
Shrimp enjoys widespread popularity on dinner tables globally. Many people often underestimate its significant nutritional value. This seafood is a lean source of protein, packed with essential nutrients. Some believe shrimp is high in cholesterol and unhealthy. However, dietary cholesterol has less impact on blood cholesterol levels than previously thought. Shrimp provides high-quality protein and offers many health benefits, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. This post provides clear facts on shrimp nutrition 101 for healthy and informed consumption, highlighting its role in overall health and good nutrition.
Key Takeaways
Shrimp is a great source of lean protein. It helps build and repair muscles.
Shrimp has many important vitamins and minerals. These include iodine, phosphorus, and vitamin B12.
Shrimp contains good fats called omega-3s. These fats are good for your heart.
Eating shrimp can help your thyroid work well. It also boosts your immune system.
Cook shrimp fully to stay safe. Choose shrimp from good sources for the best health benefits.
Shrimp Nutrition Facts: A Lean Profile

Calorie and Macronutrient Breakdown
Shrimp offers excellent shrimp nutrition. It stands out as a lean source of protein. Many people seek clear shrimp nutrition facts to understand its benefits. A 3.5-ounce serving of cooked shrimp contains about 140 calories. A smaller 1-ounce serving has 40 calories.
Serving Size | Calories |
|---|---|
1 oz cooked | 40 |
3.5 oz cooked | 140 |
Shrimp is primarily protein. A 3-ounce serving provides 20.31 grams of protein. Each ounce delivers 6 grams of protein. Shrimp has very little saturated fat. It contains no carbohydrates. It also provides unsaturated fat and some omega-3 fatty acids.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Beyond its impressive protein content, shrimp is rich in nutrients. Its nutritional values are truly remarkable. Shrimp offers many essential vitamins and minerals. For example, a 3-ounce serving provides 260.1 mg of phosphorus and 12.8 mcg of iodine.
A 3.5-ounce serving contains 41 μg of iodine, 237 mg of phosphorus, and 1.66 μg of vitamin B12. A 4-ounce serving of shrimp gives 30% of the daily recommended intake for vitamin B12 and iodine. It also provides 50% of the daily recommended intake for phosphorus. This chart shows the amounts of key nutrients:
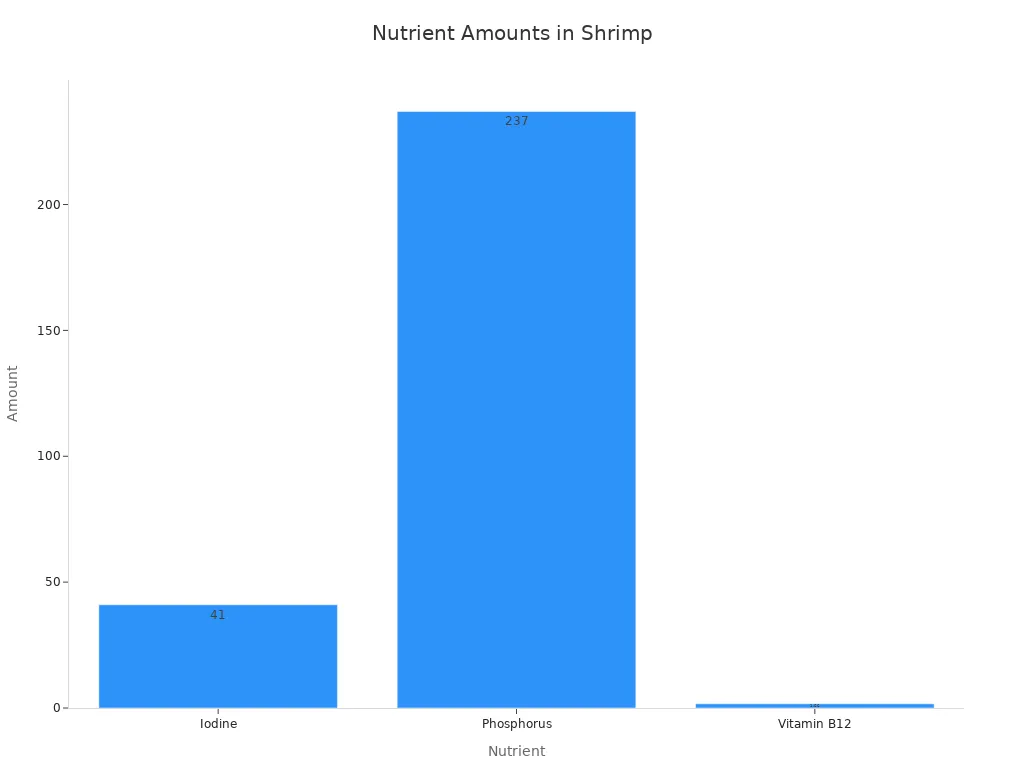
Shrimp also contains calcium. This adds to its overall nutrition profile.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids Content
Shrimp also contains beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are important for overall health. Cooked shrimp provides 0.12 grams of omega-3 fatty acids per 3 ounces. It contains 0.1 grams of total omega-3 fatty acids per 100 grams. This makes shrimp a good source of omega-3. The presence of omega-3 fatty acids further enhances the shrimp nutrition facts.
Shrimp Health Benefits: Protein & More
Shrimp offers many health benefits. Its nutritional composition provides impressive advantages for the body. The protein content in shrimp is comparable to other lean meats. These shrimp benefits contribute to overall well-being. The nutritional benefits of shrimp extend beyond just protein, supporting various bodily functions.
Muscle Building and Repair
Shrimp is an excellent source of protein. This protein is crucial for building and repairing muscles. Research shows shrimp protein hydrolysate (Shr) promotes muscle growth. A study on rats with muscle injuries found Shr led to greater muscle growth than casein. This suggests increased protein synthesis and less fat in non-injured muscles.
Shrimp protein hydrolysate contains high levels of essential amino acids like isoleucine, lysine, and threonine. These amino acids boost its ability to build muscle. They also improve muscle fiber growth. The hydrolysis process creates biological peptides. These peptides help amino acids become available faster for protein accretion after meals.
Another study on juvenile white shrimp showed leucine promotes protein synthesis. It does this through the TOR signaling pathway. Replacing fishmeal with threonine-hydrolyzed protein (THP), which has leucine, increased growth and crude protein in shrimp muscle. This indicates better nutrient use and protein synthesis. Leucine is an essential amino acid. It stimulates protein synthesis and is crucial for growth.
Heart Health and Cholesterol Management
Many people wonder about shrimp’s impact on heart health. Shrimp contains dietary cholesterol. However, its effect on blood cholesterol levels is often misunderstood. A study showed that eating 300g of shrimp daily increased LDL (bad) cholesterol by 7.1%.
It also increased HDL (good) cholesterol by 12.1%. This led to no negative effect on the ratios of total cholesterol to HDL or LDL to HDL. Shrimp consumption also reduced triglycerides by 13%. This indicates an overall positive impact on cholesterol profiles, with a net improvement of 18%.
Scientists from Harvard and Rockefeller University also found that a shrimp diet increased HDL more than LDL. This resulted in a favorable HDL to LDL ratio. Shrimp contains several compounds beneficial for the heart. These include selenium, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants. These nutrients help protect against inflammation. They also increase good cholesterol and defend against free radicals. All these factors contribute to better heart health.
Thyroid Function and Metabolism Support
Shrimp is a good source of iodine. Iodine is an essential trace mineral. The body must get it from food or supplements. It is necessary for producing thyroid hormones. These hormones are thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Thyroid hormones regulate many important biochemical reactions. These include protein creation and enzyme activity. They are critical for regulating normal metabolism. Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) controls thyroid hormone production. TSH secretion increases the thyroid’s uptake of iodine. This stimulates the synthesis and release of T3 and T4. Without enough iodine, TSH levels stay high. This can lead to goiter as the body tries to get more iodine.
Immune System Boost
Shrimp contains selenium. Selenium is an essential trace element. It plays a role in the glutathione peroxidase enzyme. This enzyme reduces peroxides that damage cells and tissues. This boosts the immune system.
Organic selenium supplementation increased the total hemocyte count (THC) and survival of Chinese white shrimp infected with a virus. Selenium doses also increased THC and lysozyme activity in juvenile Chinese mitten crab under stress. Organic selenium increased prophenoloxidase (PO) and lysozyme activity in giant freshwater prawn.
Inorganic and organic selenium increased PO, respiratory burst (RB), and phagocytic activity (PA). They also enhanced disease resistance against bacteria in giant freshwater prawn. Higher PO activity in selenium-treated shrimp shows improved immunity. It directly helps fight bacteria through the melanization process. Selenium acts as an effective antioxidant. It eliminates and prevents oxidative stress. It also increases the number of SOD enzymes in the body. Hemocytes are crucial for immunity in crustaceans. Lysozyme activity is a key indicator of innate immunity. It acts as an antibacterial, antiviral, and anti-inflammatory agent.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Shrimp contains astaxanthin. Astaxanthin is a powerful antioxidant. It has strong anti-inflammatory properties. Astaxanthin reduces inflammation by regulating target genes. These include inflammatory biomarkers, acute phase proteins, and cytokines.
It promotes certain signaling pathways like PI3K/AkT and Nrf2. It also blocks pathways like NF-κB, ERK1/2, JNK, p38 MAPK, and JAK-2/STAT-3. This helps reduce inflammation. Specifically, it stops IκB-α degradation and NF-κB nuclear translocation.
This inhibits the expression of MCP-1, IL-6, VEGFs, ICAM-1, VEGFR-1, and VEGFR-2. Astaxanthin also lessens airway inflammation. It does this by balancing Th1/Th2. It inhibits IL-4 and IL-5 release and increases IFN-γ. It decreases mRNA expression levels of IL-1β, IL-6, CCL2, and CXCL2. It also suppresses mRNA and protein expressions of eotaxin, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF), IL-4, and IL-5. Astaxanthin reduces the production of pro-inflammatory molecules. These include tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). This modulates inflammatory pathways and reduces tissue damage.
Eye Health and Antioxidant Protection
The astaxanthin in shrimp also offers benefits for eye health. As a potent antioxidant, astaxanthin protects the eyes from oxidative damage. Oxidative stress can harm eye cells. Antioxidants like astaxanthin neutralize free radicals. This helps maintain good vision and overall eye health. These benefits contribute to the overall health advantages of including shrimp in your diet.
Is Shrimp Healthy? Addressing Concerns
Many people ask, “is shrimp healthy?” This section addresses common questions and potential risks. It provides balanced information for informed choices.
Dietary Cholesterol: Understanding the Impact
Shrimp contains dietary cholesterol. A typical serving has about 189 milligrams. Many people worry about this. However, current dietary guidelines have changed. They no longer recommend a specific daily limit for cholesterol intake. Instead, experts suggest keeping dietary cholesterol consumption as low as possible. This should not compromise the diet’s nutritional value. The focus is more on limiting saturated fats to less than 10% of daily calories. Prioritizing unsaturated fats helps maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
Allergic Reactions and Sensitivities
Some people experience shellfish allergies. Shrimp is a common allergen. Up to 1.3% of the population in the United States has a shrimp allergy. Symptoms range from mild to severe. Life-threatening anaphylaxis can occur. Accidental exposure often leads to emergency room visits. Anaphylaxis happens in up to 50% of individuals with shrimp allergy. People with shellfish allergies must avoid shrimp.
Sourcing and Contaminant Concerns
Concerns about contaminants in shrimp are valid. However, commercially available shrimp generally have low levels of mercury. The table below shows typical levels in various shrimp types.
Shrimp Type (Origin) | T-Hg (ng/g) | MeHg (ng/g) | Se (ng/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
Black Tiger (Imported) | 15.8 | 14.4 | 415 |
Vannamei (Imported) | 11.4 | 11.2 | 292 |
White Shrimp (Imported) | 26.8 | 26.1 | 396 |
Shiba (Japanese) | 15.9 | 15.0 | 270 |
Kuruma (Japanese) | 79.9 | 75.9 | 390 |
Ashiaka (Japanese) | 36.1 | 34.1 | 303 |
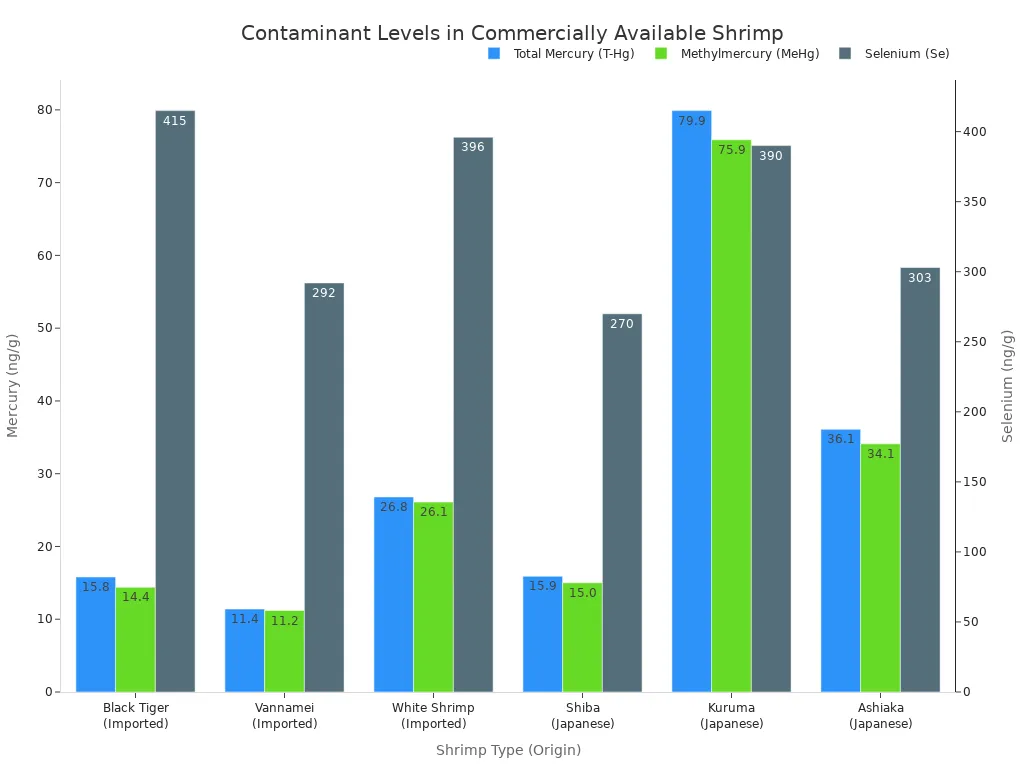
All methylmercury levels were below Japanese regulations. This indicates shrimp is a safe choice for health.
Risks of Raw Shrimp Consumption
Eating raw or undercooked shrimp carries risks. Raw shrimp can contain dangerous infections. Thorough cooking is crucial for safety. Pregnant individuals should avoid raw seafood due to infection risks. Shrimp harvested from unsafe waters can have high contaminant levels. Cooking does not eliminate these contaminants. They can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and headaches. Spoiled shrimp also poses health risks. It has rancid, fishy, sour, or ammonia smells. Do not eat spoiled shrimp. Proper preparation ensures you get the protein benefits safely.
Practical Uses and Healthy Preparation

Incorporating shrimp into a balanced diet is easy. People can enjoy its many benefits by choosing quality products and preparing them safely.
Choosing Quality Shrimp
Selecting high-quality shrimp is important for both taste and health. Look for shrimp from responsible sources. These sources minimize impact on natural resources like land, energy, and water. They also protect wild fish. Certified seafood, such as that from the Aquaculture Stewardship Council (ASC), ensures strong environmental standards.
These standards include science-based metrics for resource use. For farmed shrimp, look for practices that avoid habitat loss, like mangrove destruction. They should also manage antibiotic and chemical use well. For wild-caught shrimp, choose those from well-managed fisheries. These fisheries use gear that reduces bycatch, such as turtle excluder devices (TEDs).
They also manage impacts from bottom trawling. Certifications like Best Aquaculture Practices (BAP) and ASC are good signs for farmed shrimp. Some U.S. buyers also accept ‘Best Choice’ or ‘Good Alternative’ ratings from Seafood Watch. High-quality, sustainably sourced shrimp also addresses human rights. Certifications often include social audits and labor standards. This helps prevent forced labor and other abuses in the supply chain. Choosing such healthy seafood supports both personal well-being and ethical practices.
Safe Handling and Storage
Proper handling and storage prevent foodborne illnesses. Always keep raw shrimp refrigerated or frozen. Thaw frozen shrimp in the refrigerator overnight or under cold running water. Cook shrimp immediately after thawing. Avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw seafood.
Healthy Cooking Methods
Cooking shrimp properly ensures safety and preserves its flavor. Cook shrimp until it turns pearly or white and opaque. This indicates it is fully cooked.
Food Type | Cooking Guideline |
|---|---|
Shrimp | Cook until flesh is pearly or white, and opaque |
Healthy cooking methods include grilling, baking, broiling, and stir-frying. These methods use less added fat. Avoid deep-frying, which adds unnecessary calories and unhealthy fats.
Versatile Recipe Ideas
Shrimp is a versatile ingredient. It fits into many delicious and healthy options. People can make Orange Sesame Shrimp with Rice for a quick weeknight meal. Thai Coconut Shrimp offers a crisp texture with a flax coating. Cajun Shrimp Cakes are filling and protein-rich. For a stir-fry, try Coconut Shrimp Stir-Fry with broccoli and shiitake mushrooms. Other ideas include Grilled Lemon Shrimp, which is quick and flavorful. Shrimp Tacos with Cabbage and Brussels Sprouts make a fast dinner. Shrimp Scampi with Baby Greens and Sorghum offers a dairy-free and gluten-free meal. These recipes show how easily shrimp can be part of a nutritious diet.
Shrimp offers impressive shrimp nutrition and many health benefits. It is a lean protein source packed with essential vitamins and minerals. When people choose shrimp wisely and prepare it healthily, it becomes a highly nutritious food.
Readers can confidently add shrimp to their balanced diets. This dispels any lingering doubts about its healthfulness.
Enjoy this versatile seafood for its great nutrition and many benefits.
FAQ
Is shrimp high in cholesterol?
Shrimp contains dietary cholesterol. However, experts now know dietary cholesterol has less impact on blood cholesterol levels. Shrimp also provides beneficial nutrients like omega-3s. These nutrients support heart health.
What are the main protein benefits of eating shrimp?
Shrimp is an excellent source of lean protein. This protein helps build and repair muscles. It also supports overall body functions. The amino acids in shrimp boost muscle growth and recovery. 💪
Can everyone eat shrimp safely?
Most people can eat shrimp safely. However, some individuals have shellfish allergies. These allergies can cause severe reactions. People with allergies should avoid shrimp. Always cook shrimp thoroughly to prevent foodborne illnesses.
What important vitamins and minerals does shrimp provide?
Shrimp offers many essential vitamins and minerals. It provides iodine, which supports thyroid function. Shrimp also contains phosphorus for bone health and vitamin B12 for energy. Selenium boosts the immune system.
Does shrimp contain omega-3 fatty acids?
Yes, shrimp contains beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. These fats are important for heart health and reducing inflammation. Including shrimp in your diet contributes to your omega-3 intake. 🦐

