribute to muscle soreness.
Blueberries, in particular, contain polyphenolic compounds. These compounds support muscle repair and recovery. Blueberry-derived anthocyanins can activate antioxidant enzyme systems. This helps reduce exercise-induced oxidative stress. Some studies show that blueberry polyphenols reduce oxidative stress more effectively than vitamin C.
Tart cherries are another excellent berry for recovery. They reduce markers of oxidative stress after intense physical activity. Tart cherries also decrease muscle soreness after resistance exercise or sprints. A tart cherry beverage can reduce exercise-induced muscle soreness. Tart cherry juice aids recovery after intermittent exercise. These berries are essential foods for reducing inflammation and supporting your recovery.
6. Quinoa
Quinoa is a powerful grain for muscle recovery. It is a complete protein. This means it contains all nine essential amino acids your body needs. This makes it an excellent plant-based protein source.
One cooked cup of quinoa offers 8 grams of protein. It also contains over 5 grams of dietary fiber.
Nutrient | Amount per cooked cup (185g) |
|---|---|
Protein | 8.14 grams |
Fiber | 5.18 grams |
Quinoa is rich in lysine, an amino acid often scarce in other grains. It also contains methionine, which is frequently deficient in many legumes. This unique amino acid profile makes quinoa a complete protein. Quinoa is also a complex carbohydrate. It provides sustained energy and helps replenish glycogen stores. Its fiber content aids digestion and overall gut health. You can use quinoa as a base for meals, in salads, or as a side dish. It is a versatile and essential food for your recovery.
7. Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. These nutrients are vital for overall cellular health and recovery. Spinach and kale are excellent examples. They provide a wide array of micronutrients that support your body’s healing processes.
Leafy greens contain vitamins like C, A, and various B vitamins. They also offer minerals such as potassium, magnesium, and folate. These are crucial for immune function and tissue repair. Antioxidants like flavonoids, polyphenols, and carotenoids neutralize harmful free radicals. This reduces inflammation and protects your cells from damage.
Vitamin C, found in spinach and kale, assists with muscle recovery and helps reduce inflammation. Iron-rich greens like spinach and kale are recommended post-workout. They replenish essential nutrients. These foods are fundamental for supporting your body’s recovery and overall well-being.
Optimizing Recovery: Timing and Hydration
You need to consider more than just food choices for effective muscle recovery. Meal timing and adequate hydration play critical roles. These elements significantly enhance your body’s ability to repair and refuel.
The Anabolic Window
The “anabolic window” refers to a specific time after exercise. During this period, your body is highly receptive to nutrients. These nutrients help with muscle repair and growth. Traditionally, people believed this window lasted only 30-60 minutes after your workout. You consume protein and carbohydrates during this time. This helps prevent muscle breakdown and replenishes energy stores.
However, recent science shows this window might be longer. It can extend to 5-6 hours around your training. If you exercise in a fasted state, this post-exercise timing becomes even more important for muscle recovery. Muscle protein synthesis is most active immediately after exercise, lasting up to 2 hours. You should aim for 20-40 grams of protein or 10-12 grams of essential amino acids within this period. For overall muscle recovery after intense exercise, consume 1g/kg of carbohydrates and 0.5g/kg of protein within 30 minutes. Remember, your total daily protein intake is often more important for muscle growth than strict timing. This helps your muscle recovery.
Hydration: The Unsung Hero of Recovery
Water is vital for your body. It transports nutrients, supports metabolic processes, and helps cells function. This makes hydration an unsung hero for muscle recovery. You lose fluids through sweat during exercise. Even a small amount of dehydration can affect your performance. Losing just 1% to 2% of your body weight from fluid can impair athletic performance. This impairment becomes worse with more dehydration.
You must replace water during and after exercise. Water makes up nearly 75% of every muscle cell. Electrolytes are crucial for moving water in and out of cells. They support rehydration and muscle repair. During exercise, drink 7-10 ounces of water every 10-20 minutes. For longer or more intense activities, or if you sweat a lot, consider a sports drink with electrolytes. These drinks replace lost salts. They also contain glucose, which helps pull electrolytes and water into your body. Proper hydration is essential for optimal muscle recovery.
You now understand the importance of these 7 essential foods for enhanced muscle recovery. Incorporate these vital foods into your post-workout diet. This supports optimal muscle recovery. Proper nutrition, strategic timing, and good hydration are key to maximizing your muscle gains and overall well-being. Experiment with these foods. Observe the positive impact on your recovery and performance. This approach boosts your muscle recovery. You build a stronger, more resilient muscle body through informed dietary choices for superior muscle recovery.
FAQ
What is the best time to eat for muscle recovery?
You should aim to consume nutrients within a few hours after your workout. This period helps your body repair muscles and replenish energy stores. Eating protein and carbohydrates soon after exercise supports optimal recovery.
What nutrients are most important for muscle repair?
Protein is crucial for rebuilding muscle fibers. Carbohydrates replenish your energy stores. Healthy fats help reduce inflammation. Micronutrients like electrolytes and antioxidants support overall cellular function and combat stress.
What foods help reduce muscle soreness?
Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon, reduce inflammation. Berries, especially tart cherries and blueberries, provide antioxidants. These compounds combat oxidative stress and can lessen muscle soreness after exercise.
What role does hydration play in muscle recovery?
Water transports vital nutrients throughout your body. It supports metabolic processes and helps your cells function correctly. Staying well-hydrated replaces fluids lost through sweat, which is essential for effective muscle repair and overall recovery.

