
Is chicken breast healthy? Yes, boneless skinless chicken breast stands as a prime lean protein source. Many people choose boneless skinless chicken breast for a healthy diet. This popular chicken provides excellent protein. This blog explores chicken breast nutrition. It details the health benefits of this versatile chicken. We also look at its many uses. Boneless skinless chicken breast offers great nutrition. This guide covers all the benefits of this lean protein.
Key Takeaways
Chicken breast is a great source of protein. It helps your muscles grow and repair.
Eating chicken breast can help you manage your weight. It makes you feel full and reduces hunger.
Chicken breast has important vitamins and minerals. These help your bones stay strong and boost your immune system.
Cook chicken breast in healthy ways. Try grilling, baking, or roasting it to keep it lean.
Always handle and store chicken safely. Cook it well to avoid getting sick.
Chicken Breast Nutrition Facts

Boneless skinless chicken breast is a nutritional powerhouse. It offers an impressive profile of macronutrients and essential micronutrients. This section details the precise nutritional breakdown of boneless skinless chicken breast. It highlights why many consider it a staple in healthy eating plans.
Macronutrient Breakdown
Boneless skinless chicken breast stands out as a lean protein source. It provides significant protein with minimal fat. This makes it an excellent choice for those managing their weight or building muscle. A typical 100-gram serving of boneless skinless chicken breast contains a balanced set of macros.
Here is a look at the macronutrient content for 100 grams of boneless skinless chicken breast:
Nutrient | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Calories | 120 |
Total Fat | 2.6g |
Cholesterol | 73mg |
Sodium | 45mg |
Protein | 22.5g |
This table shows the calories in chicken breast are relatively low. It also confirms its status as a low-fat protein. Another source indicates boneless, skinless chicken breast contains approximately 85 milligrams of cholesterol per 100 grams. This variation shows average values can differ slightly. The high protein content makes boneless skinless chicken breast a complete protein source. This means it provides all nine essential amino acids the body needs. This makes it a high in protein food. Understanding these chicken breast macros helps people make informed dietary choices.

This chart visually represents the excellent nutrition found in boneless skinless chicken breast. It clearly shows its low calorie and low fat nature.
Key Vitamins and Minerals
Beyond its impressive protein content, boneless skinless chicken breast is a nutrient-dense food. It supplies several essential nutrients vital for overall health. This chicken provides important vitamins and minerals.
Chicken breast is particularly rich in B vitamins. These vitamins play crucial roles in energy metabolism and nerve function. It contains significant amounts of vitamin B3 (niacin) and vitamin B6 (pyridoxine).
Here are some key B vitamins and their daily value percentage in a 3.5-ounce serving of boneless skinless chicken breast:
B Vitamin | % of Daily Value (3.5-oz serving) |
|---|---|
Niacin (B3) | 86% |
Pyridoxine (B6) | 35% |
Cobalamin (B12) | 14% |
The chicken breast nutrition also includes important minerals. These minerals support various bodily functions.
Nutrient | Amount (per serving) |
|---|---|
Magnesium | 28.0 mg |
Selenium | 22.8 μg |
Zinc | 0.7 mg |
These minerals contribute to bone health, immune function, and antioxidant defense. Selenium, for example, is a powerful antioxidant. Zinc supports the immune system. Magnesium is important for muscle and nerve function. The overall nutrition of boneless skinless chicken breast makes it a valuable addition to any diet.
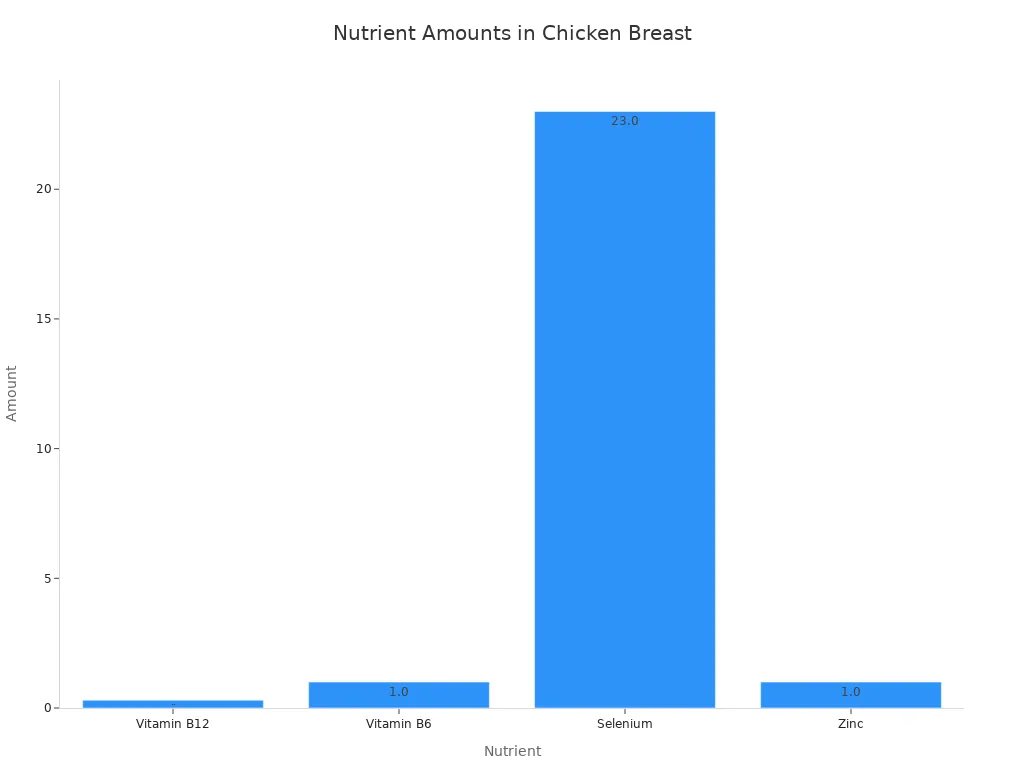
This chart further illustrates the presence of these essential nutrients in boneless skinless chicken breast. It reinforces its reputation as a nutrient-dense food.
Health Benefits of Chicken Breast
Boneless skinless chicken breast offers numerous health benefits. Its rich nutrient profile contributes significantly to overall well-being. The nutrients in this lean protein support various bodily functions. They help with appetite control, mood regulation, and even sleep quality. This makes boneless skinless chicken breast a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Muscle Growth and Repair
Chicken is an excellent source of high-quality protein. This protein is crucial for muscle growth and repair. The body uses amino acids from protein to build and maintain muscle tissue. Athletes and individuals engaging in regular physical activity benefit greatly from including boneless skinless chicken breast in their diet. It provides the necessary building blocks for strong muscles.
Weight Management Support
Boneless skinless chicken breast plays a key role in weight management. Its high protein content helps curb hunger and promotes satiety. This contributes to feelings of fullness. A lean protein snack like chicken breast can help prevent late-night snacking. Its high protein content keeps individuals full and reduces overall calorie intake. It also supports lean muscle mass preservation during a calorie deficit. This is vital for maintaining metabolic rate.
Research supports these benefits. A 2007 study in the Journal of the American College of Nutrition found that high-protein diets, including chicken, preserved muscle and reduced fat. Postmenopausal women on a calorie-restricted, chicken-based diet lost more fat and preserved more muscle compared to those on a higher-carb plan. Another study in Appetite (2011) showed that high-protein meats like chicken breast, beef, and pork generated similar satiety responses. This supports boneless skinless chicken breast’s role in reducing hunger and aiding weight management.
Bone Health and Strength
The minerals found in boneless skinless chicken breast contribute to strong bones. Phosphorus, for example, works with calcium to build and maintain bone density. Selenium also plays a role in bone metabolism. Including this nutrient-dense food in your diet helps support long-term bone health and strength.
Heart Health Advantages
Lean protein sources like boneless skinless chicken breast can benefit heart health. Two controlled-feeding Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) investigated lean chicken intake on blood lipids in hypercholesterolemic males. Both studies found that diets including lean poultry, lean beef, or lean fish, as part of an American Heart Association-style diet, reduced total cholesterol and LDL cholesterol. One study also noted reductions in apolipoprotein B, total to HDL cholesterol ratio, and triglycerides. No significant differences appeared between the protein sources.
Another RCT further supported these findings. It showed reductions in total and LDL cholesterol with lean chicken or lean beef diets. Again, no differences appeared between the two. A separate controlled-feeding RCT by Bergeron et al. involved generally healthy adults. This study compared lean poultry, lean red meat, and nonmeat protein sources. It found that a nonmeat diet, but not poultry or beef diets, reduced total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, non-HDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, apolipoprotein B, and apolipoprotein A1, independent of saturated fat intake. Protein source did not affect triglycerides or total to HDL cholesterol ratio. These studies suggest that boneless skinless chicken breast can be part of a heart-healthy eating plan.
Immune System Boost
Boneless skinless chicken breast contains essential nutrients that boost the immune system. Zinc in chicken is significant in reducing the incidence of certain diseases. This indicates its beneficial effect on health, which includes immune support. Chicken breast also contains selenium. Selenium is a trace mineral essential for proper immune function. It contributes to immune function through its antioxidant properties. These nutrients help the body fight off infections and maintain overall immune health. The health benefits of this chicken are clear.
Healthy Uses and Preparation

People can easily add boneless skinless chicken breast to a healthy diet. Proper cooking methods maintain its lean profile. This section offers practical ways to enjoy this versatile chicken. It focuses on healthy cooking and smart portioning.
Lean Cooking Techniques
Cooking boneless skinless chicken breast healthily is simple. Lean cooking techniques help keep the fat content low. Grilling is an excellent choice. It adds flavor without extra oil. Baking or roasting boneless skinless chicken breast in the oven also works well. People can use herbs and spices for seasoning. Stir-frying with plenty of vegetables is another great option. Poaching or boiling boneless skinless chicken breast creates a tender result. These methods avoid adding unnecessary fats. This careful preparation ensures the chicken remains a lean protein source.
Healthy Chicken Breast Recipes
Many healthy chicken breast recipes exist. They make incorporating boneless skinless chicken breast into meals easy. For example, grilled chicken can top a fresh salad. Baked boneless skinless chicken breast pairs well with steamed vegetables. Stir-fried chicken with broccoli and bell peppers makes a quick dinner. People can also shred cooked chicken for healthy wraps or sandwiches. These chicken breast recipes highlight the versatility of boneless skinless chicken breast. They offer delicious ways to enjoy this nutritious chicken.
Optimal Serving Sizes
Understanding optimal serving sizes helps with portion control. A typical serving of boneless skinless chicken breast is about 3 to 4 ounces. This is roughly the size of a deck of cards. This amount provides a good source of protein without excess calories. People can adjust serving sizes based on their individual dietary needs. Consistent portion control supports overall health goals. This careful preparation helps people manage their intake of chicken.
Important Considerations
People should consider several factors when they include boneless skinless chicken breast in their diet. These factors ensure safety, maximize health benefits, and address individual needs.
Storage and Food Safety
Proper handling and storage of chicken are very important. This prevents foodborne illnesses. Always refrigerate raw chicken promptly. Store it below 40°F (4°C). Cook chicken to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C). This kills harmful bacteria. Avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw chicken.
Processed Chicken Products
Not all chicken products offer the same health benefits. Fresh, skinless, cooked chicken breast is very lean. A 100g serving contains about 3.6g of fat and 50-60mg of sodium. However, processed chicken products can differ greatly.
Processed meats, including processed chicken products, frequently contain elevated levels of preservatives such as sodium and nitrates. These additives have been associated with increased risks of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes.
When purchasing chicken that has undergone processing, it is crucial to examine the nutrition facts panel. For instance, if you opt for ground poultry over ground beef, assuming it’s healthier, always verify the label. Ground poultry can contain as much, or even more, fat than ground beef, especially if the processor includes dark meat and skin. Similarly, processed chicken products may have added salt, so reviewing the sodium levels on the nutrition facts panel is very important for any processed food or poultry item.
Always check labels for added fats, sodium, and other ingredients in processed chicken.
Organic vs. Conventional
People often wonder about the differences between organic and conventional chicken. Both types of chicken can have bacterial contamination. However, conventional chicken has a 33% higher risk of carrying bacteria resistant to three or more antibiotics.
Organic chicken is raised without antibiotics, hormones, or synthetic pesticides. This means the meat is free from these residues. Some organic farms also avoid chlorine washing.
Here is a comparison of organic and conventional chicken:
Feature | Organic Chicken Breast | Conventional Chicken Breast |
|---|---|---|
Fat Content | Higher | Lower |
Mineral Substances | More | Less |
pH Value | Higher | Lower |
Cooking Loss | Higher | Lower |
Water Holding Capacity | Higher | Lower |
Alpha-linoleic Acid | Higher | Lower |
Docosahexaenoic Acid | Higher | Lower |
Salmonella spp. | Detected (66.66%) | Detected (100%) |
This table shows some nutritional differences. Organic chicken often has higher fat content but also more beneficial fatty acids.
Potential Dietary Concerns
Some individuals may experience dietary concerns with chicken. Chicken meat allergy is a rare but serious condition. Symptoms can appear immediately or several hours later.
Common symptoms include:
Urticaria (Hives)
Angioedema
Anaphylaxis (a severe, life-threatening reaction)
Abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea
Runny nose, coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath
Causes of chicken allergy include specific proteins like parvalbumin. Genetic factors and bird-egg syndrome can also play a role. People with asthma or eczema may have a higher risk. If you suspect a chicken allergy, consult a healthcare professional.
Chicken breast nutrition offers a highly nutritious, versatile, and beneficial food for a healthy diet. It provides lean protein, which supports muscle health and aids in weight management. Readers should thoughtfully incorporate chicken into their meals. Healthy preparation methods are important.
Making informed dietary choices empowers individuals to achieve their health goals.
FAQ
Is chicken breast good for weight loss?
Yes, chicken breast is excellent for weight loss. It provides high protein, which helps individuals feel full and reduces overall calorie intake. This supports maintaining lean muscle mass while losing fat.
Can someone eat chicken breast every day?
Yes, people can eat chicken breast daily as part of a balanced diet. It offers essential nutrients. Varying protein sources is also beneficial for a wider range of nutrients.
What is the healthiest way to cook chicken breast?
Grilling, baking, roasting, or poaching are the healthiest ways to cook chicken breast. These methods require minimal added fats. They help maintain its lean profile and nutritional value.
Does chicken breast contain carbohydrates?
No, chicken breast is naturally carbohydrate-free. It is a pure protein source. This makes it suitable for low-carb diets.

