
Taste the tropics with mango, a truly delicious superfruit! Its vibrant flavor and rich vitamin content make it a popular choice. This sweet fruit offers more than just great taste. How much do you really know about its health power? Discover the incredible mango nutrition benefits. Explore its specific nutritional advantages and learn how to incorporate this amazing fruit into a healthy lifestyle for optimal well-being. Uncover the full spectrum of its nutrition.
Mango Nutrition: A Powerhouse of Vitamins

Mangoes offer impressive mango nutrition. They contain over 20 vitamins and minerals. This makes them a true nutritional powerhouse.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
A single cup of mango provides about 50% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C. This high dose of vitamin C supports many body functions. Mangoes also supply significant amounts of Vitamin A, Vitamin E, Vitamin K, and folate. These vitamins are crucial for overall health. Beyond vitamins, mangoes offer important minerals. Here are some key nutrients per serving:
Nutrient | Value (per 207g serving) |
|---|---|
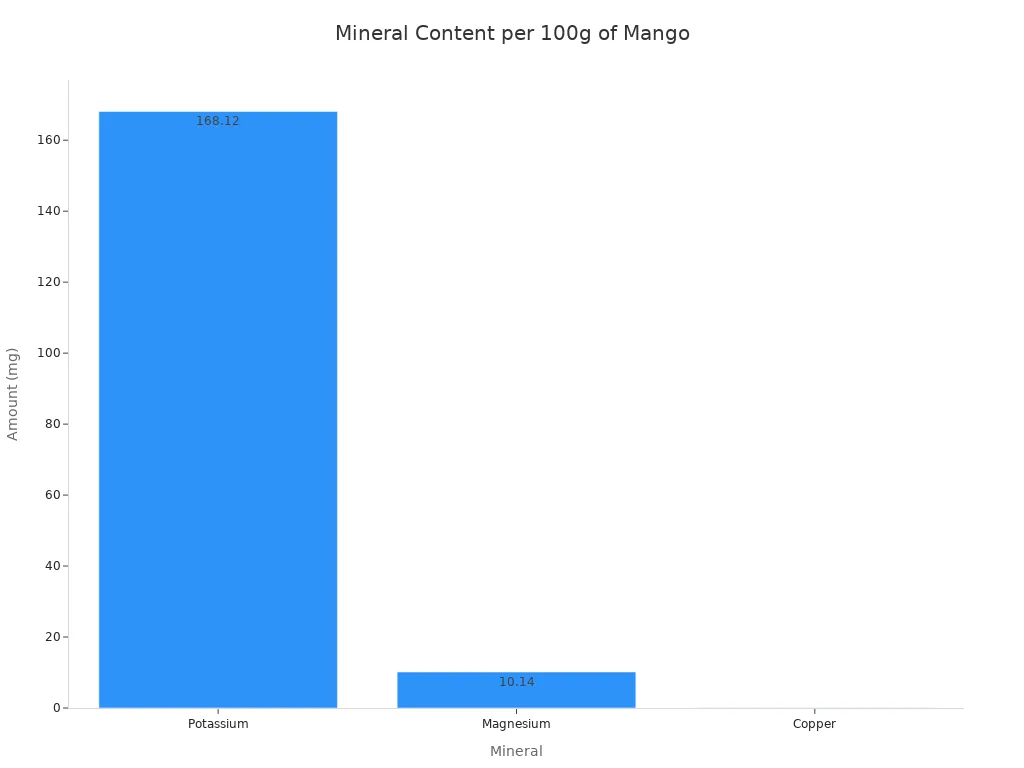
Potassium | 348 mg |
Copper | 0.2 mg |
Magnesium | 21 mg |
Fiber and Antioxidant Profile
Mangoes are a good source of dietary fiber. One cup contains about 2.6 grams of fiber. This fiber includes starch and pectins. These components contribute to digestive health.
Source | Fiber Content (g per 100g) |
|---|---|
Fruit dry weight basis | 0.85–1.06 |
USDA Nutrient Database | 1.6 |
Colombian food composition table | 2.6 |
Mangoes also boast a rich antioxidant profile. They contain polyphenols, flavonoids, and vitamins like ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and Vitamin E. Specific compounds include mangiferin, quercetin, and gallic acid. These compounds help fight oxidative stress in the body.
H3: Macronutrients and Calorie Count
Mangoes are relatively low in calories. One cup contains about 99 calories. They primarily consist of carbohydrates. They have very little fat and protein. This makes them a light and healthy snack.
Nutrient | Value per 100g |
|---|---|
Calories | 65 |
Total Fat | 0.27 g |
Carbohydrates | 17 g |
Protein | 0.51 g |
This detailed nutrition breakdown shows why mango nutrition is so beneficial.
Mango Health Benefits: Unlocking Wellness
Mangoes offer many impressive mango health benefits. These benefits come from their rich nutrient profile.
Immune System Support
Mangoes provide strong immune system support. Their high vitamin C content is key. Vitamin C, along with vitamin A and antioxidants like fisetin and quercetin, supports immune cell function. This enhances the body’s ability to fight off pathogens. Adequate vitamin C intake enhances the production and effectiveness of white blood cells. These cells are critical for fighting infections. These mango nutrition benefits help keep the body healthy.
Digestive Health and Gut Wellness
The fiber in mangoes supports digestive health. One cup of mango contains about 2.6 grams of fiber. This fiber helps maintain regular bowel movements. It also promotes a healthy gut environment. The fiber and water content in mangoes contribute to overall gut wellness.
Cardiovascular Health
Mangoes are great for our hearts. Research suggests mangiferin, a compound found in mangoes, may decrease oxidized LDL particles. This impacts cardiovascular health. A study supported by the National Mango Board found daily mango consumption reduced total cholesterol and LDL (‘bad’) cholesterol levels in postmenopausal women. Dr. Roberta Holt noted that lowering these markers can positively impact cardiovascular health. However, some studies in overweight adults found no significant changes in LDL after 12 weeks.
Skin, Hair, and Eye Health
Mangoes contribute to healthy skin, hair, and eyes. They are a significant source of Vitamin A. One cup provides nearly 25% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin A is vital for healthy vision, especially in low-light conditions. It plays a key role in forming rhodopsin, a protein for night vision. This contribution helps reduce the risk of age-related eye conditions like macular degeneration. As people age, absorbing Vitamin A becomes less efficient. So, eating Vitamin A-rich foods like mangoes is crucial for maintaining vision health. These health benefits of mangoes extend to skin and hair health too.
Antioxidant Properties and Cancer Prevention
Mangoes contain powerful antioxidants. These compounds offer potential anticancer effects. Mango pulp contains mangiferin, gallic acid, and quercetin. Mango peel and seed are also rich in mangiferin and other beneficial compounds. A study by Noratto et al. (2010) indicates that polyphenolics from mango varieties possess anticarcinogenic properties. These antioxidant properties help reduce cancer risk.
Blood Sugar Regulation and Weight Management
Mangoes can help with blood sugar regulation. Studies show regular mango consumption improved glucose regulation. It increased insulin sensitivity. This reduced the amount of insulin needed to maintain normal glucose levels. One study found consuming two cups of mango daily lowered insulin concentration levels. It also enhanced insulin sensitivity in overweight adults. These improvements happened without changes in body weight. This counters misconceptions about mango’s sugar content. The health benefits of mango also include helping to aid in weight loss by promoting satiety.
How to Enjoy Mangoes: Sweet Fruit Integration

Mangoes offer a delightful taste and many health benefits. People can easily add this sweet fruit into their daily meals. Its versatility makes it a favorite for many different dishes.
Fresh and Versatile Serving Ideas
Enjoying fresh mango is simple and delicious. People can peel and slice it for a quick snack. They can also add diced mango to breakfast cereals or yogurt. Fresh mango brightens up any fruit salad. Its sweet flavor pairs well with both sweet and savory dishes.
Culinary Creations with Mangoes
Mangoes go beyond just eating them fresh. They are a star ingredient in many culinary creations. People use mangoes in various beverages, such as refreshing mango juice or creamy mango lassi. They also make delicious condiments like spicy mango chutney or fresh mango salsa with diced onions and cilantro. For desserts, mango mousse, panna cotta, or the classic mango sticky rice are popular choices. People also add mango to smoothies, salads, and grain bowls for extra flavor and nutrition. Even mango peels find use, dried and powdered for smoothies, or pickled.
Selecting and Storing Ripe Mangoes
Choosing a ripe mango ensures the best flavor. Do not rely on color alone, as it often shows the mango variety, not its ripeness. Instead, use your senses. A ripe mango will have a delicious, sweet fragrance, especially near its stem. Gently squeeze the mango. The skin should give slightly when pressed, similar to a ripe peach. If it feels too mushy, it is overripe. A slightly firmer mango with tight skin will last a few days. Store ripe mangoes in the refrigerator to slow down ripening. Store unripe mangoes at room temperature until they soften.
Mangoes: Considerations and Warnings
Mangoes offer many health benefits. However, people should consider a few things when eating this sweet fruit.
Natural Sugars and Moderation
Mangoes contain natural sugars. This gives them their sweet taste. The sugar content varies by variety.
Mango Variety | Sugar Content (grams per 100g) |
|---|---|
Tommy Atkins, Haden, Kent, Keitt | 13.6 |
Columbian | 13.7 |
Ataulfo | 14 |
African varieties (e.g., Sudanese) | 10.5 – 32.4 (percent sugar) |
People should eat mangoes in moderation, especially those watching their sugar intake. The natural sugars are part of a healthy diet. Yet, large amounts can add up.
Potential Allergies and Sensitivities
Some people may have allergic reactions to mangoes. The mango peel often triggers these reactions. Urushiol is a substance found in the peel. It is also in poison ivy and poison oak. Contact with urushiol can cause skin rashes. Other compounds in mangoes can also cause sensitivities. These include:
Man I 1 (40kDa; GAPDH)
Man I 2 (30kDa)
Man I 3 (profilin, similar to mugwort Art v 1)
5-resorcinol (found in mango peel, related to urushiol)
Limonene
Cardol
β-pinene
People with known allergies to poison ivy should be careful with mango peels.
Nutritional Value and Ripeness
The nutritional content of a mango changes as it ripens. Ripe mangoes have more sugar and less vitamin C than raw mangoes. Raw mangoes are rich in Vitamin C. Ripe mangoes are rich in Vitamin A.
Nutrient | Raw Mango | Ripe Mango |
|---|---|---|
Calories | 60 kcal | 74 kcal |
Carbohydrates | 15 grams | 16.9 grams |
Fiber | 1.6 grams | 2.0 grams |
Protein | 0.8 grams | 0.6 grams |
Fat | < 0.4 grams | < 0 grams |
Sugars | 13 grams | 14 grams |
Vitamin C | High | Moderate |
Vitamin A | Moderate | High |
Water Content | 23.5% | 82.9% |
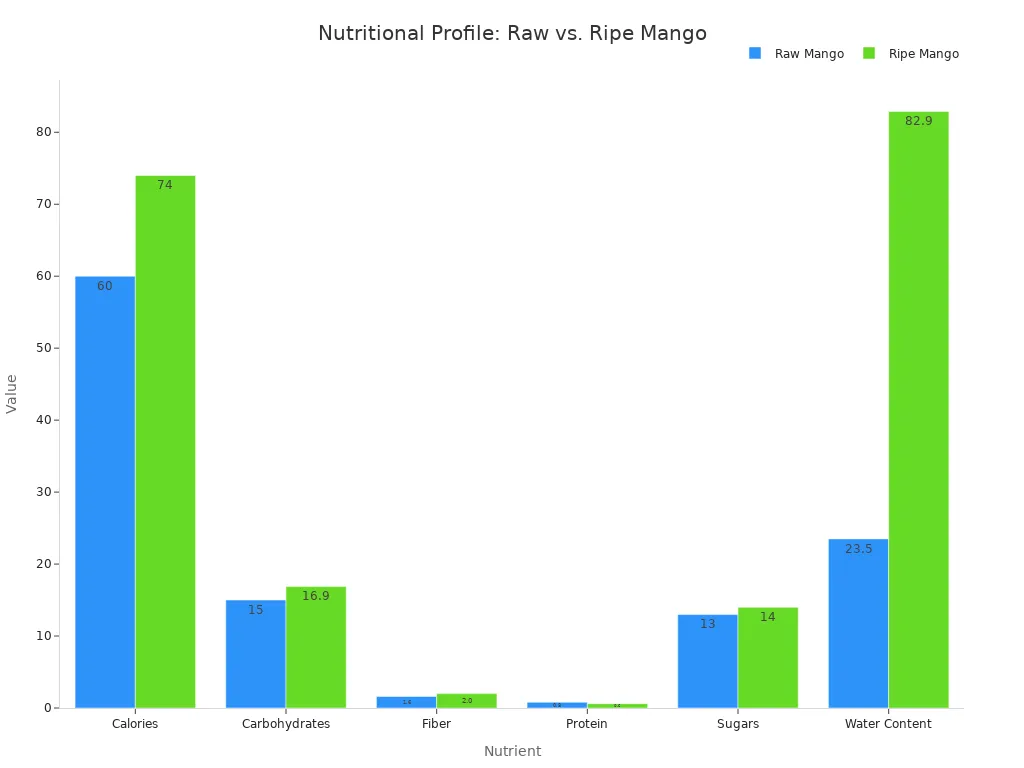
Unripe mangoes have much less water. They contain 23.5% water. Ripe mangoes contain 82.9% water. Both raw and ripe mangoes offer good nutrition. They provide different benefits.
Raw Mango: It has high Vitamin C. This boosts immunity. It promotes healthy skin. It also has fiber for digestion.
Ripe Mango: It has Vitamin A. This is good for vision and skin. It also has beta-carotene. This acts as an antioxidant.
The extensive mango nutrition benefits highlight its value. This superfruit provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Mangoes are both versatile and delicious. Readers should regularly include them in their diet for overall well-being. Incorporating mangoes can significantly contribute to a healthier lifestyle. Explore new mango recipes or share your favorite ways to enjoy this sweet fruit!

