
Chokeberry, also known as aronia berry, gives you a fruit packed with nutrients and powerful antioxidants. You get high levels of polyphenols, flavonoids, and trace elements such as iron, manganese, and zinc. These help your body fight oxidative stress and support your heart, blood sugar, and immune system.
Here is how chokeberry compares to other parts of the plant:
Nutrient | Chokeberry Fruit | Chokeberry Pomace | Chokeberry Leaves |
|---|---|---|---|
Total Polyphenols | Higher than Pomace | Highest | Twice that of Fruit |
Flavonoids | Higher than Pomace | Lower | Higher than Fruit |
Iron (Fe) | Lower than Leaves | Lower | Highest |
Manganese (Mn) | Lower than Leaves | Lower | Highest |
Zinc (Zn) | Lower than Leaves | Lower | Highest |
Chokeberry Nutrition stands out because you get strong antioxidant potential from polyphenols and vitamin C. Scientific studies show chokeberries help prevent oxidative stress, which can lower your risk for many diseases.
Key Takeaways
Chokeberries are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, making them a powerful addition to your diet.
Regular consumption of chokeberries can support heart health by improving cholesterol levels and reducing inflammation.
Chokeberries may help manage blood sugar levels, making them beneficial for those with diabetes.
Incorporating chokeberries into your meals can boost your immune system and improve gut health.
Start with purple chokeberries for a balanced flavor, and consider using them in juices, jams, or baked goods.
What Are Aronia Berries?

Aronia berries are small fruits that grow on shrubs native to North America. You may know them as chokeberries. These berries stand out because of their high nutritional value and strong antioxidant properties. When you look at aronia, you see clusters of white or light pink flowers in spring. The leaves appear green and glossy during summer, then turn orangish-red or purple in fall. The berries themselves show bright red or deep purple-black colors, depending on the type.
Types of Aronia
You can find three main types of aronia berries. Each type has unique features and nutritional content.
Type of Aronia Berry | Nutritional Content (per 100g) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
Red Chokeberry (Aronia arbustifolia) | Sweeter taste, vibrant red color | Used as food dye substitute |
Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) | Slightly bitter, deep purple-black hue | Commonly used in juices |
Purple Chokeberry (Aronia prunifolia) | Combination of tartness and sweetness | Hybrid of red and black varieties |
Red chokeberry gives you a sweeter flavor and looks appealing in salads.
Black chokeberry contains more beneficial compounds and works well in juices.
Purple chokeberry offers a balance of tartness and sweetness, making it a good choice if you are new to aronia berries.
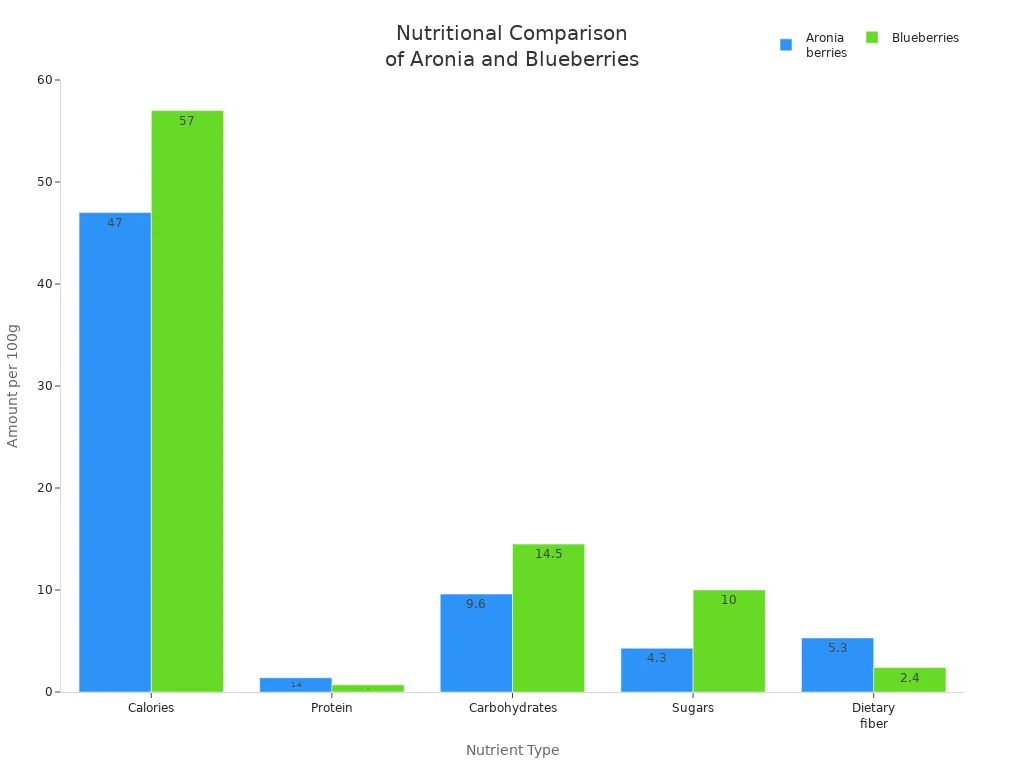
Aronia berries differ from other berries like blueberries. You get more vitamin C, B vitamins, potassium, calcium, magnesium, iron, and zinc. The chart below shows how aronia berries compare to blueberries.
Taste and Uses
You will notice that aronia berries taste tart and slightly bitter. The red chokeberry tastes sweeter, so you can eat it fresh or add it to salads. Black chokeberry has a more bitter flavor, which makes it popular for juices and jams. Purple chokeberry gives you a mix of tart and sweet, making it versatile for many dishes.
Type of Aronia Berry | Taste Profile Description |
|---|---|
Red Chokeberry (Aronia arbutifolia) | Sweeter, suitable for fresh consumption and salads. |
Black Chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) | Slightly bitter, often used in juices. |
Purple Chokeberry (Aronia prunifolia) | Balanced tartness and sweetness, versatile for various dishes. |
You can use aronia berries in jams, jellies, baked goods, and smoothies. Their tart flavor works well in recipes that need a strong fruit taste. Many people also use aronia berries for their health benefits, thanks to their high levels of antioxidants and tannins.
Tip: If you want to try aronia berries, start with purple chokeberry for a balanced flavor.
Chokeberry Nutrition
Vitamins and Minerals
You get a wide range of vitamins and minerals from chokeberry nutrition. Chokeberry gives you vitamin C, which helps your body fight infections and heal wounds. You also receive B vitamins, including B2 and B6, which support energy production and brain function. Vitamin K in chokeberry helps your blood clot properly.
Chokeberry is a strong source of micronutrients. You find zinc, magnesium, and iron in every serving. Zinc helps your immune system work well. Magnesium supports your muscles and nerves. Iron helps your body carry oxygen in the blood. Chokeberry nutrition also includes potassium and calcium, which keep your heart and bones healthy.
Nutrient | Role in Your Body | Amount in Chokeberry (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
Vitamin C | Immune support, antioxidant | 21 mg |
Vitamin K | Blood clotting | 13 mcg |
Vitamin B2/B6 | Energy, brain function | 0.1 mg / 0.2 mg |
Zinc | Immune system, wound healing | 0.3 mg |
Magnesium | Muscle, nerve function | 20 mg |
Iron | Oxygen transport | 1.2 mg |
Potassium | Heart health | 160 mg |
Calcium | Bone strength | 30 mg |
Chokeberry nutrition stands out because you get a fruit that is a source of micronutrients and rich in antioxidants. You can add chokeberry extract to your diet to boost your intake of these important nutrients.
Antioxidants in Chokeberry
Chokeberry is high in antioxidants. You find polyphenols, anthocyanins, and procyanidins in every berry. These compounds protect your cells from damage caused by free radicals. Chokeberry nutrition gives you high levels of antioxidants, which help lower your risk of chronic diseases.
You may wonder how chokeberry compares to other berries. The table below shows that chokeberry contains higher levels of polyphenols and anthocyanins than blueberries and cranberries.
Berry Type | Polyphenols Level | Anthocyanins Level |
|---|---|---|
Chokeberries | Higher | Significantly Higher |
Blueberries | Lower | Lower |
Cranberries | N/A | N/A |
Polyphenols in aronia berries help reduce inflammation and support your heart. Anthocyanins give chokeberry its deep color and strong antioxidant properties. Procyanidins also help protect your cells and may lower your risk of some cancers.
Chokeberry extract is rich in antioxidants and offers strong antioxidant properties. You can use chokeberry extract to get the benefits of these compounds. Many people choose chokeberry extract because it is a concentrated source of micronutrients and antioxidants.
Note: Chokeberry nutrition works best when you eat a good-sized handful each day. You can also consume 3-5 chokeberries three times a day to keep high flavonoid levels in your bloodstream.
Chokeberry nutrition gives you a fruit that is rich in antioxidants and a strong source of micronutrients. You get high in antioxidants, polyphenols, anthocyanins, and procyanidins. Chokeberry extract provides a convenient way to enjoy these benefits. You can use chokeberry extract in juices, smoothies, or supplements.
Health Benefits of Aronia Berries
Chokeberry gives you a wide range of health benefits. You get strong antioxidant properties from the high levels of polyphenols and anthocyanins. These beneficial antioxidants help your body fight free radicals and lower your risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions. The health benefits of aronia berries come from their unique mix of vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds.
Heart Health
You support your heart health when you add chokeberry to your diet. The antioxidants in chokeberry help protect your blood vessels and lower inflammation. You may see improvements in cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Chokeberry can help reduce your risk of heart disease and improve overall cardiovascular health.
Here is what clinical studies show about chokeberry and heart health:
Finding | Description |
|---|---|
Blood Pressure | Consumption of chokeberry products modestly lowered blood pressure in participants with untreated, mildly elevated BP. |
Lipid Profile | Improved lipid profile and flow-mediated dilatation in mildly hypercholesterolemic men. |
Inflammation | Reduced low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress in patients with metabolic syndrome. |
You also get anti-inflammatory effects from chokeberry extract. It can inhibit the activity of molecules that cause blood vessel inflammation. Chokeberry helps improve lipid balance, lowering total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides. These benefits help protect your heart and lower your risk of heart disease.
Finding | Description |
|---|---|
Anti-inflammatory Effect | Chokeberry extract inhibited TNFα stimulated transcription of adhesion molecules in human aortic endothelial cells. |
Monocyte Adhesion | Reduced adhesion of peripheral blood mononuclear leukocytes to the endothelium, a key factor in atherosclerosis. |
Lipid Balance | Improved lipid balance in individuals with metabolic syndrome, decreasing TAG, TC, and LDL levels. |
You may notice that chokeberry supplementation does not always show significant effects in every study. Some research found no major changes in blood pressure for people with type 2 diabetes after three months. However, other studies saw small reductions in systolic and diastolic blood pressure. You may benefit most if you have high cholesterol or mildly elevated blood pressure.
Chokeberry supplementation showed no significant effects on cardiometabolic outcomes overall.
Subgroup analysis indicated potential reductions in total cholesterol and LDL-C for individuals with baseline total plasma cholesterol <200 mg/dL.
Systolic blood pressure reductions were noted with interventions containing more than 50 mg/day anthocyanin.
You get heart health benefits from chokeberry, especially if you want to lower cholesterol or support your cardiovascular health.
Blood Sugar Control
Chokeberry helps you manage blood sugar levels. The strong antioxidant properties of chokeberry come from polyphenols and anthocyanins. These compounds help your body use insulin better and keep blood sugar stable. You may see improvements in fasting glucose and HbA1c if you have diabetes.
Study Type | Findings | Sample Size | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
Randomized Controlled Trial | Significant reductions in fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, and lipid profiles | 35 patients | 3 months |
Animal Studies | Improved insulin secretion and reduced blood glucose levels | N/A | N/A |
In Vitro/In Vivo Studies | Lower blood glucose levels, improved insulin sensitivity | N/A | N/A |
You may notice that daily consumption of chokeberry juice led to improvements in LDL-cholesterol and glycated hemoglobin levels in people with type 2 diabetes. The antioxidant capacity of chokeberries helps manage diabetes by lowering blood sugar and improving insulin sensitivity.
A study involving 35 type 2 diabetic patients showed that daily consumption of chokeberry juice led to improvements in various health parameters, including LDL-cholesterol and glycated hemoglobin levels.
The study evaluated the effects of chokeberry juice supplementation on type 2 diabetic patients over three months, showing significant health improvements.
The antioxidant capacity of chokeberries is attributed to their polyphenol content, which may aid in managing type 2 diabetes.
Some studies have shown reductions in LDL cholesterol and fasting blood glucose levels, although results are mixed.
Further research is needed to confirm chokeberry’s therapeutic effects on glucose metabolism.
Chokeberry extracts, especially those rich in anthocyanins, enhance insulin sensitivity by downregulating SOCS3, a negative regulator of insulin signaling. You get improved glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in insulin-resistant cells. These benefits help you manage blood sugar and lower your risk of diabetes complications.
Chokeberries, particularly their anthocyanin extracts (AMAE), enhance insulin sensitivity by downregulating SOCS3, a negative regulator of insulin signaling.
The extracts improve glucose uptake and glycogen synthesis in insulin-resistant cells, indicating their potential in managing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
The study shows that reducing SOCS3 levels significantly amplifies the insulin-sensitizing effects of AMAE.
Immune Support
You get immune support from chokeberry. The health benefits come from anthocyanins, proanthocyanidins, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. These compounds help your body fight viruses and boost your immune system. Chokeberry helps you stay healthy and may lower your risk of infections.
Compound Type | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
Anthocyanins | Show antiviral activity against influenza viruses by inhibiting virus replication and stimulating the immune system. |
Proanthocyanidins | Inhibit virus replication directly and indirectly, including blocking viral surface glycoproteins. |
Flavonoids and Phenolic Acids | Contribute to antioxidative activities and support immune modulation, potentially aiding in chronic disease prevention. |
Chokeberry also affects your immune cells. You get increased phagocytic activity in macrophages and higher production of nitric oxide and interleukin-1β in dendritic cells. Chokeberry helps increase the number of T and B lymphocytes, which protect you from illness.
Effect on Immune Cells | Description |
|---|---|
Macrophages | Altered proportions and increased phagocytic activity. |
Dendritic Cells | Up-regulation of nitric oxide and interleukin-1β production. |
T and B Lymphocytes | Increased proportions and differentiation of interferon-γ-producing T cells. |
You get immune support from chokeberry and its beneficial antioxidants. These benefits help you stay healthy and fight off infections.
Anticancer Effects
Chokeberry gives you anticancer effects because of its high phenolic content. The health benefits come from caffeic acid and chlorogenic acid, which help stop the growth of cancer cells. You get the most benefits from black chokeberry, which has the highest antioxidant activity.
Chokeberry Species | Growth Inhibitory Activity | Total Phenolic Content | Antioxidant Activity | Key Phenolic Acids |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Aronia arbutifolia (red) | Moderate | N/A | N/A | Caffeic acid, Chlorogenic acid |
Aronia prunifolia (purple) | Moderate | N/A | N/A | Caffeic acid, Chlorogenic acid |
Aronia melanocarpa (black) | Highest | Highest | Highest | Caffeic acid, Chlorogenic acid |
You may lower your risk of cancer by eating chokeberry. The strong antioxidant properties help protect your cells from damage. You get health benefits from the phenolic acids and antioxidants in chokeberry.
Gut Health
Chokeberry supports your gut health. You get health benefits from the way chokeberry changes your gut microbiome. Studies show that chokeberry increases the abundance of beneficial bacteria like Anaerostipes and Bacteroides. These changes help improve digestion and support your immune system.
Study | Findings | Microbial Genera Affected |
|---|---|---|
Istas et al. | Increased abundance of Anaerostipes (+10.6%) and Bacteroides (+193%) | Anaerostipes, Bacteroides |
Wu et al. | Modulation of microbial composition with increased Anaerostipes | Anaerostipes |
Yu et al. | Significant increase in Bacteroides richness | Bacteroides |
You get gut health benefits from chokeberry. The health benefits include better digestion, improved immune function, and a more diverse gut microbiome.
Tip: You can enjoy the health benefits of chokeberry by adding it to your daily meals. Try chokeberry juice, dried berries, or supplements for easy ways to boost your heart, immune system, and gut health.
How to Eat Chokeberry

Fresh and Dried
You can eat chokeberry fresh or dried. Fresh chokeberry gives you the highest anthocyanin content. Drying at high temperatures lowers the antioxidant levels by up to four times. Freeze-drying keeps more nutrients, with less than a two-fold decrease in anthocyanins. Dried chokeberry works well as a snack or topping for desserts. Many cultures use dried chokeberry in baked goods and jams.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
Dried Fruit | Chokeberries can be dried to create a snack or topping for desserts. |
Jam | A spread made from chokeberries, commonly used on bread or desserts. |
Baked Goods | Added to cakes, muffins, pies, and tarts for flavor. |
Tip: Choose fresh chokeberry for the most antioxidants. Use dried chokeberry for convenience and longer shelf life.
Juices and Supplements
Chokeberry juice is a popular way to enjoy the fruit. You find chokeberry juice in many cultures as a refreshing drink. Aronia juice is another name for this beverage. Chokeberry juice contains high levels of anthocyanins and polyphenols. You get strong antioxidant potential from chokeberry juice. Drinking chokeberry juice gives you a quick way to boost your intake of antioxidants.
Whole chokeberry fruit gives you more fiber, vitamins, and minerals. You feel fuller when you eat the whole fruit. Chokeberry juice lacks fiber and contains more free sugars. High intake of chokeberry juice can lead to weight gain and health risks like Type 2 diabetes and hypertension. Supplements made from chokeberry offer standardized active substances. You can choose chokeberry juice or supplements to fit your needs.
Form of Chokeberry | Antioxidant Potential | Key Compounds |
|---|---|---|
Juice | High | Anthocyanins, Polyphenols |
Supplements | Variable | Standardized Active Substances |
Juice
Jam
Syrup
Nutritional supplements
Recipe Ideas
You can use chokeberry in many recipes. Chokeberry preserves add flavor to breakfast. Chokeberry vinaigrette works well on salads. Chokeberry muffins make a tasty snack. Many people enjoy chokeberry syrup as a sweetener. You can add chokeberry juice to smoothies or mix it with honey for extra antioxidants. Adding chokeberry polyphenol honey to dishes increases antioxidant activity by up to eight times.
A simple preserves of aronia berries or chokeberries (Aronia melanocarpa) you can make that actually tastes good. This recipe helps the flavor by adding citrus zest and spices, and uses apple sauce for texture and natural pectin.
Chokeberry preserves
Chokeberry vinaigrette
Chokeberry muffins
Note: You can use chokeberry juice in recipes for extra flavor and nutrition. Try aronia juice in smoothies or baked goods.
Side Effects and Precautions
Digestive Issues
When you eat chokeberry, you may notice some digestive issues. These problems often appear if you eat large amounts. The most common side effects include:
Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
Constipation | Difficulty in bowel movements. |
Diarrhea | Frequent loose or watery stools. |
Nausea | Feeling of sickness with an urge to vomit. |
You might also feel stomach upset or bloating. Some people report both diarrhea and constipation after eating chokeberry. These symptoms usually go away when you reduce your intake. If you have a sensitive stomach, start with a small amount.
Tip: Drink plenty of water when you try chokeberry for the first time. This can help your digestion.
Allergies
Allergic reactions to chokeberry are rare, but they can happen. You should watch for signs like itching, swelling, or a rash after eating the fruit. If you have a known allergy to other berries, use caution. Some people may also feel mild headaches or dizziness. This can happen because chokeberry has a high level of flavonoids, which may affect sensitive individuals.
If you notice any allergic symptoms, stop eating chokeberry and talk to your doctor.
Who Should Avoid
You should avoid chokeberry if you have a history of berry allergies. People with chronic digestive problems, such as irritable bowel syndrome, may also want to limit their intake. Children and pregnant women can eat chokeberry in small amounts, but they should check with a healthcare provider first. If you take medication for blood pressure or blood sugar, ask your doctor before adding chokeberry to your diet.
Note: Always introduce new foods like chokeberry slowly. This helps you watch for any side effects.
Chokeberry gives you a rich supply of polyphenols, anthocyanins, and essential vitamins. You find potassium, calcium, iron, and zinc in every serving. The antioxidants in chokeberry help reduce inflammation and support your body’s defenses. You can enjoy chokeberry as juice, jelly, or mixed with other berries. Chokeberry may improve metabolic health and lower cholesterol. If you have a history of oxalate stones, limit your intake and drink plenty of water. Chokeberry offers a simple way to boost your nutrition.
FAQ
What is the best way to store chokeberries?
You should keep fresh chokeberries in the refrigerator. They stay good for up to one week. For longer storage, freeze them in airtight bags. Dried chokeberries last several months in a cool, dry place.
What nutrients do you get from chokeberries?
You get vitamin C, vitamin K, B vitamins, iron, zinc, magnesium, and potassium. Chokeberries also give you polyphenols and anthocyanins. These nutrients help your body fight stress and support your health.
What makes chokeberries different from other berries?
Chokeberries have more antioxidants than most berries. You get higher levels of polyphenols and anthocyanins. The taste is more tart and bitter compared to blueberries or strawberries.
What are common uses for chokeberries?
You can eat chokeberries fresh, dried, or in juice. Many people add them to jams, muffins, or smoothies. Some use chokeberry powder in yogurt or oatmeal for extra nutrition.
What side effects can you expect from eating chokeberries?
Most people eat chokeberries without problems. You might feel mild stomach upset, constipation, or diarrhea if you eat too many. Allergic reactions are rare. Start with a small amount to see how your body reacts.

