
You may know red sage as Salvia miltiorrhiza, a plant valued in herbal medicine for centuries. People use red sage to support health because it promotes blood circulation and relieves pain.
Red sage has helped treat cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases for over 2000 years.
Extensive cultivation meets high demand, but wild sage populations are declining from overharvesting.
Understanding both the Health Benefits and possible risks of red sage helps you make informed choices.
Key Takeaways
Red sage supports heart health by improving blood circulation and reducing the risk of heart attacks. Consider adding it to your routine for cardiovascular benefits.
This herb may help manage diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and lowering blood sugar levels. Consult your doctor before using it as part of your diabetes management plan.
Red sage promotes liver health by protecting against toxins and reducing inflammation. It can be beneficial for those looking to support liver function.
Use red sage in various forms, such as capsules, powders, or teas. Choose the form that best fits your lifestyle and follow dosage instructions carefully.
Be aware of potential side effects like stomach upset or dizziness. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting red sage, especially if you take other medications.
What is Red Sage

Botanical Overview
You may recognize red sage by its vivid red flowers. This plant, also called danshen, belongs to the Salvia genus. You often see it growing in hot, dry places. Red sage thrives in poor soils and does not need much water. Gardeners value its adaptability, as it grows well in sunny spots and fits into both wild and cultivated gardens.
Here is a table showing how red sage stands out from other types of sage:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Flower Color | Striking red flowers make red sage easy to identify among other sage species. |
Drought Tolerance | Red sage survives in arid climates and needs little water. |
Adaptability | You can grow red sage in many settings, from natural landscapes to home gardens. |
You may find different species, such as Salvia miltiorrhiza and Salvia coccinea, used for their resilience and diverse benefits. Many people use sage in xeriscaping because it handles dry conditions well.
Traditional Use
Danshen has a long history in traditional chinese medicine. You see it mentioned in ancient texts like the Shennong Bencao Jing, dating back to around 100 CE. Healers first used danshen for heart and abdominal problems. Over time, people discovered more uses for red sage.
In traditional chinese medicine, you find danshen used for:
Improving blood circulation
Treating bleeding disorders
Addressing abnormal menstruation
Helping with miscarriage recovery
Reducing swelling
Easing insomnia
Treating hepatitis
Recent studies show that danshen helps with blood vessel problems in the heart and brain. You may notice that red sage now plays a major role in supporting cardiovascular health and emotional well-being. Its cultural importance comes from its link to blood health and healing.
Here is a table showing common uses of danshen in traditional chinese medicine:
Use | Description |
|---|---|
Heart health | Supports heart function and helps prevent heart disease. |
Blood circulation | Promotes healthy blood flow. |
Heart disease treatment | Used for atherosclerosis, thrombosis, and hypertension. |
You see that red sage, or danshen, remains a key herb in traditional chinese medicine for both physical and emotional health.
Health Benefits of Red Sage
Red sage offers a wide range of health benefits. You may find it helpful for your heart, blood sugar, liver, reproductive system, and as a source of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Many people use red sage because of its long history in herbal medicine and growing scientific support.
Heart Health
You can support your heart health with red sage. This herb has a strong reputation for helping with cardiovascular problems. Researchers have studied red sage in many clinical trials. They found that it can improve blood flow, protect heart muscle cells, and lower the risk of heart attacks. Red sage may also help reduce blood clots and relax blood vessels, which supports healthy circulation.
Here is a table showing what studies have found about red sage and cardiovascular health:
Study Type | Findings |
|---|---|
Clinical Trials | Analyzed 39 trials involving red sage for cardiovascular disease treatment. |
Pharmacological Activity | Over 200 compounds isolated from Danshen with heart disease treatment potential. |
Blood Circulation | Promotes blood circulation and coronary blood flow, reduces heart attack risk. |
Clinical Evidence | Suggests improvement in angina pectoris and myocardial infarction symptoms. |
You may notice that red sage is often used to help with angina, high blood pressure, and other heart conditions. Its potential benefits for cardiovascular health make it a popular choice in both traditional and modern medicine.
Studies indicate red sage may help dilate blood vessels.
Reduces blood clot formation.
Protects heart muscle cells from ischemic damage.
Diabetes Support
Red sage may help you manage diabetes. Scientists have found that extracts from this herb can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels in animal studies. Some small human studies suggest that red sage may help control blood sugar when used with other treatments. The herb works by supporting insulin signaling and reducing harmful compounds that form in diabetes.
Here is a table that shows what research says about red sage and diabetes:
Evidence Type | Findings |
|---|---|
Preclinical Studies | Extracts from Red Sage may improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood glucose levels. |
Mechanisms Proposed | Enhancement of insulin signaling, inhibition of advanced glycation end-products, anti-inflammatory effects. |
Clinical Evidence | Limited human studies suggest modest improvements in glycemic control as adjunct therapy. |
A meta-analysis of three trials indicated that sage supplementation significantly reduced fasting blood sugar and HbA1c levels. You may find red sage helpful as part of your diabetes management plan, but you should always talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Liver Health
Red sage supports liver health in several ways. Traditional medicine has used this herb to treat liver diseases for centuries. Modern research shows that red sage can improve blood flow in liver cells and protect against toxins. In animal studies, red sage helped prevent liver damage by reducing inflammation and improving the structure of liver tissue.
You may benefit from red sage if you want to protect your liver or support its function. The herb can reduce fat buildup in the liver and improve important blood markers. It also boosts the liver’s antioxidant defenses, which helps prevent damage from harmful substances.
Red sage, in the form of Salvia—Nelumbinis naturalis (SNN), exhibits hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities.
It reduces liver lipid deposition and improves serum biochemical indices.
Enhances hepatic antioxidant capability, contributing to protection against liver damage.
Reproductive Health
You may use red sage to support reproductive health, especially if you follow traditional Chinese medicine. Practitioners often recommend this herb to regulate menstrual cycles and address issues like amenorrhea. Red sage is believed to promote blood circulation, which is important for reproductive organs. Historical texts describe its use for conditions such as painful periods, endometriosis, and some types of infertility.
Red sage is used in traditional Chinese medicine to support the reproductive system, particularly in women.
It is commonly employed to regulate menstrual cycles and address amenorrhea (absence of menstruation).
The herb is believed to promote blood circulation, which is considered vital for reproductive health.
Historical texts describe its use in formulas aimed at ‘moving blood’ and resolving ‘blood stasis,’ which are related to conditions like dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, and certain types of infertility.
Current scientific studies focus more on the cardiovascular and anti-inflammatory effects of red sage. Only early research hints at possible benefits for reproductive health, such as improving blood flow to the uterus or affecting hormones. Most of the support for red sage in this area comes from traditional use rather than strong scientific proof.
Antioxidant & Anti-Inflammatory
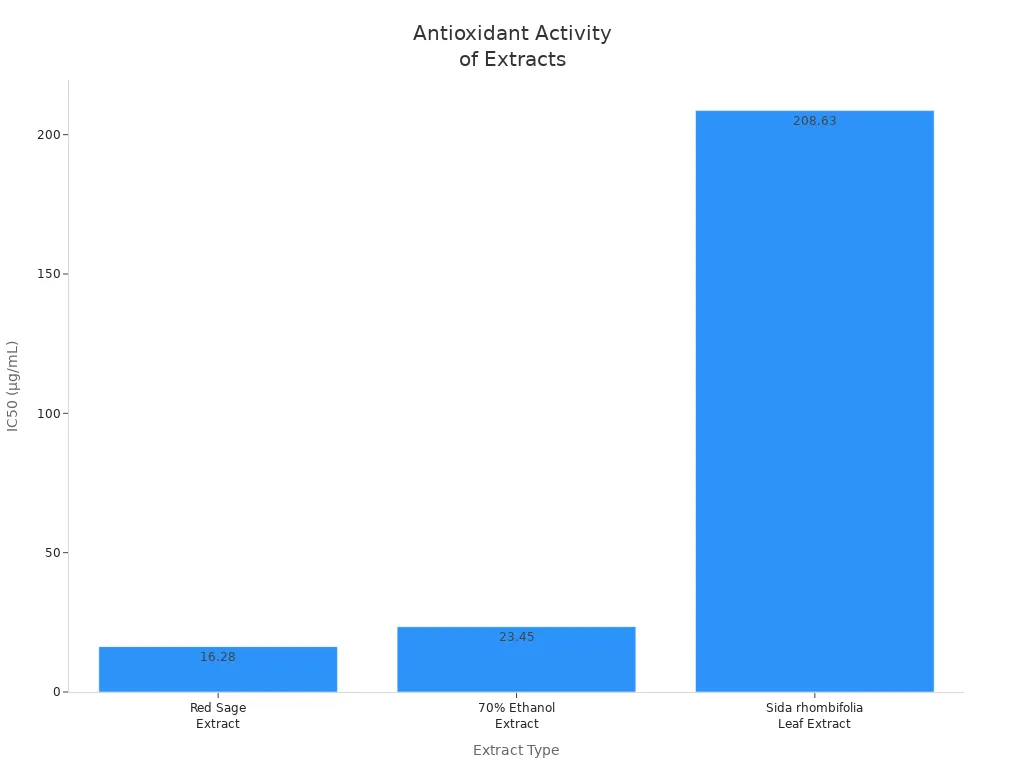
Red sage contains powerful antioxidant compounds. These compounds help protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. Laboratory tests show that red sage extract has strong antioxidant activity, even stronger than some other plant extracts.
Compound | IC50 (µg/mL) | Comparison |
|---|---|---|
Red Sage Extract | 16.28 | Lower than ascorbic acid (4.81) |
70% Ethanol Extract | 23.45 | Less effective than optimized extract |
Sida rhombifolia Extract | 208.63 | Significantly lower activity than red sage |
Red sage also shows strong anti-inflammatory effects. The active ingredients, such as tanshinones and salvianolic acids, block the release of substances that cause inflammation. Animal studies show that red sage can reduce swelling and tissue damage in conditions like arthritis and liver injury. The herb works by stopping certain pathways in the body that lead to inflammation.
Study Focus | Findings |
|---|---|
Anti-inflammatory activity | Demonstrated substantial anti-inflammatory activity at nanomolar concentration by inhibiting PMN proteases and leukocyte adhesion receptor P-selectin. |
Cytokine inhibition | Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine release by blocking TLR2 and TLR4. |
Pathogen suppression | Suppressed growth of pathogens associated with periodontitis. |
Tissue damage prevention | Attenuated LPS induced pro-inflammatory mediators and MMP-9 in cell culture models. |
Study Focus | Findings |
|---|---|
Cytokine inhibition | Inhibition of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. |
Signaling pathway suppression | Suppressed activation of NF-κB and MAPK pathways. |
Conditions studied | Reduced tissue damage in arthritis, atherosclerosis, and liver injury models. |
You may find these antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects helpful for protecting your body from chronic diseases and supporting overall health.
Using Red Sage

Forms
You can find red sage in several forms. Most stores offer it as capsules, powders, or liquid extracts. Some products use liposomal technology, which helps your body absorb the herb better. Liposomal extracts come in liquid, capsule, and powder forms. These options make it easy for you to choose the best way to add sage to your routine.
Here is a table showing the most common types and their bioavailability:
Product Type | Bioavailability Profile |
|---|---|
Liquid Liposomal Red Sage Extract | Enhanced absorption due to liposomal encapsulation |
Capsule Liposomal Red Sage Extract | Enhanced absorption due to liposomal encapsulation |
Powder Liposomal Red Sage Extract | Enhanced absorption due to liposomal encapsulation |
You may notice that liposomal forms offer better absorption than regular extracts. This means your body can use more of the active compounds for health support.
Preparation
You can prepare red sage in different ways. Many people use dried root slices to make tea. You simply add hot water and let the slices steep for about 10 minutes. Some choose tinctures, which you can mix with water or juice. Capsules and powders do not need special preparation. You just swallow them with water. Liquid extracts often come with a dropper, so you measure the dose and add it to your drink.
Tip: Always follow the instructions on the product label. This helps you get the most benefit from sage and avoid taking too much.
Dosage
You should check the dosage on each product. Most capsules contain 250 to 500 mg of red sage extract. For teas, people often use 3 to 9 grams of dried root per day. Liquid extracts usually suggest 1 to 2 milliliters, taken one to three times daily. Your ideal dose depends on your age, health, and reason for using sage. You should talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Side Effects
When you use red sage, you should know what side effects and risks may appear. Most people tolerate sage well, but some experience mild reactions. You may notice stomach upset, dry mouth, or dizziness. Allergic reactions are rare, but they can happen. If you feel itchy or have trouble breathing, stop using the herb and seek help.
Risks
Red sage carries some risks, especially if you have certain health conditions or take specific medicines. You may face increased bleeding if you use sage with blood thinners. Some people report low blood pressure or changes in heart rate. Children, pregnant women, and breastfeeding mothers should avoid red sage because safety data is limited.
Note: Always check with your doctor before using red sage if you have a medical condition.
Here is a table showing who should avoid red sage:
Population Group |
|---|
Under the age of 18 |
Pregnant or breastfeeding individuals |
Taking blood thinners or digoxin |
Interactions
Red sage can interact with many prescription drugs. You may see increased sedation if you use sage with medicines for sleep or anxiety. Some drugs may lose their effect or become stronger when combined with sage. Always tell your doctor about all supplements you use.
Drug Name | Interaction Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
pentobarbital | Minor | Both increase sedation. |
perphenazine | Minor | Both increase sedation. |
phendimetrazine | Minor | Sage increases, phendimetrazine decreases sedation; unclear effect. |
phenobarbital | Minor | Both increase sedation; sage decreases effects by antagonism. |
phentermine | Minor | Sage increases, phentermine decreases sedation; unclear effect. |
phenylephrine | Minor | Sage increases, phenylephrine decreases sedation; unclear effect. |
phenytoin | Minor | Sage decreases effects by antagonism; theoretical interaction. |
primidone | Minor | Both increase sedation; sage decreases effects by antagonism. |
prochlorperazine | Minor | Both increase sedation. |
promethazine | Minor | Both increase sedation. |
repaglinide | Minor | Sage increases effects by synergism. |
risperidone | Minor | Both increase sedation. |
valproic acid | Minor | Sage decreases effects by antagonism; theoretical interaction. |
ziprasidone | Minor | Both increase sedation. |
Precautions
You should take precautions when using red sage with other medicines. Some drugs, like anticoagulants and antihypertensives, may cause problems if you use them with sage. People with ulcers or diabetes should avoid red sage. Always inform your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines and supplements you take.
Precaution | Description |
|---|---|
Anticoagulants | Do not use simultaneously with anticoagulants. |
Antihypertensive | Avoid use with antihypertensive medications. |
Vasodilators | Do not combine with vasodilators. |
Health Conditions | Not recommended for individuals with ulcers or diabetes. |
Pregnancy/Breastfeeding | Should be avoided during pregnancy and breastfeeding. |
Drug Interactions | Sage has moderate interactions with Topiramate and mild interactions with at least 223 different drugs. |
Consultation | Always inform your doctor or pharmacist of all medications you are taking before starting sage. |
Tip: You can lower your risks by following dosage instructions and talking to your healthcare provider.
You can use red sage to support heart health, manage diabetes, and protect your liver. Research shows that sage may lower cholesterol and help with blood circulation. You should always talk to a healthcare provider before starting sage, especially if you take medications or have health concerns. Risks include possible effects on blood pressure, seizures, and hormone-sensitive conditions.
Practical Step | Description |
|---|---|
Consult your doctor | Get advice before using red sage or combining it with other treatments. |
Start with a low dose | Use 3-6 grams of dried herb or 200-600 mg of extract daily. |
Monitor for side effects | Watch for changes in blood pressure or allergic reactions. |
Tip: Weigh the benefits of red sage against possible risks. Choose safe products and follow instructions for best results.
FAQ
What is the best way to take red sage?
You can take red sage as tea, capsules, or liquid extract. Choose the form that fits your needs. Always follow the instructions on the product label.
What should you watch for when using red sage?
You should watch for side effects like stomach upset, dizziness, or dry mouth. If you notice allergic reactions, stop using red sage and contact your doctor.
What drugs interact with red sage?
Red sage may interact with blood thinners, sedatives, and diabetes medicines. You should tell your doctor about all supplements and medicines you use.
What makes red sage different from common sage?
Red sage contains unique compounds called tanshinones and salvianolic acids. These support heart health and blood circulation. Common sage does not have these benefits.
What should you do before starting red sage?
You should talk to your healthcare provider. Ask about safe dosage and possible risks. This helps you use red sage safely and effectively.

