
Blueberries often earn the title of “superfood.” Their vibrant appeal hints at powerful internal qualities. These small berries offer rich nutrition. They provide significant health benefits, especially for brain health. This article explores blueberries nutrition, the comprehensive health benefits of blueberries, and their specific brain-boosting properties. Discover the power of blueberries. Learn about their many benefits and why these small fruits contribute so much to overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways
Blueberries are a superfood. They have few calories but many nutrients. They give you important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
Blueberries are good for your brain. They help improve memory and focus. They also protect your brain cells.
Blueberries help your body in many ways. They support your heart and digestion. They also help control blood sugar and boost your immune system.
You can easily add blueberries to your diet. Eat them fresh or frozen. Put them in breakfast, snacks, or even main meals.
Blueberries Nutrition: Superfood Profile

Blueberries offer impressive blueberries nutrition. They are a true superfood. These small fruits pack many beneficial compounds. They provide essential vitamins, minerals, and potent antioxidants. This makes them a valuable addition to overall nutrition.
Low Calorie, Nutrient-Dense
Blueberries are low in calories but rich in nutrients. This makes them nutrient-dense berries. One cup of raw blueberries contains about 80 to 84 calories. For example, CalorieKing reports 84 calories per cup. The Mayo Clinic Health System states 80 calories per cup. UH Hospitals notes 82.65 kcal per cup. People can enjoy these blueberries without consuming many calories.
Essential Vitamins and Minerals
Blueberries provide many essential vitamins. One cup of blueberries offers 24 percent of the recommended daily allowance of vitamin C. A half-cup serving provides 25 percent of the daily value for vitamin C. These berries also contain important minerals.
Mineral | Fresh Berry (wet µg/g) |
|---|---|
Calcium | 230 |
Copper | 1.5 |
Iron | 0.91 |
Magnesium | 99 |
Manganese | 31 |
Phosphorus | 190 |
Potassium | 780 |
Zinc | 1.33 |
Copper and Manganese are particularly notable among these minerals. They are present in amounts considered proximal to daily values.
Potent Antioxidants: Anthocyanins
Blueberries are among the top antioxidant foods. They contain a high concentration of antioxidants. Anthocyanins are the primary antioxidants in blueberries. These compounds give blueberries their vibrant blue color. Anthocyanins protect against free radical damage in several ways. They chelate metal ions like iron. This prevents these metals from starting free radical formation. Such reactions would otherwise harm DNA and other cell parts. Anthocyanins also activate the Nrf2 pathway. This pathway is key for the cell’s own antioxidant systems. It protects cells from oxidative stress. Furthermore, anthocyanins act as reducing agents. They donate electrons to free radicals, neutralizing them.
Fiber Content for Digestive Health
Blueberries are a good source of dietary fiber. One cup of blueberries contains approximately 3.5 to 4 grams of fiber. This fiber contributes significantly to digestive health. Blueberry fiber acts as a natural source of prebiotic fiber. Prebiotic fiber feeds beneficial gut bacteria, called probiotics. This helps probiotics grow and supports overall gut function. The fiber also helps absorb “bad” cholesterol. It then aids in its natural removal from the body. This process supports healthy blood flow to the brain. It works through the gut-brain axis, which is vital for good digestion.
Blueberries for Brain Health: Cognitive Benefits
Blueberries offer significant brain health benefits. They contain compounds that protect the brain and enhance its functions. These small fruits contribute to overall cognitive function and mental well-being.
Blueberries to Improve Memory and Cognition
Blueberries can improve memory and overall cognition. Studies show that consuming blueberries leads to better cognitive performance. This includes improvements in short-term memory, long-term memory, and spatial memory. Researchers found these benefits across different age groups, from children to older adults.
Blueberry phytochemicals reach vital brain regions. Scientists found anthocyanins from blueberries in the hippocampus and neocortex after blueberry consumption. These areas are crucial for cognitive function. Other studies found blueberry phytochemicals in the cerebellum, cortex, hippocampus, and striatum in rats. These areas are essential for memory and learning.
Polyphenolic compounds, especially anthocyanins, contribute to these benefits. They increase neuronal signaling in brain regions linked to memory function. Anthocyanins also improve glucose disposal. This helps prevent neurodegeneration. Flavonoids, another type of compound in blueberries, cross the blood-brain barrier. They influence neuron chemistry. Flavonoids regulate enzymes vital for maintaining synaptic integrity and brain-cell activity. This process supports boosting brain cells.
Protecting Against Cognitive Decline
Blueberries play a role in protecting against cognitive decline. They mitigate markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain. Blueberries suppress microglial activation, which helps restore brain homeostasis. They reduce pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. For example, aged rats on a blueberry diet showed lower levels of NF-κB, similar to young rats. Blueberry supplementation also reduces the number of microglia and decreases the production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in microglial cells.
The anti-inflammatory activity of blueberries comes from non-nutrient phytochemicals, especially polyphenols. These compounds reduce age-related sensitivity to inflammation. Blueberries also show anti-amyloidogenic properties. They reduce the progression of amyloid fibril formation. This can decrease amyloid toxicity to neurons.
Daily blueberry consumption has shown promising results in human studies. Middle-aged participants with subjective cognitive decline improved their performance in memory and lexical access. They also reported reduced memory encoding difficulty in daily life. A large study found that higher blueberry intake slowed cognitive decline in older women by an estimated 2.5 years. Another analysis linked higher anthocyanin and berry intake to a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease.
Enhancing Focus and Mental Clarity
Blueberries enhance focus and mental clarity by improving blood flow to the brain. Flavonoids in blueberries are key to this benefit. A study showed that daily consumption of concentrated blueberry juice increased brain activity and blood flow in healthy older adults. This effect was noticeable after only a few weeks. The antioxidants, especially flavonoids, promote these improvements. Improved cerebral blood flow is a proposed mechanism. It benefits both heart and brain health. This helps maintain brain function and supports concentration.
Supporting Mental Well-being
Blueberries can also support mental well-being. Acute consumption of blueberry flavonoids improves mood in children and young adults. Some studies suggest that blueberry interventions can influence cognitive performance and mood. However, the long-term effects on mood can vary. One study on young adults with depressive symptoms showed that a single dose of blueberries improved mood and executive function. This might be due to changes in cerebral blood flow or neurotransmitter levels. Yet, six weeks of daily blueberry supplementation did not show the same long-term benefits for depression recovery in this group. This suggests that while acute intake may offer benefits, long-term daily supplementation might not be as effective for improving mental health indices in this demographic. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term impact of blueberries on mood and mental health.
Health Benefits of Blueberries: Beyond Brain Function
Blueberries offer many health benefits beyond their positive effects on the brain. These small fruits support various body systems. They contribute to overall well-being.
Cardiovascular System Support
Blueberries significantly support the cardiovascular system. Regular intake of blueberries improves blood pressure. They also enhance endothelial function. This means the lining of blood vessels works better. Blueberries improve blood lipid levels. They also reduce inflammatory markers. These benefits help maintain a healthy heart. They contribute to lower blood pressure.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Blueberries have strong anti-inflammatory properties. They reduce systemic inflammation markers. For example, studies show that blueberry powder reduces inflammatory markers like IL-6 and TNF-α. Anthocyanins in blueberries decrease inflammation by suppressing certain signaling pathways. Blueberry metabolites also reduce inflammation in blood vessel cells. This helps protect against damage.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Blueberries help regulate blood sugar. Their glycemic index (GI) is 53. This classifies them as a low GI food. This means blueberries have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels. Clinical studies show blueberries can increase insulin sensitivity in adults with insulin resistance. This helps the body use insulin more effectively. These benefits come from their rich polyphenol content.
Vision Protection
Blueberries protect vision. They contain compounds that support eye health. Key components include anthocyanins, vitamin C, and vitamin E. Flavonoids, phenolic acids, and stilbenes also contribute. These compounds help keep eyes healthy.
Immune System Boost
Blueberries boost the immune system. Compounds called stilbenoids in blueberries work with vitamin D. They increase the expression of a gene important for immune function. Daily consumption of blueberries increases natural killer (NK) cell counts. Blueberries also reduce oxidative stress. They increase anti-inflammatory cytokines. This enhances immune health.
Muscle Recovery Aid
Blueberries aid in muscle recovery after exercise. Their antioxidants and polyphenols reduce muscle soreness. They lower inflammatory markers. This accelerates muscle repair. Blueberries improve muscle strength recovery. Anthocyanins support a faster return to peak performance. These benefits help muscles heal faster.
Incorporating Blueberries into Your Daily Diet
People can easily add blueberries to their daily meals. These versatile fruits fit into many dishes. They offer great taste and nutrition.
Fresh vs. Frozen Blueberries
Both fresh and frozen blueberries provide excellent nutrition. Freezing preserves most of their beneficial compounds. Frozen blueberries are convenient for year-round use. Fresh blueberries are perfect for immediate enjoyment. Choose either option based on availability and preference.
Breakfast Ideas with Blueberries
Blueberries enhance many breakfast dishes. They add flavor and nutrients. Consider these popular options:
Blueberry French Toast Bake
Blueberry Banana Oatmeal
Blueberry Protein Smoothie
Blueberry Greek Yogurt Parfait
Blueberry Cobbler Muffins
Blueberry Pancakes
Blueberry Almond Overnight Oats
Blueberry Chia Pudding
Snacks and Smoothies
Blueberries make great snacks. They are also perfect for smoothies. People can enjoy them alone or in creative combinations. Try these snack ideas:
Balsamic Blueberries & Peaches
Citrusy Kale Salad with Blueberries & Pepitas
Greens With Blueberries, Feta & Almonds
Honeyed Cantaloupe With Blueberries
Fresh Blueberries With Lemon Cream
Blueberry Cheesecake Bars
Blueberry Chicken Salad
Blueberry Oat Squares
Culinary Uses in Meals and Desserts
Blueberries are not just for breakfast or dessert. They can add a unique twist to main dishes. For example, people can make Buttermilk Corn Waffles with Berry Syrup. These waffles pair well with savory toppings like crab cake. Grilled Steak with Berry Barbecue Sauce offers a sweet and savory combination. A quick homemade blueberry barbecue sauce works well with pork, beef, and fish.
Optimal Storage Tips
Proper storage keeps blueberries fresh longer. Store them in a low-humidity section of the refrigerator. Use a container that allows some ventilation. Keep blueberries cold, ideally near 32 degrees Fahrenheit. This slows decay. Avoid the crisper drawer due to its higher humidity. The middle rack towards the front of the fridge works well. If a refrigerator opens frequently, transfer blueberries to an airtight container. Line it with a paper towel to absorb moisture. If a refrigerator opens infrequently, leave them in their original clamshell. Still, line it with a paper towel.
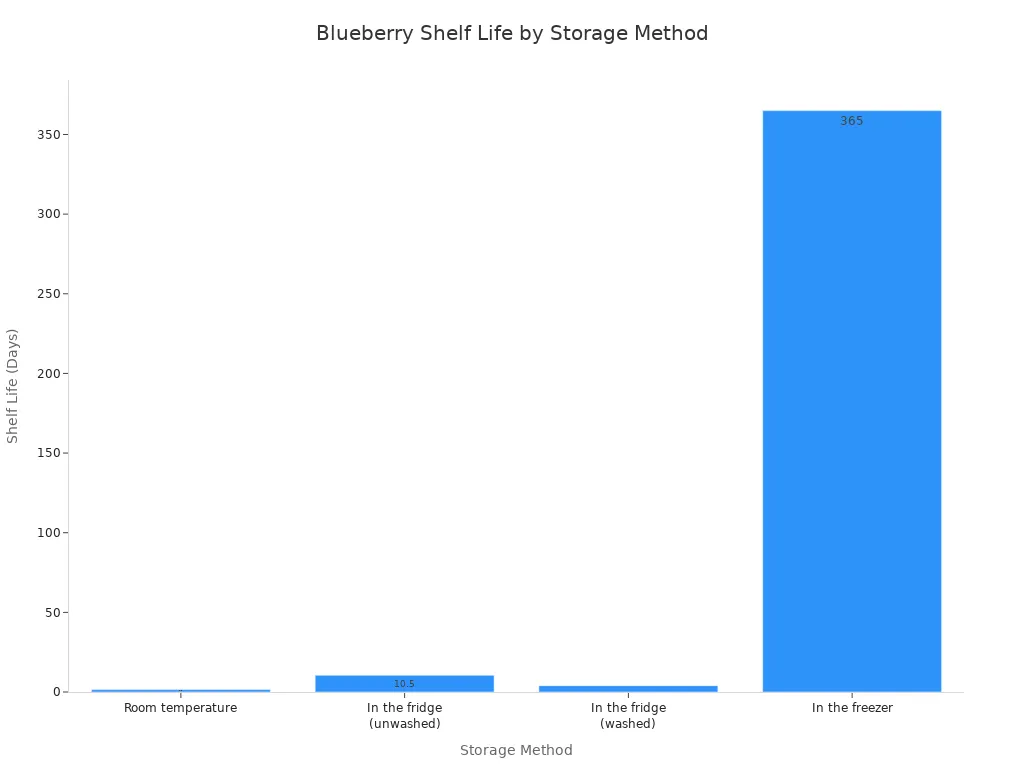
Storage Method | Shelf Life |
|---|---|
Room temperature | 1–2 days |
In the fridge (unwashed) | 7–14 days |
In the fridge (washed) | 3–5 days |
In the freezer | Up to 12 months |
Proper storage at approximately 0°C with 90-95% relative humidity extends their shelf life to 10–18 days. Controlled atmosphere storage can maintain quality for 5 to 8 weeks at 0-1°C.
Blueberries are a true superfood. They offer impressive blueberries nutrition. These small fruits provide many health benefits. They significantly impact brain health and overall well-being. These berries boost brain function, support heart health, and improve gut health. They also aid muscle recovery and help regulate blood sugar. The power of blueberries lies in their rich antioxidant and flavonoid content. Make them a regular part of your diet. Enjoy them fresh or frozen. This simple step can enhance your health. Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized dietary advice.
FAQ
What makes blueberries a “superfood”?
Blueberries earn their “superfood” title due to their rich nutrient profile. They contain many antioxidants, especially anthocyanins. These compounds protect cells from damage. Blueberries also provide essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber. These nutrients support overall health and well-being.
How do blueberries help the brain?
Blueberries offer significant brain benefits. They improve memory and focus. Their antioxidants protect brain cells from oxidative stress. They also enhance blood flow to the brain. This supports better cognitive function. Blueberries may also help protect against cognitive decline.
Can frozen blueberries provide the same benefits as fresh ones?
Yes, frozen blueberries offer similar health benefits to fresh ones. Freezing preserves most of their nutrients and antioxidants. People can enjoy frozen blueberries year-round. They are a convenient and healthy option for smoothies, baking, or snacks.
Are there any side effects of eating too many blueberries?
Eating blueberries in moderation is generally safe. However, consuming very large amounts might cause mild digestive upset. This is due to their fiber content. People should enjoy blueberries as part of a balanced diet. They contribute to overall health without adverse effects.

