
Olives, a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet, boast a rich, ancient history. These versatile fruits have graced tables for millennia. Many different types of olives exist, each offering unique flavors and uses. Global olive production reached 2,743,216.64 tons in 2022-23, showing their widespread appeal. This blog explores the diverse olive varieties, their distinct flavor profiles, and their nutritional differences. Each variety possesses a unique taste profile. Understanding these different varieties and their unique flavor will enhance culinary experiences and health choices.
Key Takeaways
Olives change color and taste as they ripen; green olives are firm and tangy, while black olives are soft and mild.
Different olive types, like Manzanilla or Kalamata, have unique flavors and textures for various dishes and snacks.
Olives are good for your heart because they have healthy fats and special compounds that fight bad things in your body.
Olives give you important vitamins and minerals that help your body work well.
You can stuff olives with many things, like cheese or garlic, to make them taste even better for snacks or appetizers.
Green vs Black Olives: Ripeness and Taste

Ripening Process Explained
The primary factor differentiating green vs black olives is their ripeness. Olives begin as green fruits and gradually darken as they mature on the tree. This ripening process involves significant chemical changes. For instance, total phenolic compounds increase as the olive ripens. In some varieties, these substances can more than double from the green stage to fully ripened black. Anthocyanins, which are pigments, begin to accumulate during the later stages of ripening. These pigments give black olives their characteristic dark color. Concurrently, oleuropein content decreases due to increased enzymatic activity. This change contributes to a less bitter taste in ripe olives.
Different processing methods also play a crucial role in the final product. Spanish green olives, for example, are hand-picked when unripe. They undergo a lye bath to remove bitterness, then soak in a strong salt brine for fermentation. This process develops their tartness. Black ripe ‘Turning Colour’ olives, often called Californian style, are debittered with alkali lye and then darkened through oxidation. They are packed in brine and heat-sterilized. Kalamata style olives are placed directly into brine for natural fermentation. Dry Greek olives are ripe, soft olives. Workers gently smash them, layer them with salt for weeks, and then rinse them. They are often coated with olive oil before packing.
General Flavor and Texture
The ripeness level directly impacts the general flavor and texture of olives. Green olives are picked before they are fully ripe. They typically have a firmer texture. Their flavor is often tangy, with distinct briny or salty notes. This comes from their curing process. Black olives, harvested at full ripeness, have a softer texture. They offer a milder, richer, and often earthy or buttery flavor. They have less bitterness compared to their green counterparts. The curing process for both types enhances their unique characteristics. Green olives tend to have a lower oil content, while black olives generally have a higher oil content. This difference also contributes to their distinct flavor profiles.
Characteristic | Green Olives | Black Olives |
|---|---|---|
Ripeness | Picked before fully ripe | Harvested at full ripeness |
Texture | Firmer, dense | Softer |
Flavor | Tangy, often briny/salty | Milder, richer, earthy, buttery |
Bitterness | More bitter | Smoother flavor with less bitterness |
Popular Green Olive Varieties

Many green olive varieties offer distinct tastes and textures. These olives are picked before full ripeness. They provide unique culinary experiences. Understanding these different types enhances any Mediterranean meal.
Manzanilla Olives
Manzanilla olives are small to medium-sized. They are plump and meaty. Their shape features a rounded top and a flat base, without a nipple. Their flesh easily separates from the pit. These manzanilla olives have a balanced olive taste. They offer a fine, delicate flavor without strong bitterness or aftertaste. When brine-cured, they can have a slight almond, bitter, or smoky taste. They also carry nutty almond notes. Initially, these table olives show higher bitterness, crunchiness, hardness, and saltiness. These levels decrease during fermentation. People often stuff them. They are excellent in martinis, salads, and stews. They pair well with aged Swiss cheese or spicy sausage.
Picholine Olives
Picholine olives have a crisp, firm texture. They possess a distinct almond shape. Their flavor profile is mild and fruity. They also carry fragrant floral notes. These olives can taste tangy, salty, and subtly bitter. They offer an intense taste. Some describe their flavor as lemony, with a mild contrast of briny and buttery notes. Others find hazelnut, herbaceous, or a unique peppery touch. Their flesh is crunchy and firm.
Cerignola Olives
Cerignola olives are among the largest olives in the world. They are super-sized and plump. They come in green, red, and black colors. Green ones are the firmest. Black ones are the softest. These olives have a meaty, mild, and fruity flavor profile. They are also briny and buttery. They offer a meaty bite and a crisp texture. Their smooth, buttery flavor includes deep umami and a balanced saltiness. They have a savory taste. Some find an earthy taste with a perfect balance of saltiness and sweetness. This gives them a pleasingly piquant quality.
Castelvetrano Olives
Castelvetrano olives are known for their unique curing process. This process quickly removes bitter compounds. It also maintains their crispness and meaty texture. This method develops a buttery, mild olive flavor. Castelvetrano olives have a natural buttery and creamy taste. They feature mild brininess and a touch of natural sweetness. This contributes to their tender and crisp texture. They are sweet and mild, not bitter. They offer fruity and nutty notes, with subtle hints of apple and almond. Castelvetrano olives have a delicate sweetness and low salt content. This variety is irresistibly buttery.
Renowned Black Olive Varieties
Black olives offer a different experience from green ones. They are fully ripe when harvested. This gives them a softer texture and a richer taste. Many distinct black olive varieties exist, each with its own unique characteristics.
Kalamata Olives
Kalamata olives are famous for their plump, wrinkly appearance. They have a meaty texture. Workers often dry-cure them and then age them in brine. This process gives them an aromatic flavor. These Kalamata olives undergo a natural brine fermentation. This method uses only water and salt. It transforms the hard fruit into tender, savory table olives. This process takes about three months. After curing, producers often immerse Kalamata olives in wine vinegar or olive oil. This enhances their rich and meaty texture. Their flavor profile is intense and briny. It has a pleasant smoky finish. They offer a bold olive taste. Many describe their flavor as complex and intense. It can be tart and fruity, similar to red wine vinegar, with notes of smokiness. They are firm and have an oily texture, with fruity notes and a distinct tanginess.
Niçoise Olives
Niçoise olives come from the Mediterranean region. They have an intense black color. They possess a pleasantly bitter, nutty flavor. You can detect notes of almonds and hazelnuts. Niçoise olives are inherently salty and savory. This comes from their curing in a salt brine. Their flavor is complex. It features fruitiness with hints of prune and cherry. They have a slight bitterness without being sharp or acidic. The aroma of these olives can smell like ‘old wines and leather.’ This fruit-forward profile with bitterness complements peppery, lemony, and garlicky Mediterranean flavors. People enjoy them in Niçoise salad, Pissalidière, and Stockfisch. They also serve them as hors d’oeuvres or use them in olive tapenade.
Gaeta Olives
Gaeta olives are small and oval-shaped. They have dark purple flesh. They often appear wrinkled and dark brown to black in color. These olives have a meaty texture. They combine a pleasant blend of tart and salty notes. Their flavor is slightly salty and intensely earthy. It includes a hint of bitterness. Gaeta olives have soft, tender flesh. They are creamy, plump, and extremely complex in taste.
Mission Olives
Mission olives hold historical significance in California. Spanish missions along El Camino Real developed this olive variety in the late 18th century. It is the only American olive cultivar listed by the International Olive Council. Franciscan missionaries first brought olive trees to California. The ‘Mission’ olive is likely the first olive tree in California. It originated from seeds transported from South America. When cured using traditional methods, Mission olives possess a fruity, more buttery flavor. This represents the “True Taste of California olive oil.” Some American producers developed a unique process for Mission olives. This process removes any trace of flavor. This makes them suitable for children’s food or decorative purposes.
Other Notable Types of Olives
This section explores additional olive varieties. These types of olives do not always fit neatly into green or black categories. They are also less common but still important. They offer unique characteristics and culinary uses.
Arbequina Olives
Arbequina olives are small with a soft texture. They have a delicate, buttery flavor. Harvesters often pick them early. This gives them a pale green or brownish color. They also have a subtle, fruity aroma. Their flavor profile includes mild saltiness and a creamy bite. They offer notes of almond and apple. They have low bitterness and balanced acidity. These characteristics make them versatile for both snacking and cooking. When pressed, they produce a golden extra virgin olive oil. This oil has a sweet, grassy aroma and a smooth finish. Arbequina olives offer a pleasingly fruity and buttery taste. They have a firm and meaty texture, despite their small size. They pair well with tangy goat cheese or feta. They also go well with dried figs, pears, and almonds. This olive variety is popular as both an oil variety and table olives.
Gordal Olives
Gordal olives are known for their generous size. They have a juicy texture and exceptional flavor. People recognize them for their large size and meaty, juicy texture. Many describe them as having a buttery richness. Their name means ‘the fat one.’ This refers to their significantly larger size compared to average olives. Gordal olives are large, plump olives with firm flesh and a meaty bite. They have a mild, slightly sweet flavor. They also offer a juicy, crisp texture. They provide a clean, refreshing taste with a buttery finish. This is unlike some overly briny or sharp green olives. They have a fine and delicate flavor, similar to Manzanilla olives. They possess a firm, crunchy, meaty texture.
Sevillano Olives
Sevillano olives are large and oval-shaped. They ripen to a green or purple-black color. They are highly valued for both table use and oil production. The fruit is large and meaty. This makes it ideal for stuffing, brining, or as a standalone snack. When processed into oil, Sevillano olives produce a rich, robust flavor. This enhances many culinary creations. These include dressings and marinades. The Sevillano olive is prized for its large size and balanced flavor profile. It features a mild fruity taste with a hint of bitterness and peppery notes. These olive varieties are plump and crisp green. They have meaty flesh and a smooth, buttery, briny bite. Their size ranges from extra-large to colossal. Their color ranges from grassy to straw-green. They taste tart, bright, and briny with a buttery, smooth presence. They are ideal for stuffing with ingredients like cheese, garlic, nuts, and peppers. This is due to their texture and easy pitting. They pair well with tangy cheeses like feta or goat cheese. They often appear on charcuterie platters and in dirty martinis.
Flavor Profiles and Culinary Uses
Olives offer a wide range of flavor profiles. These profiles depend on the olive variety, its ripeness, and its curing method. Understanding these distinct flavor profiles helps people choose the best olives for different recipes and culinary applications.
Briny and Salty Olives
Many olives are known for their distinct briny and salty flavor. This taste often comes from their curing process in salt brine. Kalamata olives, for example, have an intense, briny flavor with a smoky finish. Gaeta olives also offer a deeply briny taste with an earthy base note. Sevillano olives are large and round. They are salt-brine cured with lemon and bay leaf. They have a briny, nutty flavor. Spanish olives, which are large, light, and meaty, are also salt-brine cured. They have a light, meaty flavor. These olives pair well with strong cheeses like Feta or Goat Cheese. They also complement dry Spanish Cava or Fino wines.
Buttery and Mild Olives
Some olives provide a smooth, buttery, and mild flavor. These olives often have a less intense saltiness. Lucque olives are buttery and not overtly salty. Cerignola olives are large and plump. They offer a buttery and sweet flavor. Castelvetrano olives also have a buttery and sweet flavor with a crisp texture. They feature hints of apple and almond. These olives are excellent with hard cheeses like Parmigiano-Reggiano or soft cheeses such as burrata. They also pair well with aperitivo cocktails or sparkling wines like Prosecco. Crisp white wines, such as Pinot Grigio, also complement their mild profile.
Fruity and Sweet Olives
Certain olive varieties present a fruity and sweet flavor. This sweetness often balances their natural brininess. Alfonso olives are extra-juicy, plump, and sweet upfront. They have a fruit-forward profile. Cerignola and Castelvetrano olives, as mentioned, also exhibit sweet and buttery notes. Liguria olives are small and black. They are brine-cured with bay leaves, rosemary, and thyme. They have a vibrantly flavorful profile. These olives pair well with robust red wines. They also complement mild cheeses like Brie or fresh Mozzarella. Chardonnay and Pinot Noir wines are good choices with these fruity olives.
Pungent and Bitter Olives
Other olives are characterized by a pungent or slightly bitter flavor. This bitterness adds complexity and depth. Kalamata olives, while briny, also have a slightly bitter and aromatic flavor. Nyon olives are tiny and black with prune-like skin. They are dry-cured and aged in brine. They have a slightly bitter flavor. Niçoise olives are brown or black. They are brine-cured and packed in olive oil. They have a licorice-like flavor with a pleasant bitterness. Oil-cured olives, such as Moroccan black olives, are super pungent and wrinkly. They have concentrated sugars. These olives pair well with herbs like rosemary and thyme. They also complement fragrant, spiced tagines or tuna in a Salade Niçoise.
Best for Snacking and Appetizers
Many olives are perfect for snacking and serving as appetizers. Their diverse flavor and texture make them popular choices.
Castelvetrano Olives: These olives are known for their bright green skins and buttery flesh. They have a meaty and juicy texture. Their bright nutty green flavor and creamy flesh offer hints of lemony brightness. People consider them delectable and palatable. They are excellent for charcuterie boards and snacking.
Bella di Cerignola Olives: These olives have rich, tender flesh and smooth, taut skins. Their elongated shape and eye-catching chartreuse color make them a must-have for entertaining. They are a fun new olive to try for snacking.
Manzanilla Olives: Especially those with pimiento, Manzanilla olives have a smoky, sweet flavor that complements their saltiness. Their firm texture holds its shape well. This makes them ideal for snacking.
Great Value Stuffed Jalapeño Green Olives: These flashy green olives are incredibly tasty. They offer a fun change of pace for those who enjoy a little spice in their snacking.
These varieties provide a delightful experience for casual snacking or elegant appetizer spreads.
Best for Cooking and Salads
Olives also play a vital role in cooking and salads, especially in Mediterranean cuisine. Their unique characteristics enhance many dishes.
Olive Variety | Characteristics (Flavor/Texture) | Applications (Cooking/Salads) | Advantages for Use |
|---|---|---|---|
Cerignola (Bella di Cerignola) | Mild, sweet, buttery flavor; firm (green) to softer (black) texture. | Salads, pasta dishes, fish dishes, chicken entrees. | Versatile for various cooked dishes and salads due to mild flavor and adaptable texture. |
Gaeta | Tart, salty flavor; soft texture. | Salads, pasta dishes, pizzas, antipasto platters. | Enhances flavor in Mediterranean and Italian cuisine; pairs well with bold ingredients. |
Picholine | Tangy, slightly salty with subtle fruity undertone; crisp, firm texture. | Salads, pasta dishes, tapenades. | Ideal for snacking or adding to salads and pasta due to crisp texture and complex flavor. |
Queen (Sevillano, Gordal) | Briny, nutty flavor; firm, meaty texture. | Tapenades, antipasto platters, mezze spreads. | Meaty texture and robust flavor make them suitable for spreads and appetizers. |
Kalamata | Rich, meaty flavor; soft texture. | Salads, pizzas, tapenade. | Classic choice for salads and pizzas due to distinctive rich flavor. |
Castelvetrano (Nocellara del Belice) | Mild, buttery flavor with hints of sweetness and nuttiness; firm bite. | Chicken dishes, fish dishes, tapas, charcuterie. | Mild flavor and meaty texture complement poultry and fish without overpowering. |
Nicoise | Intensely sour, briny, pleasantly bitter flavor. | Salade Nicoise. | A staple for the classic French Salade Nicoise, offering a distinct bitter and briny profile. |
Mission | Mild yet peppery flavor. | Pizzas, sandwiches, salads. | Popular for salads and as a topping due to its mild, peppery taste. |
Calabrese (Oliva Schiacciate) | Slightly bitter flavor balanced by pleasant fruit and nut undertones; firm, meaty texture. | Antipasto platters, salads, pasta dishes, pizzas. | Adds depth and complexity to Italian dishes, suitable for various cooked and fresh applications. |
These olives bring unique tastes and textures to many Mediterranean dishes. They are essential ingredients for enhancing the overall flavor of a meal.
Nutritional Differences and Benefits
Olives offer more than just flavor; they also provide significant nutritional value. Their composition varies based on ripeness and processing. Understanding these differences helps people make informed dietary choices.
Green vs Black Olives Nutrition
Green and black olives show distinct nutritional profiles. These differences primarily stem from their ripeness at harvest and their curing methods.
Nutrient | Green Olives | Black Olives |
|---|---|---|
Fat | Higher | Lower |
Carbohydrates | Higher | Lower |
Fiber | Higher | Lower |
Sodium | About two times higher | Lower |
Calcium | Lower | Higher |
Iron | Lower | Higher |
Calories | Very similar to black olives | Very similar to green olives |
Protein | Very similar to black olives | Very similar to green olives |
Vitamin E | Good source | Good source |
Antioxidants | Good source | Good source |
Copper | Good source | Good source |
Green olives generally contain higher amounts of fat, carbohydrates, and fiber. They also have about twice the sodium compared to black olives. This higher sodium content often results from their curing process, especially for brine-cured varieties. Black olives, on the other hand, typically contain more calcium and iron. Both types offer similar calorie and protein levels. They both serve as good sources of Vitamin E, antioxidants, and copper. While green olives might have a slightly lower calorie count, black olives often show a slightly higher fat content. This fat primarily consists of heart-healthy monounsaturated fats.
Antioxidant Power
Olives are rich in powerful antioxidants. These compounds contribute significantly to their many health benefits. Olive polyphenols are responsible for various recognized pharmacological properties. These include anti-atherogenic, antihepatotoxic, hypoglycemic, anti-inflammatory, antitumoral, antiviral, analgesic, purgative, and immunomodulatory activities. They also offer protection against neurodegeneration associated with aging.
Specific phenolic compounds found in olives and extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) include:
Oleuropein: This is the most abundant antioxidant in fresh, unripe olives. Researchers link it to many health benefits.
Hydroxytyrosol: This powerful antioxidant forms during olive ripening.
Tyrosol: Prevalent in olive oil, it may have anti-cancer effects.
Oleanolic acid: This compound may help prevent liver damage and reduce inflammation.
Quercetin: This antioxidant may lower blood pressure and improve heart health.
These molecules demonstrate antimicrobial, hypoglycemic, vasodilator, antihypertensive, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. The presence of these compounds makes olives a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Healthy Fats and Heart Health
Olives are an excellent source of healthy fats. These fats are crucial for maintaining good heart health. They contain unsaturated fats, including both monounsaturated and polyunsaturated types. These fats are typically liquid at room temperature. When people consume them in moderation and use them in place of saturated and trans fats, they can help improve blood cholesterol levels. This action reduces the risk of heart disease.
Monounsaturated fats, abundant in olives, remain liquid at room temperature. They become semi-solid or cloudy when refrigerated. Substituting these fats for saturated fats can significantly improve blood cholesterol levels. This contributes to better cardiovascular health. Olives also contain beneficial properties like vitamin E and other antioxidants. These compounds further protect against heart disease. Extra-virgin olive oil, a product of olives, also contains polyphenols. These antioxidants are strongly linked to heart health. Incorporating olives into a mediterranean diet supports overall cardiovascular well-being.
Vitamins and Minerals
Olives provide a range of essential vitamins and minerals. These nutrients play vital roles in various physiological processes within the body.
Table olives contain alpha-tocopherol (α-TOH), a form of Vitamin E, ranging from 1.3 to 9 mg/100 g edible portion. They also contain beta-carotene, a precursor to Vitamin A, with values from 0.04 to 0.26 mg/100 g edible portion. The overall mineral content in table olives varies from 2.0 to 6.9 g/100 g edible portion. Green olives, such as Gordal, Manzanilla, Hojiblanca, and Verdial varieties, have mineral content between 4.2 and 5.5 g/100 g edible portion. Hojiblanca ripe olives contain 2.0 g/100 g edible portion, while Hojiblanca naturally black olives have 6.9 g/100 g edible portion.
Sodium content can be notably high in some preparations due to processing methods. Italian table olives report values of ≥1.5 g/100 g edible portion for sodium and ≥3.75 g/100 g edible portion for salt. Conversely, table olives have a very low potassium level, contributing minimally to the recommended daily intake.
Olives contain several essential trace elements. Iron (Fe), zinc (Zn), manganese (Mn), and copper (Cu) are identified as crucial nutrients for humans. They are integral components of numerous enzyme systems. They play vital roles in various physiological processes within the body.
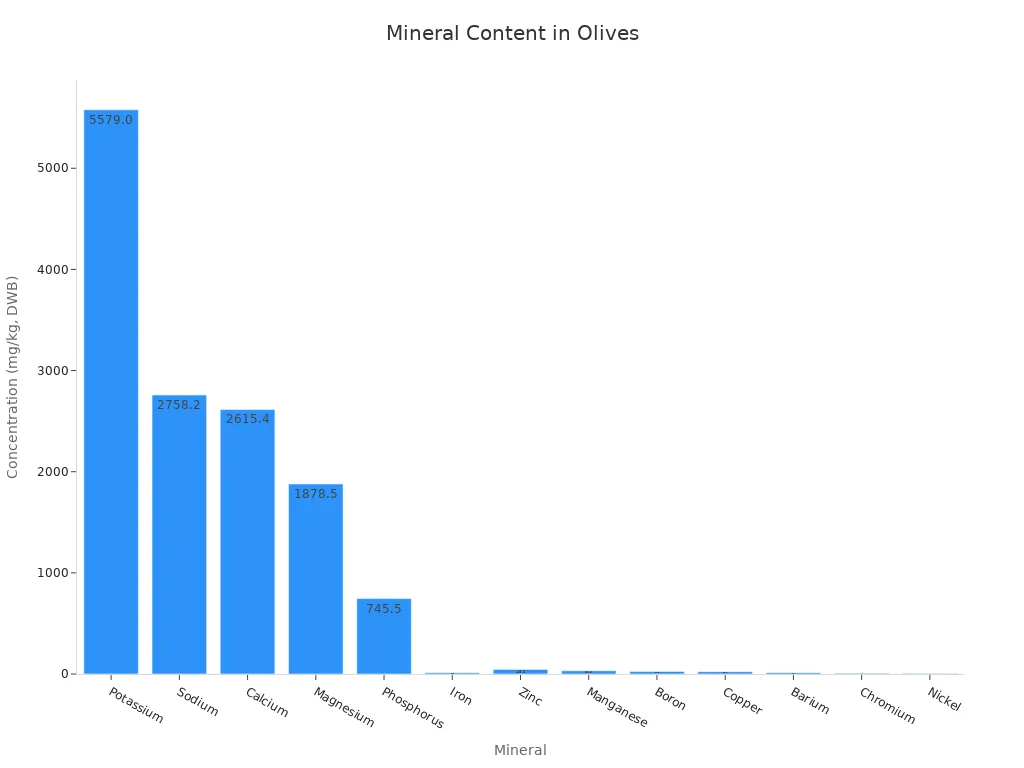
This chart illustrates the concentration of various minerals in olives. Potassium shows the highest concentration, followed by sodium and calcium. Olives also contain B group vitamins, provitamin A, and vitamin E, though in low amounts. Vitamin E is particularly noted for its significant antioxidant effects. The vitamin C content is generally low, but enrichment with ascorbic acid can increase it. While vitamin C may decrease during shelf life, consuming olives closer to their production date can make them a source of this vitamin. These vitamins and minerals contribute to the overall health benefits of olives. They support various bodily functions and contribute to the reputation of the mediterranean diet for promoting long-term health benefits.
Stuffed Olives
People enjoy olives in many ways. Stuffed olives offer a delightful twist. They combine the olive’s natural taste with various fillings. This creates new and exciting flavor experiences. Stuffing olives adds complexity and texture. It makes them perfect for snacks or appetizers.
Common Fillings
Many ingredients can fill olives. Cheeses are very popular. People often use crumbled Gorgonzola cheese or softened cream cheese. Other cheese options include blue cheese, Brie, Boursin (especially with garlic or shallots), and goat cheese. Some people prefer a spicy kick. They might use chili powder or cayenne. Pimento cheese also works as an alternative filling. For a savory flavor, anchovies are a classic choice. Garlic, either roasted cloves or minced, adds a strong aroma. Fresh herbs like thyme, oregano, dill, or basil bring freshness. Some fillings offer a richer texture. These include smoked salmon, crab meat, or various nuts like almonds. Lemon zest can add a bright, citrusy note.
Popular Combinations
Creative combinations enhance the olive’s natural flavor. Feta cheese and blue cheese are popular choices. Garlic and jalapeño create a spicy and pungent flavor. Pimento is a traditional filling. The “Rocket” combination features both jalapeño and garlic. For creamy options, Boursin cheese mixed with a little cream works well. Cream cheese blended with jalapeño or other flavored spreads also provides a smooth texture. Anchovy paste gives a savory kick. Olive or tomato tapenade adds a Mediterranean flair. Harissa combined with mayo offers a spicy and creamy option. Some unique combinations include spicy cheddar olives, which blend cream cheese, shredded cheddar, Dijon mustard, and cayenne pepper. Sweet and savory blueberry olives use blueberry goat cheese, cream cheese, and dried basil. Creamy tomato olives combine cream cheese, Gorgonzola cheese, and sun-dried tomato pesto. Each combination offers a distinct flavor profile.
This exploration reveals the vast diversity among types of olives. Each variety offers a unique flavor profile and distinct nutritional benefits. From briny Manzanillas to buttery Castelvetranos, different types of olives provide a rich culinary experience. Their varied flavor profiles enhance many dishes. Understanding each olive’s specific flavor helps in culinary choices. Olives contribute healthy fats, antioxidants, and essential vitamins to the Mediterranean diet. Readers should explore and experiment with these diverse fruits. They bring rich culinary heritage and significant health advantages to our tables.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between green and black olives?
The main difference lies in their ripeness. Green olives are picked before they fully ripen. They have a firmer texture and a tangy, often briny flavor. Black olives are harvested when fully ripe. They offer a softer texture and a milder, richer, or buttery taste. 🫒
What makes Kalamata olives distinct from other black olives?
Kalamata olives are known for their plump, wrinkly appearance and meaty texture. They undergo a natural brine fermentation. This process gives them an intense, aromatic flavor with a slightly bitter and smoky finish. They often have a complex, tart, and fruity taste.
What are Castelvetrano olives known for?
Castelvetrano olives are famous for their bright green color and buttery, mild flavor. Their unique curing process quickly removes bitterness. This method maintains their crisp, meaty texture. They offer a delicate sweetness and low salt content, with hints of apple and almond. 🍏
What nutritional benefits do olives provide?
Olives are a good source of healthy monounsaturated fats, which support heart health. They also contain powerful antioxidants like oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol. These compounds offer anti-inflammatory and protective properties. Olives provide Vitamin E, copper, and iron. 💪
What is the purpose of stuffing olives?
Stuffing olives enhances their flavor and texture. It creates new and exciting culinary experiences. Fillings like cheese, garlic, or pimento add complexity. This makes stuffed olives perfect for snacks, appetizers, or as a garnish in cocktails. 🍸

