
For years, people feared fat, often due to beliefs not rooted in science. This old view ignored fat’s vital role in your diet. On a ketogenic diet, or any low carb diet, you need quality fat for sustained energy. A keto diet uses fat as its main fuel. Not all fats are equal. Choosing the right healthy fats helps your body thrive. These fats provide steady energy, boost satiety, and support your overall health on a low-carb lifestyle. Your body relies on these fats for energy when your carb intake is low. For keto and low carb diets, selecting proper fat sources is essential for your low carb journey. This ketogenic diet demands low carb fat sources.
Key Takeaways
Healthy fats are very important for a keto diet. They give your body steady energy when you eat few carbs.
Good fat sources include avocados, nuts, seeds, full-fat dairy, pasture-raised meats, and fatty fish. These foods help you feel full and support your health.
You should avoid processed vegetable oils and trans fats. These fats can harm your body and cause health problems.
Balance your fat intake to match your energy needs. This helps you stay in ketosis and manage your weight.
Why Healthy Fats are Key for Keto
Healthy fats are vital for your success on a ketogenic diet. When you follow a low carb diet, your body changes how it gets energy. This shift makes healthy fats your primary fuel source.
Fueling with Ketones
Your body needs energy every day. On a ketogenic diet, you severely restrict carb intake. You typically limit daily carb consumption to about 20–50 grams. This low carb approach forces your body to transition into ketosis. In ketosis, your body uses fat for energy instead of glucose. Dietary fats, or triglycerides, first break down into fatty acids. This happens through a process called lipolysis. These fatty acids then undergo beta-oxidation, producing acetyl CoA. When there is too much acetyl CoA, your body starts ketogenesis. During ketogenesis, acetyl CoA converts into ketone bodies, like beta-hydroxybutyrate. These ketone bodies then provide energy for your brain and body. This process ensures you have steady energy even with low carb intake.
Boosting Satiety
Healthy fats play a big role in how full you feel. They help reduce cravings, which aids in weight management. When you consume fats, especially unsaturated fatty acids, your body releases hormones. For example, unsaturated fatty acids significantly increase cholecystokinin (CCK) secretion. This hormone makes you feel full and reduces hunger. Studies show that a keto diet can diminish hunger and reduce your desire to eat. High levels of ketosis, indicated by BHB levels, strongly link to fewer food cravings. This means a keto diet helps you feel satisfied longer.
Supporting Overall Health
Beyond energy and satiety, healthy fats support your overall health. They are crucial for absorbing fat-soluble vitamins. Vitamins A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble. Your body needs dietary fat to absorb these vitamins into your bloodstream. Without enough fat, you cannot properly use these essential nutrients. Fats also serve as building blocks for hormones. Hormones influence many body functions. Omega-3 fatty acids, for instance, can improve lipid and hormonal profiles. They can also help regulate blood glucose. This shows the deep connection between healthy fats and your body’s complex systems. A well-formulated keto diet provides these vital fats for your health.
Top Healthy Fat Sources

You need to choose your fat sources wisely on a ketogenic diet. A typical ketogenic diet consists of 60-80% fat. Here are some of the best healthy sources of fat to fuel your keto diet.
Avocados and Oils
Avocados are excellent healthy fats. They offer many nutrients. A 1/3 medium (50g) serving of avocado provides 80 calories. It also gives you 20 different nutrients.
Nutrient | Amount per 1/3 medium (50g) serving |
|---|---|
Calories | 80 |
Total Fat | 8g (10% DV) |
Saturated Fat | 1g (5% DV) |
Monounsaturated Fat | 5g |
Polyunsaturated Fat | 1g |
Cholesterol | 0mg (0% DV) |
Sodium | 0mg (0% DV) |
Total Carbohydrate | 4g (1% DV) |
Dietary Fiber | 3g (11% DV) |
Total Sugars | 0g |
Protein | 1g |
Vitamin D | 0mcg (0% DV) |
Calcium | 10mg (0% DV) |
Iron | 0.3mg (2% DV) |
Potassium | 250mg (6% DV) |
Vitamin C | 4mg (4% DV) |
Vitamin E | 1mg (6% DV) |
Vitamin K | 11mcg (10% DV) |
Folate | 45mcg DFE (10% DV) |
Magnesium | 15mg (4% DV) |
Copper | 0.1mg (10% DV) |
You also find monounsaturated fats in olive oil. These heart-healthy fats help lower LDL (‘bad’) cholesterol. This reduces your risk of heart disease and stroke. Monounsaturated fats also help your cells develop and stay healthy. They can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce inflammation.
Coconut oil and ghee are other great oils for your keto diet. Unrefined coconut oil has a smoke point of 350°F (177°C). You can use it for baking and low-heat cooking. It adds a coconut taste to your food. Refined coconut oil has a higher smoke point of 450°F (232°C). You can use it for higher heat cooking. It is flavorless. Ghee has a smoke point of 482°F. This makes it ideal for high-heat cooking like frying. Ghee is pure and tastes buttery. You can add it to drinks or brush it on vegetables.
Nuts and Seeds
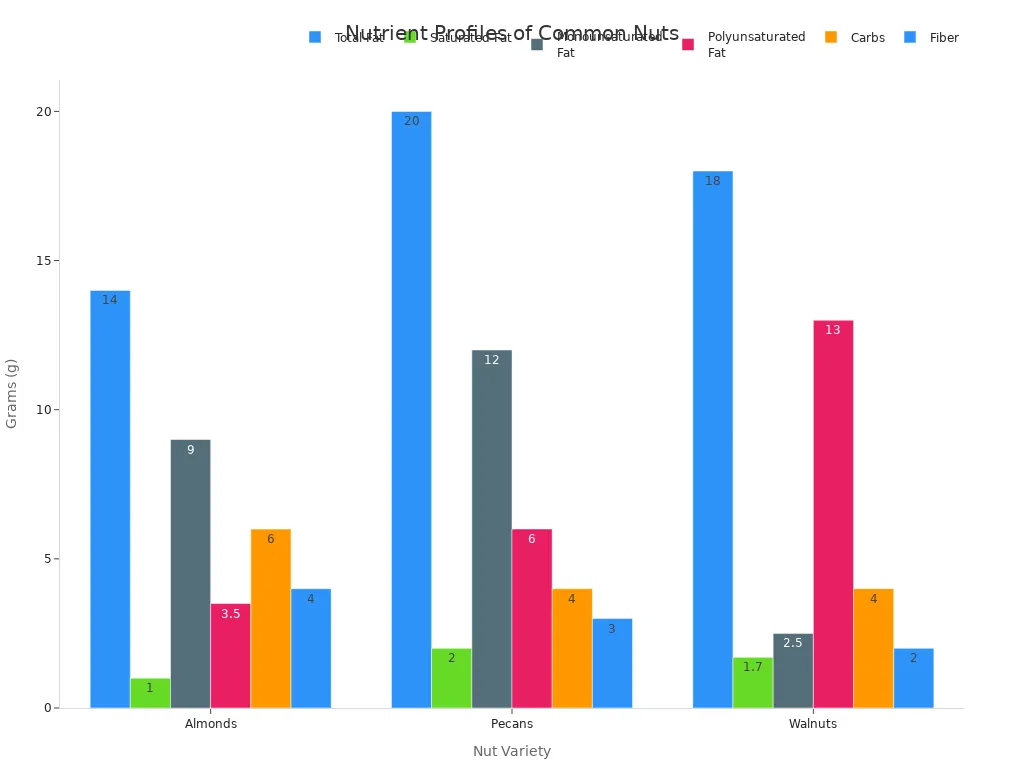
Nuts and seeds are perfect for a low carb diet. They are high in fat and low in carb content. You can enjoy pistachios, walnuts, almonds, pecans, cashews, and Brazil nuts. Many seeds like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and pumpkin seeds also fit your keto diet.
Nuts are rich in fats. Pecans are about 72% fat. Almonds are about 50% fat. Both have mostly unsaturated fats. Pecans have more polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. They are richer in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Walnuts also offer many healthy fats.
Nut | Total SFA (g/100g) | Palmitic 16:0 (g/100g) | Stearic 18:0 (g/100g) | Total MUFA (g/100g) | Oleic 18:1 (g/100g) | Total PUFA (g/100g) | Linoleic 18:2 (g/100g) | Linolenic 18:3 (g/100g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Almond | 3.802 | 3.083 | 0.704 | 31.551 | 31.294 | 12.329 | 12.324 | 0.003 |
Walnut | 6.126 | 4.404 | 1.659 | 8.933 | 8.799 | 47.174 | 38.093 | 9.080 |
Almonds have a good fatty acid profile. They contain 60% monounsaturated and 30% polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Polyunsaturated fats, including omega-3 and omega-6 fats, are essential. Your body cannot make them. They are vital for brain function and cell growth. Omega-3 fatty acids benefit your heart. They reduce triglycerides and lower the risk of irregular heartbeat. Omega-6 fatty acids help control blood sugar. They reduce the risk of diabetes and lower blood pressure. Linoleic acid is a major polyunsaturated fat in many seeds and nuts. It links to a lower risk of chronic diseases. These include cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
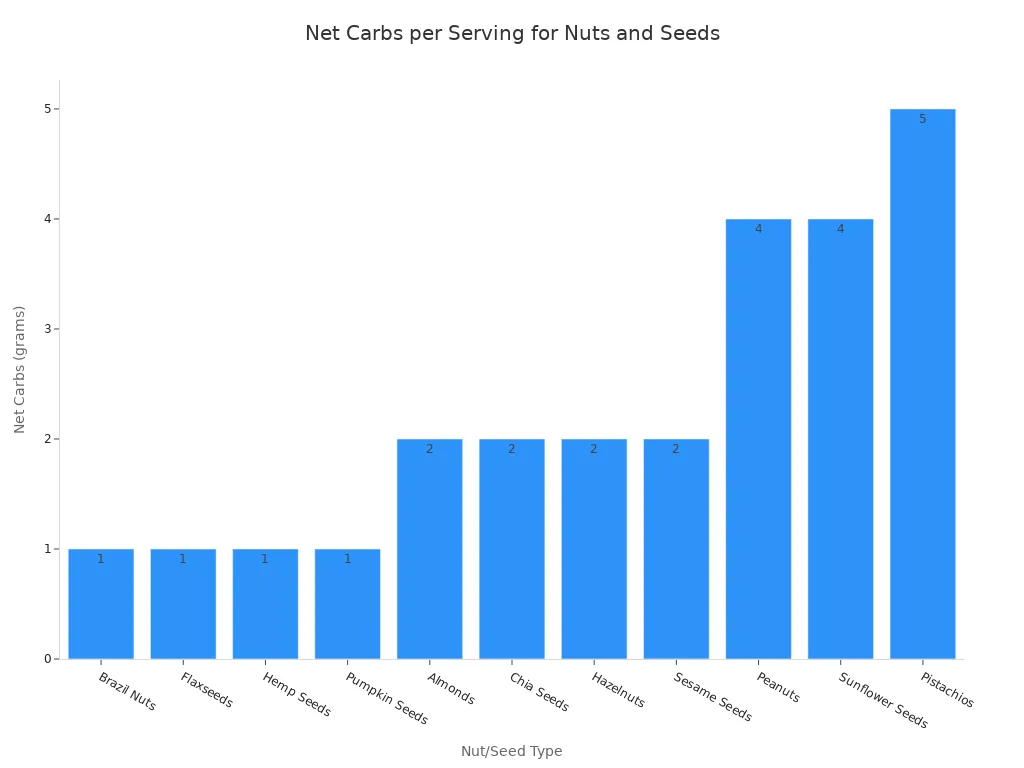
You need to watch your portion sizes for nuts and seeds. This helps you stay in ketosis. A serving size is about 1-2 ounces. This is a small handful. For example, 24 almonds or 15 pecan halves make one serving.
Here is a look at net carb content for various nuts and seeds:
Dairy and Animal Fats
Full-fat dairy options are great for your keto diet. These include full-fat Greek yogurt, heavy cream, and cheese. Some older beliefs suggested low-fat dairy was better. However, recent science challenges this. High-fat dairy may not cause obesity or diabetes. It might even help prevent them. Specific fatty acids in dairy fat can improve insulin sensitivity. They can reduce the risk of type II diabetes.
Pasture-raised meats are another excellent source of fat. These meats offer a better fatty acid profile. This is because the animals eat more forage. Pasture-raised chicken meat has higher omega-3s. It has a lower omega-6:3 ratio. It also contains more antioxidants like Vitamin E. Pasture-raised eggs also have more omega-3s and Vitamin D. Grass-fed beef has more beneficial fats. It has more anti-inflammatory omega-3 fats. It also has more antioxidants and Vitamin K2. Pasture-raised pigs have higher levels of Omega-3 fats. They also have more micronutrients. These include Vitamin E, iron, and zinc.
Fatty Fish
Fatty fish are crucial for your keto diet. They provide essential omega-3 fatty acids. Salmon and mackerel are top choices. Mackerel offers 4,580 mg of EPA and DHA combined per 3.5 oz serving. Salmon provides 2,150 mg of EPA and DHA combined.
Fish | Omega-3 Content (mg per 3.5 oz/100g serving) |
|---|---|
Mackerel | 4,580 mg (EPA and DHA combined) |
Salmon | 2,150 mg (EPA and DHA combined) |
Omega-3 fatty acids offer many health benefits. They can lower your risk for cardiovascular disease. They reduce inflammation. They also help prevent certain cancers. Omega-3s are good for your brain function. They improve memory. They can also reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. These fats are vital for your overall well-being. You should aim to eat fish often. Some keto and low carb diets suggest eating fish at least four days a week.
Fats to Limit or Avoid
While healthy fats are crucial for your keto diet, some fats can harm your health. You should limit or completely avoid these fats.
Processed Vegetable Oils
Processed vegetable oils are a major concern. These include soybean, corn, sunflower, and canola oils. Repeated heating of these oils at high temperatures, like 160–190 °C, causes harmful changes. This process creates oxidized and polymerized lipid species. These can lead to mutagenicity and genotoxicity. Consuming repeatedly heated oils increases your risk of various cancers, including colorectal and gastrointestinal tract cancers. This happens partly due to the formation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Studies show these oils can alter blood levels, increase oxidative stress, and cause genotoxic changes. These oils also contain a very high omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, sometimes as high as 15:1 or even 20:1. This imbalance promotes inflammation. Polyunsaturated fats in these oils are prone to oxidation, forming harmful free radicals that damage cells. When these fats enter cell membranes, they make the membranes more sensitive to oxidation.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are another type of fat you must avoid. The processed food industry creates the largest amount of trans fat through partial hydrogenation of vegetable oils. You find these partially hydrogenated fats in many products. These include fast food, snack food, fried food, baked goods, shortenings, breads, cake products, cookies, crackers, salty snacks, cake frostings, sweets, and margarine. High intake of trans fats links to chronic diseases. These include heart disease, obesity, cancer, and diabetes. Trans fats increase your LDL (“bad” cholesterol) and decrease your HDL (“good” cholesterol). This promotes atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease. Trans fats are responsible for many premature coronary deaths each year. They also link to a 50% greater risk of colon cancer and an increased risk of Type-II diabetes. Research suggests trans fats can increase weight gain and abdominal fat deposits. Women with high levels of trans fatty acids have double the risk of developing breast cancer.
Certain Saturated Fats
The scientific view on saturated fats has changed. Many studies now show they generally have no effect on cardiovascular disease or total mortality. However, you should still be mindful of certain sources. Dr. Walter Willett from Harvard suggests you prioritize unsaturated fats over saturated fats. This advice comes from limited long-term studies on keto diets. It also reflects the general benefit of emphasizing unsaturated fats. You should moderate your intake of fatty cuts of meat, processed meats, lard, and butter. While not all saturated fat is bad, focusing on quality fat sources remains important for your health.
Incorporating Healthy Fats for Keto

You understand the importance of healthy fats for your ketogenic diet. Now, you need to know how to effectively include them in your daily routine. This section guides you on balancing your fat intake, choosing the right cooking fats, and selecting smart snacks for your keto diet.
Balancing Fat Intake
Achieving the right balance of fat is crucial for your ketogenic diet. For a ketogenic diet, your fat intake should typically range from 60 to 80 percent of your total daily calories. This high fat percentage helps you maintain ketosis. It also provides sustained energy. Some experts suggest a range of 70 to 80 percent. This ensures your body uses fat for fuel instead of carbs. You must prioritize quality fat sources for optimal health.
Cooking with Fats
Choosing the right fats for cooking is important on a keto diet. Different fats suit different cooking methods. For high-heat cooking, you need stable fats.
Avocado Oil: This oil has a high smoke point, around 500°F (260°C). It is excellent for high-heat cooking like frying or sautéing. Its neutral flavor makes it versatile.
Ghee: Clarified butter, ghee, has a smoke point of 400°F. It is suitable for high-heat cooking and adds a rich, buttery taste.
Coconut Oil: This oil is stable for medium-heat cooking. It provides a distinct coconut flavor.
Beef Tallow and Lard: These stable cooking oils withstand high temperatures. They are ideal for sautéing, frying, and roasting.
Olive Oil: You can use olive oil for high temperatures. Its antioxidants protect the fats from oxidizing.
These fats help you prepare delicious, low-carb meals. They also support your energy needs.
Smart Snacking
Snacking can be tricky on a low-carb diet. You need options rich in healthy fats and low in carbs. Smart snacking helps you stay in ketosis and keeps your energy levels stable.
Avocado with Sea Salt: This snack is high in fats and fiber.
String Cheese or Cheese Sticks: These provide protein and fats.
Hard-Boiled Eggs: They offer protein and healthy fats from the yolk.
Almonds or Mixed Nuts: These give you healthy fats and protein.
Fat Bombs: These are low-carb energy bites. They often contain coconut oil, nut butter, or cream cheese.
Olives: They are packed with healthy fats.
Macadamia Nuts: These nuts have the highest amount of fat in the nut family. They contain less than 4g carbs per ounce.
These snacks help you manage hunger between meals. They also keep you on track with your keto diet goals.
Embracing healthy fats transforms your ketogenic diet. You gain sustained energy, improved health, and lasting satiety. We explored top fat sources: avocados and oils, nuts and seeds, dairy and animal fats, and fatty fish. These provide essential fats for your low carb lifestyle. Experiment with these low carb options to find what works for you. Prioritize quality fat sources for long-term success on your keto diet. This low carb approach fuels your body with steady energy. Your keto journey benefits from these smart choices.
FAQ
What are healthy fats on a keto diet?
Healthy fats on a keto diet are whole food sources. They provide sustained energy and essential nutrients. These fats include avocados, olive oil, nuts, seeds, full-fat dairy, pasture-raised meats, and fatty fish. You use them to fuel your body when you eat few carbohydrates.
Why do you need so much fat on keto?
You need a lot of fat on keto because it becomes your main energy source. When you limit carbs, your body switches to burning fat for fuel. This process creates ketones. Ketones provide energy for your brain and body. Fat also helps you feel full.
What fats should you avoid on a keto diet?
You should avoid processed vegetable oils like soybean, corn, and sunflower oil. Also, stay away from trans fats found in many processed foods. These fats can cause inflammation and harm your health. Focus on whole, unprocessed fat sources instead.
How do healthy fats help with satiety?
Healthy fats help you feel full by releasing hormones. These hormones signal to your brain that you have eaten enough. This reduces hunger and cravings. Feeling satisfied helps you stick to your keto diet and manage your weight.
Can you eat too much healthy fat on keto?
Yes, you can eat too much healthy fat. While fat is crucial for keto, you still need to manage your calorie intake. Eating too many calories, even from healthy fats, can prevent weight loss. Balance your fat intake with your energy needs.

