
Is catfish a healthy choice? Many people wonder about this fish. Catfish offers key nutritional highlights, including high protein and beneficial omega-3s. This blog explores the specific nutritional benefits and health facts of catfish. It encourages readers to consider catfish for a balanced diet. Discover the amazing nutritional value of catfish. Catfish nutrition facts show its value. Catfish provides excellent protein, contributing to its catfish nutrition benefits.
Key Takeaways
Catfish is a healthy food. It has lots of protein and good fats called omega-3s. It also has important vitamins and minerals.
Catfish helps your muscles grow. It keeps your heart healthy. It also makes your brain work better.
Catfish has low mercury levels. This makes it a safe fish to eat. You can choose wild-caught or farm-raised catfish.
Cook catfish in healthy ways. Grilling, baking, or steaming are good choices. Avoid frying to keep it healthy.
Eating catfish can help you manage your weight. The protein in catfish makes you feel full. This helps you eat less.
Understanding the Nutritional Value of Catfish

Catfish offers a strong nutritional profile. It provides many essential nutrients without adding excessive calories. This fish is low in calories, low in fat, and low in sodium. It is also high in protein. This section details the overall nutritional composition of catfish.
Macronutrient Breakdown
Catfish provides a lean source of protein and healthy fats. It contains few carbohydrates.
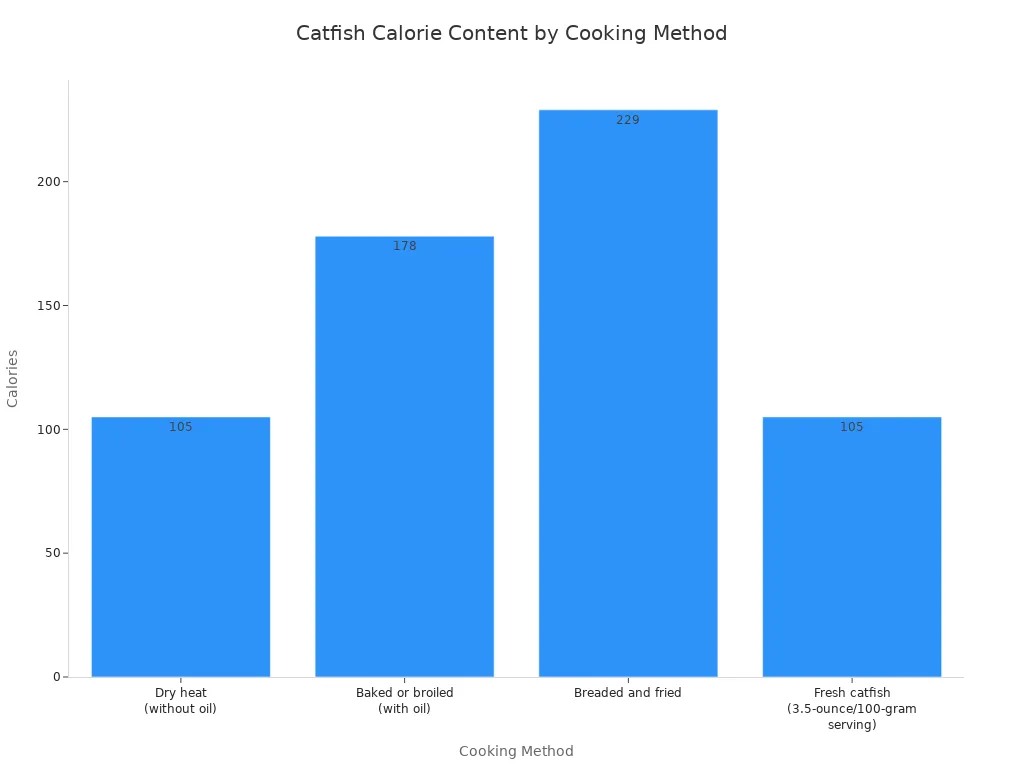
Catfish offers a low-calorie option. A typical single serving of U.S. farm-raised catfish contains 105 calories. However, cooking methods change the calorie count significantly.
Cooking Method | Calories |
|---|---|
Dry heat (without oil) | 105 |
Baked or broiled (with oil) | 178 |
Breaded and fried | 229 |
Fresh catfish (3.5-ounce/100-gram serving) | 105 |
Catfish is an excellent source of protein. It contains 18 grams of protein per 100 grams. This makes it a valuable food for muscle health.
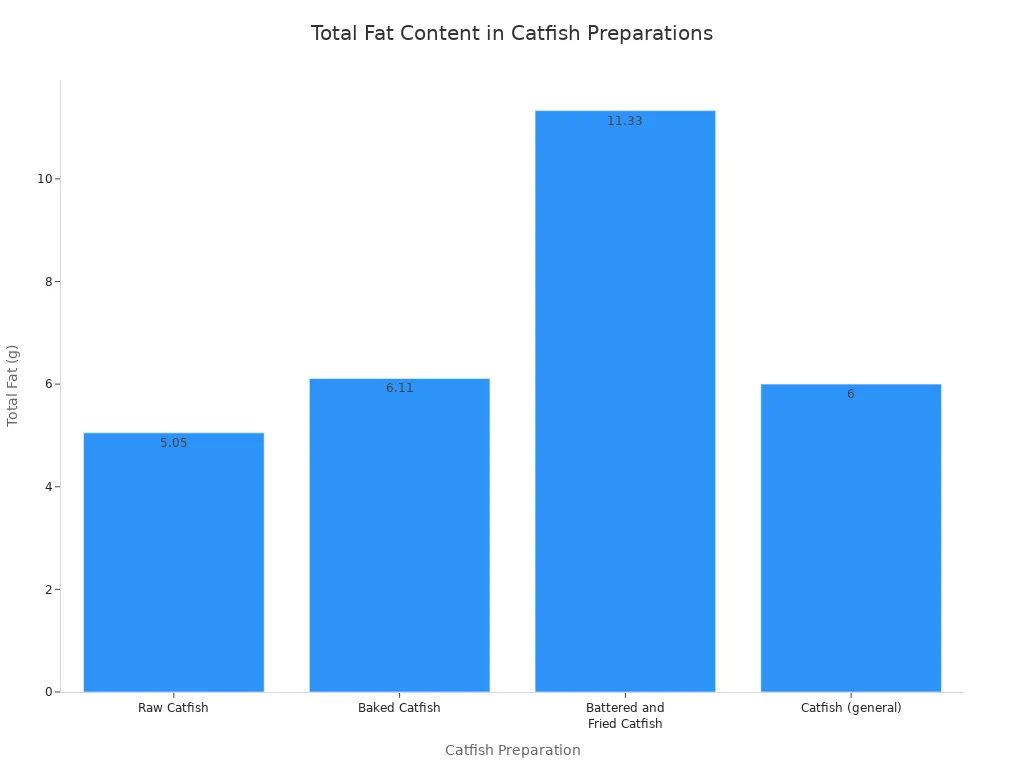
Catfish contains healthy fats. The total fat content varies with preparation.
Seafood (3 ounces) | Total Fat (g) |
|---|---|
Raw Catfish | 5.05 |
Baked Catfish | 6.11 |
Battered and Fried Catfish | 11.33 |
Catfish (general) | 6 |
This fish is a good source of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. These are important for overall health. The balance of these omega fatty acids contributes to its health benefits.
Catfish has a low carbohydrate content. For example, 100 grams of cooked, breaded, and fried channel catfish contains 7 to 8 grams of carbohydrates. Plain catfish has even fewer carbohydrates. It also contains very little sodium.
Essential Micronutrients
Catfish provides many essential nutrients. It offers a rich supply of vitamins and minerals. These micronutrients support various bodily functions.
Catfish is an outstanding source of Vitamin B12. A 100-gram serving of fresh catfish provides 121% of the Daily Value (DV) for Vitamin B12. This vitamin is crucial for energy production and nerve function.
It also contains a significant amount of Selenium. A 100-gram serving of farmed channel catfish contains 8.2 micrograms (µg) of Selenium. Selenium acts as a powerful antioxidant.
Other important nutrients include Phosphorus and Vitamin D. Phosphorus is vital for bone health and cellular processes. Vitamin D supports bone strength and immune function. The omega-3 fatty acids also contribute to its rich nutrient profile. Catfish is truly a nutrient dense food. Its comprehensive nutritional value of catfish makes it a smart dietary choice.
Protein Power: Why Catfish is a Healthy Choice
Catfish is a fantastic protein source. It offers a high-quality protein that benefits the body in many ways. This makes catfish a healthy choice for many diets.
High-Quality Protein Source
Catfish provides a good source of protein. Its protein digestibility is high, at 95.1%. This is similar to protein from terrestrial meats (80.1-97.0%), eggs (90.9%), and milk (95.0%). Aquatic animal proteins, including fish, generally have similar digestibility to these other sources. Catfish is also notably high in lysine compared to other meats. Proteins from finfish and shrimp, whether wild-caught or farmed, are considered to have similar quality to terrestrial animal proteins.
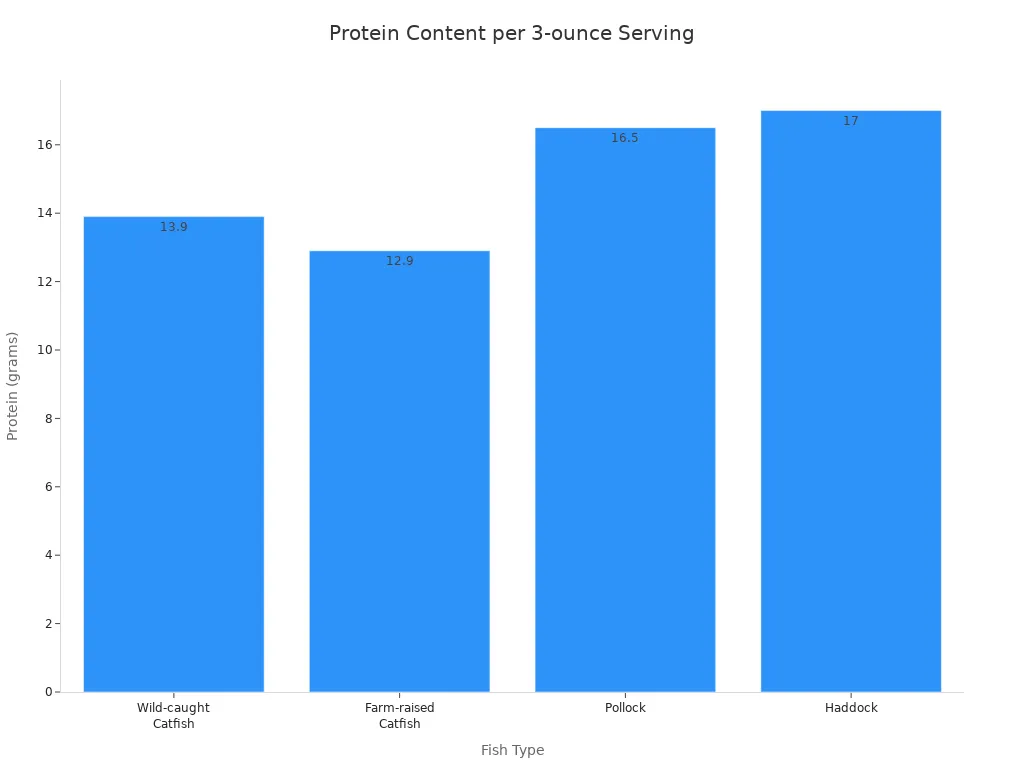
Here is how catfish protein content compares to other fish:
Fish Type | Protein per 3-ounce serving (grams) |
|---|---|
Wild-caught Catfish | 13.9 |
Farm-raised Catfish | 12.9 |
Pollock | 16.5 |
Haddock | 17 |
Muscle Growth and Repair
Catfish protein contains both essential and non-essential amino acids. Essential amino acids include isoleucine, valine, methionine, histidine, leucine, phenylalanine, lysine, and threonine. Non-essential amino acids include aspartic acid, glutamic acid, alanine, proline, tyrosine, serine, glycine, taurine, arginine, and cysteine. Lysine is particularly abundant in catfish protein, with a content of 6.81%.
Dietary leucine (Leu) improves muscle protein synthesis in hybrid catfish. It activates the AKT/TOR signaling pathway. This activation leads to increased muscle growth and protein deposition. Dietary Leu also decreases muscle protein degradation through the AKT/FOXO3a signaling pathway. These findings show how leucine helps muscle development in fish. Fish proteins are easily digestible and rich in essential amino acids, including leucine. These essential amino acids are vital for muscle growth. The high proportion of these amino acids in fish protein makes it a valuable source for supporting muscle protein synthesis.
Satiety and Weight Management
Catfish is a lean protein source. Foods high in protein help people feel full for longer. This feeling of fullness, or satiety, can reduce overall calorie intake. Eating lean protein, like catfish, can support weight management efforts. It provides essential nutrients without adding excessive fat or calories. This makes it a beneficial component of a balanced diet.
Omega-3s and Beyond: The Health Benefits of Catfish
Catfish offers many health benefits beyond its protein content. Its rich profile of omega fatty acids and other compounds contributes significantly to overall well-being. These benefits make catfish a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Heart Health and Circulation
Catfish is a heart-healthy choice. It contains beneficial omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy heart. A 3-ounce standard serving of catfish provides 237 to 240 mg of omega-3 fatty acids. This includes important types like ALA, EPA, and DHA. Specifically, a 3-ounce serving contains 46 mg of ALA, 14 mg of EPA, and 48 mg of DHA. These omega-3 fatty acids help support healthy circulation. They contribute to the overall health benefits of catfish. Eating catfish regularly can support cardiovascular function. It helps keep the heart strong.
Brain Function and Cognitive Support
The omega-3 fatty acids in catfish also support brain health. These essential fatty acids are vital for proper brain development and function. They help maintain cognitive abilities throughout life. Regular consumption of fish like catfish can enhance memory and focus. It provides the necessary nutrients for optimal brain health. The omega fatty acids in catfish contribute to better communication between brain cells. This supports overall cognitive performance.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Catfish possesses significant anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3 fatty acids are key contributors. They decrease PGE2 by reducing the catalytic monomer of COX-1 dimer. They also inhibit COX-1 oxygenation. Catfish oil contains omega-6 fatty acids. It also has omega-9 fatty acids. These omega-9 fatty acids exert anti-inflammatory effects through a PPAR-γ expression-dependent mechanism. Furthermore, catfish skin secretions contain oxysterols and furan fatty acids. These compounds reduce pro-inflammatory cytokines. They also elevate anti-inflammatory cytokines. These components work together to reduce inflammation in the body. This can help manage various inflammatory conditions.
Eye Health Improvement
Catfish also supports eye health. The omega-3 fatty acids, especially DHA, are important for vision. DHA is a major structural component of the retina. Adequate intake of these fatty acids helps maintain good eyesight. It can also protect against age-related eye conditions. Including catfish in your diet provides these essential nutrients. This contributes to long-term eye health.
Vitamins and Minerals: Catfish Nutrition Benefits
Catfish offers many important vitamins and minerals. These nutrients support various body functions. The catfish nutrition benefits extend beyond protein and omega-3s.
Vitamin B12 for Energy
Catfish is high in vitamin B12. This vitamin is crucial for energy production. It helps the body use fatty acids. Vitamin B12 also aids in making red blood cells. These cells carry oxygen throughout the body. Trace amounts of Vitamin B12 are essential for these metabolic processes. Methylmalonic acid, a byproduct, links to metabolic pathways involving amino acids or vitamin B12 metabolism. This suggests its role in broader metabolic processes.
Here are the recommended daily intakes for Vitamin B12:
Adult Group | Recommended Daily Intake (mcg) |
|---|---|
Adults over 14 | 2.4 |
Pregnant individuals | 2.6 |
Breastfeeding individuals | 2.8 |
Adults over 50 | Meet needs through supplements and fortified foods |
Vitamin D for Bone Health
Catfish also provides Vitamin D. This vitamin is vital for strong bones. It helps the body absorb calcium. Adequate Vitamin D intake supports overall bone health. This is one of the many nutritional benefits of eating catfish.
Here is the Vitamin D content in catfish:
Fish | Per 100 g (µg) |
|---|---|
Catfish | 12.9 |
Selenium for Antioxidant Defense
Catfish contains Selenium. This mineral acts as a powerful antioxidant. Selenium protects cells from damage. It helps regulate lipid metabolism and inflammation. Selenoproteins, which incorporate Selenium, influence antioxidant enzymes. These enzymes include SOD, GPX, and CAT. Selenium directly protects cell membranes from oxidative damage. It regulates glutathione peroxidase (GPX) activity. Selenium also breaks down peroxides. This prevents the buildup of reactive oxygen species and free radicals. Different forms of Selenium convert into selenoproteins. These selenoproteins then exert antioxidant effects. Nano-Se can activate the Nrf2 signal pathway. This leads to the expression of genes for antioxidant enzymes. Selenium is an essential element with significant antioxidant capacity in fish. Its antioxidant function comes primarily from selenoproteins. In yellow catfish, researchers identified 28 selenoproteins. Both Selenium and selenoproteins control antioxidant responses, lipid accumulation, and metabolism.
Phosphorus for Cellular Health
Catfish is a good source of Phosphorus. This mineral is essential for many cellular functions. It plays a key role in bone formation. Phosphorus also helps the body use energy. It is a vital component of DNA and RNA. These are the building blocks of cells. Foodstruct indicates that wild, channel catfish, cooked with dry heat, has a Phosphorus content of 304mg per 100 grams. According to Eat This Much, catfish contains 58mg of Phosphorus per 100 grams. These nutrients make catfish a truly nutrient dense food.
Safety and Sourcing: Maximizing the Benefits of Eating Catfish
Understanding where catfish comes from and how it is raised helps consumers make informed choices. This section explores important safety and sourcing considerations. These factors help maximize the benefits of eating catfish.
Mercury Levels Explained
Many people worry about mercury in fish. Catfish generally has lower mercury levels compared to larger, longer-lived predatory fish. However, mercury levels can vary depending on the fish’s environment.
Location | Catfish Type | Mercury Level (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
River Po, Italy | Catfish | 0.51 – 1.43 |
Nitra River, Slovakia | Catfish | 1.53 (highest) |
African lakes (Burkina Faso) | Giraffe Catfish | 0.006 – 0.230 |
These levels show that while some catfish can have higher mercury, many sources offer very low levels. Consumers can choose catfish with confidence.
Wild-Caught vs. Farm-Raised
The choice between wild-caught and farm-raised catfish impacts nutrition and environmental factors. Farm-raised catfish often have controlled diets. Wild-caught catfish eat what they find in their natural habitat.
Nutrient/Component | Wild-Caught Catfish | Farm-Raised Catfish |
|---|---|---|
Diet | Algae, aquatic plants, fish eggs, other fish | High protein diet (soy, corn, wheat), supplemented |
Amino Acids | Lower levels (mature fish) | Highest levels (mature fish) |
Protein | More | Less |
Fat | More (African catfish), Less (Indian butter catfish) | Less (African catfish), More (Indian butter catfish) |
Iron | Lower | Significantly elevated |
Farm-raised catfish can have higher levels of certain amino acids and iron. Wild-caught catfish may offer more protein and fiber. Both types provide nutritional benefits.
Sustainable Choices
Choosing sustainably sourced catfish helps protect the environment. Farm-raised catfish production can have environmental impacts. These include water pollution from pond effluents and contamination from pesticides. It also involves using antibiotics and poses threats to biodiversity. Some studies show aquaculture, including catfish farming, has higher greenhouse gas emissions and blue water consumption than capture fisheries. It can be comparable to or different from pork and poultry in emissions.
Consumers can look for certifications to ensure sustainable practices. The Friend of the Sea certification program promotes sustainable fish farming. The USDA-Certified | U.S. Farm-Raised Catfish program ensures safe, eco-friendly farming processes. This includes high sustainability standards. These certifications help consumers make responsible choices.
Healthy Catfish Preparation

Preparing catfish in a healthy way helps preserve its valuable nutrients. It also avoids adding unhealthy fats. Simple cooking methods and flavorful seasonings can make catfish a delicious and nutritious meal.
Best Cooking Methods
Choosing the right cooking method is important for a catfish healthy meal. Grilling is an excellent option. A study on snakehead fish fillets found that grilling was the most effective cooking method for healthy eating. It resulted in no loss of minerals compared to raw fish. Grilling preserves important minerals like calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, and manganese. It also increases dry matter, protein, ash, and sodium content. Other cooking methods, however, led to losses in important mineral content. Baking, broiling, and steaming are also great choices. These methods use little to no added fat. They allow the natural flavors of the catfish to shine. Avoid deep-frying. Frying adds a lot of unhealthy fats and calories. It can also reduce the nutritional benefits of the fish.
Flavorful Seasonings
Simple seasonings enhance the taste of catfish without adding extra calories or unhealthy ingredients. Fresh herbs like dill, parsley, and cilantro work well. Spices such as paprika, garlic powder, onion powder, and black pepper add depth. A squeeze of fresh lemon or lime juice brightens the flavor. You can also use a light marinade made with olive oil, herbs, and citrus. These choices keep the catfish light and flavorful. They ensure you get all the good nutrients without unnecessary additives.
Catfish offers significant catfish nutrition benefits. It provides high-quality protein, beneficial omega-3s, and essential vitamins and minerals. This makes catfish a truly nutrient dense food. When prepared properly, catfish is a delicious and catfish healthy addition to any balanced diet. Readers can enjoy the many benefits of eating catfish. Its versatility and health advantages make it an excellent choice. Make informed dietary choices and include this valuable fish in meals. Embrace the full catfish nutrition benefits.
FAQ
Is catfish good for heart health?
Yes, catfish supports heart health. It contains omega-3 fatty acids. These fatty acids help maintain healthy circulation. They contribute to a strong cardiovascular system. Regular consumption can benefit your heart.
Does catfish have high mercury levels?
No, catfish generally has low mercury levels. It is a safer choice compared to larger, predatory fish. Mercury levels can vary by environment. However, most catfish sources offer very low levels.
What is the difference between wild-caught and farm-raised catfish?
Wild-caught catfish eat natural diets. Farm-raised catfish have controlled diets. Farm-raised often show higher levels of certain amino acids and iron. Wild-caught may offer more protein. Both types provide good nutrition.
What is the healthiest way to cook catfish?
Grilling is a very healthy cooking method. It preserves minerals and nutrients. Baking, broiling, and steaming are also good choices. These methods use little added fat. Avoid deep-frying to keep it healthy.
Can catfish help with weight management?
Yes, catfish can help with weight management. It is a lean protein source. Protein helps people feel full for longer. This feeling of fullness can reduce overall calorie intake. It supports a balanced diet.

