
You might think you dislike brussel sprouts. For some, a genetic variant makes brussels taste very bitter. About 25% of Americans are ‘supertasters’ who find these brussels sprouts intensely sour. However, brussels sprouts are a nutritional powerhouse. This guide uncovers their facts and health benefits. You will also find simple ways to enjoy these amazing sprouts. Brussels sprouts are more than just a side dish. They offer great health.
Key Takeaways
Brussels sprouts are very nutritious. They have many vitamins and minerals.
These sprouts help your immune system. They also help your digestion.
Brussels sprouts fight inflammation. They protect your cells from damage.
They may help lower cancer risk. They are good for your bones and blood.
You can roast, sauté, or steam them. You can also add them to salads.
Brussel Sprouts Nutrition: Key Facts

You want to understand what makes brussels sprouts so good for you. These small, green vegetables, part of the Brassica oleracea family, pack a powerful nutritional punch. Let’s break down their key nutrients.
Macronutrient Profile
Brussels sprouts offer a balanced mix of macronutrients. When you eat one cup of cooked brussels sprouts, you get a good amount of energy and essential building blocks for your body.
Nutrient | Value |
|---|---|
Calories | 56 |
Fats | 1g |
Carbs | 11g |
Fiber | 4g |
Protein | 4g |
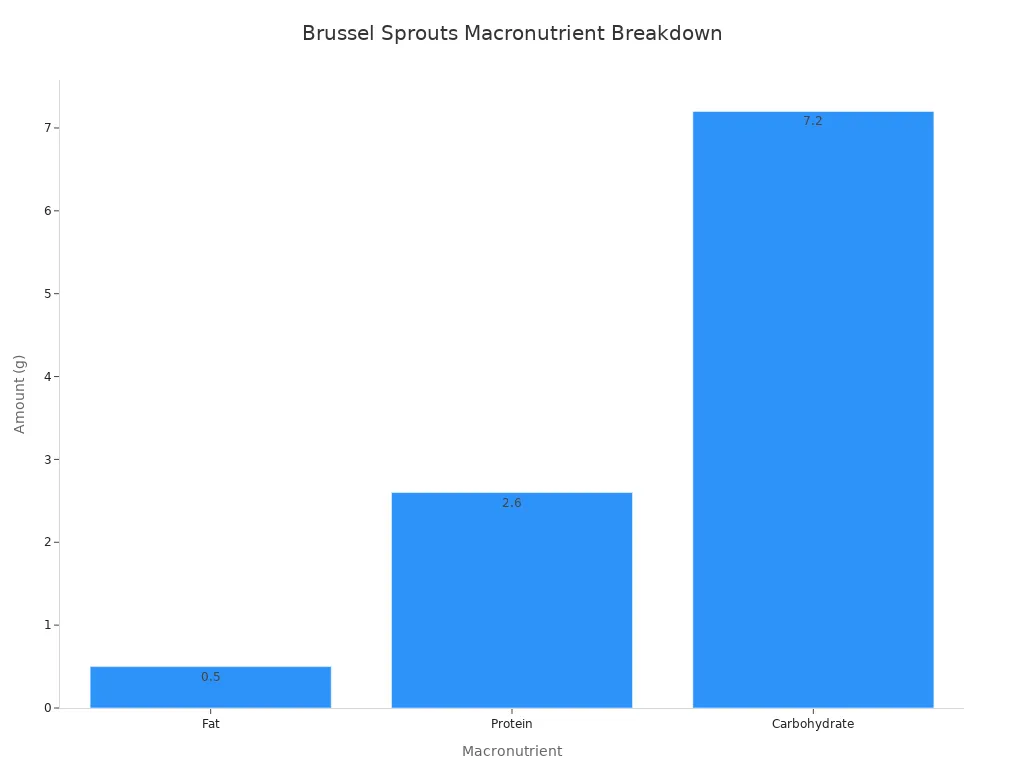
These figures show that brussels sprouts are low in fat and provide a solid amount of carbohydrates, fiber, and protein. Looking at a 100-gram serving of cooked brussels sprouts, you see a similar healthy profile:
Macronutrient | Amount per 100g (Cooked, Boiled, Drained) |
|---|---|
Calories | 56 |
Fat | 0.5g |
Protein | 2.6g |
Carbohydrate | 7.2g |
Key Vitamins: C, K, and Folate
Brussels sprouts are an excellent source of several important vitamins. You will find high levels of Vitamin C, Vitamin K, and Folate (Vitamin B9) in these sprouts.
Vitamin C: This vitamin is crucial for your immune system and skin health. Brussels sprouts provide a significant portion of your daily Vitamin C needs.
Vitamin K: Your body needs Vitamin K for blood clotting and strong bones. Brussels sprouts are especially rich in this vitamin.
Folate: Folate is vital for cell growth and function. It is particularly important during pregnancy.
Consider the daily recommended intake percentages you get from brussels sprouts:
Nutrient | Percentage of daily intake in adults |
|---|---|
Vitamin C | 83.11% for males and 99.73% for females |
Vitamin K-1 | 130% for males and 173.33% for females |
Folate | 13.43% |
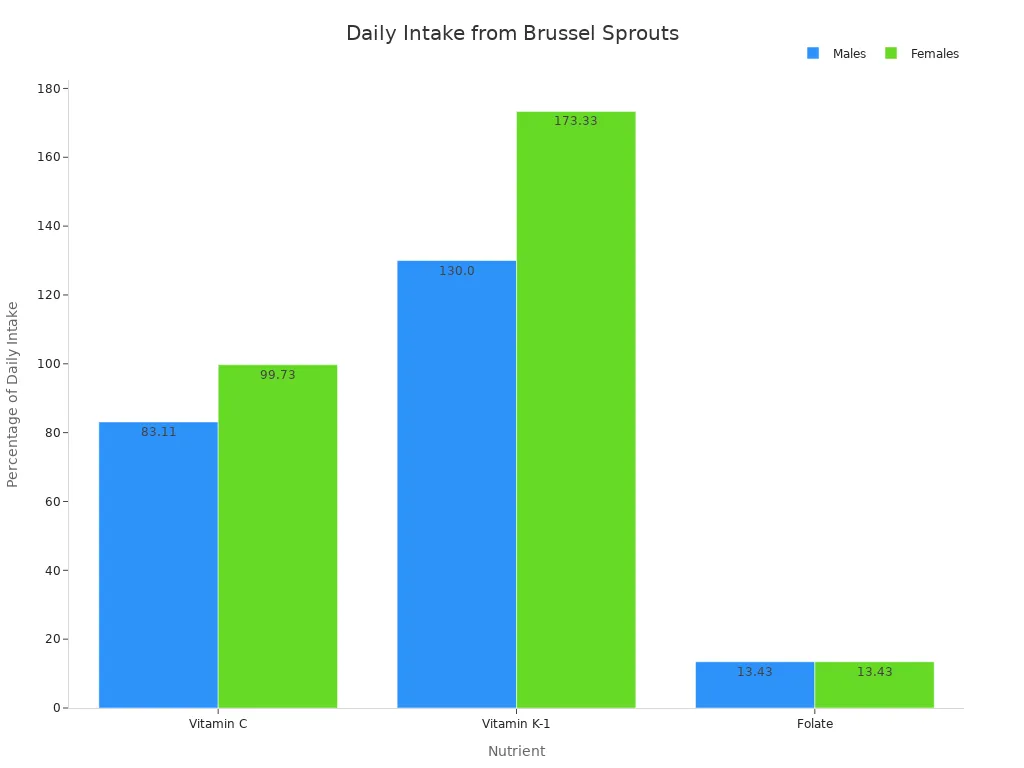
As you can see, brussels sprouts are a best source of Vitamin C and Vitamin K, providing over 50% of your daily value. They are also a good source of Folate.
Essential Minerals
Beyond vitamins, brussels sprouts also supply your body with important minerals. These minerals play many roles in your overall health.
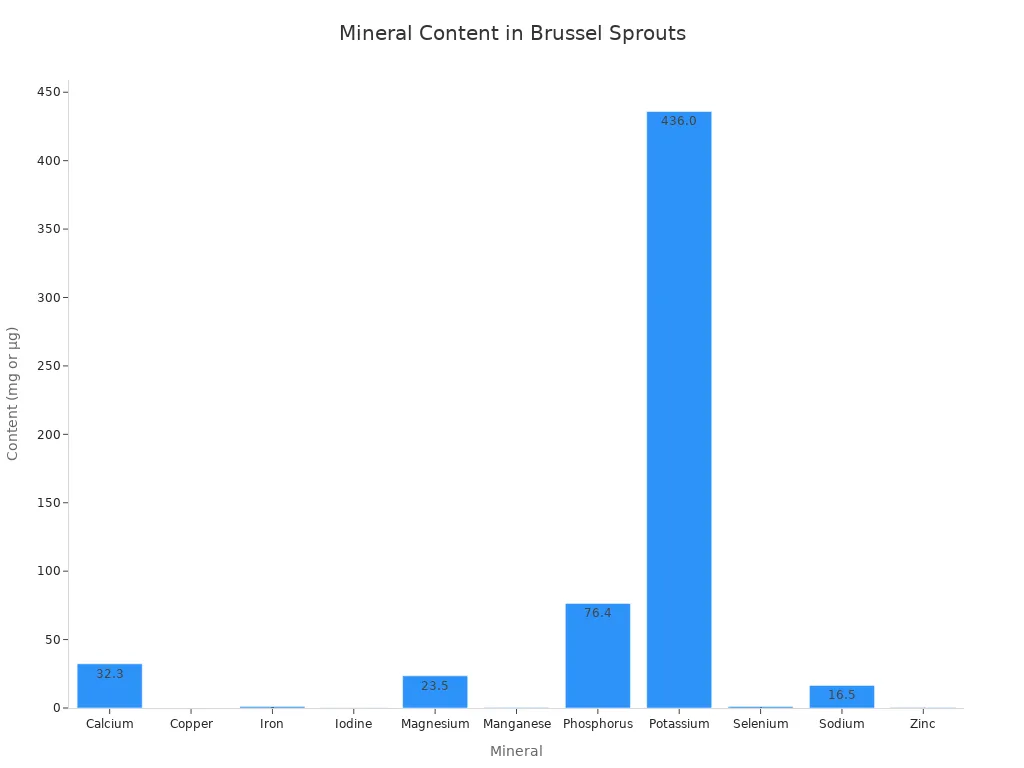
You get significant amounts of Potassium, Manganese, and Phosphorus from these sprouts. These minerals support nerve function, bone health, and energy production.
Fiber for Gut Health
Brussels sprouts are a good source of fiber, which is essential for your digestive system. The fiber in brussels sprouts helps keep things moving smoothly.
Brussels sprouts are high in fiber, which can promote regularity, support digestive health, and reduce the risk of heart disease and diabetes.
The fiber in brussels sprouts supports digestive health by promoting regular bowel movements. It also helps foster a healthy balance of gut bacteria. You find both soluble and insoluble fiber in these sprouts. Soluble fiber helps lower bad cholesterol. Brussels sprouts also contain raffinose, an indigestible fiber. Your body can find raffinose hard to digest. This can sometimes cause gas and discomfort, especially if you have conditions like IBS.
Protein Content
While not a primary protein source, brussels sprouts contribute to your daily protein intake. They offer a decent amount of protein for a vegetable.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g (Cooked Brussels Sprouts) |
|---|---|
Protein | 2.6g |
Cystine | 16mg |
Histidine | 57mg |
Isoleucine | 100mg |
Leucine | 114mg |
Lysine | 116mg |
Methionine | 24mg |
Phenylalanine | 74mg |
Threonine | 91mg |
Tryptophan | 28mg |
Valine | 117mg |
Arginine | 153mg |
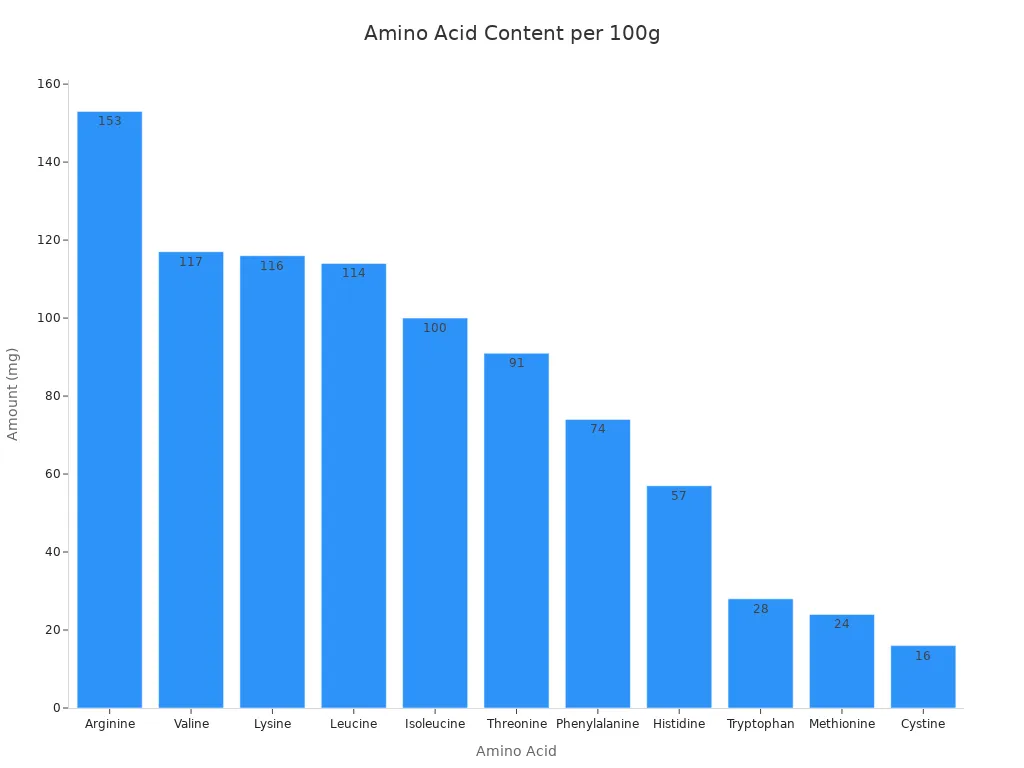
These sprouts provide various amino acids, the building blocks of protein. This makes them a valuable addition to your diet for overall nutrition.
Brussels Sprouts: Health Benefits
You now understand the nutritional makeup of brussels sprouts. Let’s explore the incredible health benefits these small vegetables offer. You gain significant advantages by adding them to your diet.
Immune System Support
Brussels sprouts are champions for your immune system. They contain vital compounds that help your body defend itself. You get a good amount of vitamin C from brussels sprouts. This vitamin is essential for proper immune function.
It also protects your cells from oxidative stress. Vitamin A, in the form of beta-carotene, helps maintain the integrity of your mucosal surfaces. These surfaces act as a barrier against harmful pathogens. Dietary fiber and phytonutrients like glucosinolates in brussels sprouts also offer anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating effects. An in vitro study showed that compounds in cooked brussels sprouts can enhance the resistance of your immune cells to DNA damage. This suggests a protective effect on your immune system at a cellular level. These health benefits make brussels a smart choice.
Digestive Wellness
Your digestive system greatly benefits from brussels sprouts. They are an excellent source of fibre. This fibre promotes regularity and supports overall gut health. Brussels sprouts contain high fiber, especially soluble fibre. This soluble fibre acts as a prebiotic. It nourishes beneficial gut bacteria. These microbes ferment soluble fibre to produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs).
Examples include butyrate, propionate, and acetate. Butyrate strengthens your gut lining and prevents chronic inflammation. Propionate influences lipid metabolism. Acetate helps regulate appetite and blood sugar balance. A thriving microbiome, supported by this fibre, links to lower systemic inflammation. Efficient fiber intake also supports regular bowel movements.
It reduces bloating and gas. It prevents the release of endotoxins into your bloodstream. This lowers your body’s inflammatory load. It improves gut motility and microbial diversity. You get about 3 grams of fiber per cup of brussels sprouts. This fulfills 11% of your daily fiber needs. This fiber aids in regulating blood sugar levels. It supports overall digestive health by feeding helpful gut bacteria. This can boost your mood, support immunity, and lower inflammation.
Anti-Inflammatory Power
Brussels sprouts possess strong anti-inflammatory properties. They contain various compounds that combat inflammation in your body. You can see some of these compounds and their actions below:
Compound | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|
Kaempferol | Protects against amyloid-beta toxicity in the brain |
Isothiocyanates | Suppress inflammatory markers and downregulate inflammation |
Sulforaphane | Activates the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor pathway, boosts longevity of brain cells, and prevents neurodegeneration |
Indole derivatives | Activate aryl hydrocarbon receptors (AhR) for intestinal immune modulation, regulating intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes and innate lymphoid cells, inducing interleukin-22, and manipulating intestinal microbiota |
Phenolic compounds, Flavonoids, Carotenoids | Offer various health benefits, including anti-inflammatory properties |
These compounds work together to reduce inflammation. This contributes to your overall health.
Bone and Blood Health
Brussels sprouts are crucial for your bone and blood health. They contain Vitamin K1. This vitamin is essential for strong bones and proper blood clotting. Vitamin K supports bone density. It activates osteocalcin, a protein that binds calcium to your bone matrix.
This strengthens your bones. It also regulates calcium levels. This ensures proper deposition in bones rather than in arteries or soft tissues. For blood clotting, Vitamin K is vital. It produces the necessary proteins involved in this process. You support these vital functions by consuming brussels sprouts. These benefits are important for your long-term health.
Antioxidant Protection
Brussels sprouts are high in antioxidants. These powerful compounds protect your cells from damage. You find several specific antioxidants in these sprouts:
Kaempferol: This flavonoid compound shows high potency in radical scavenging activity. It directly neutralizes harmful free radicals. It also provides significant protection against oxidative stress in neuronal cells. It safeguards cells from oxidative damage.
Indole-3-carbinol and Phenethyl isothiocyanate: These are also major constituents of brussels sprouts with antioxidant properties.
Glucosinolate derivatives: These compounds are abundant in cruciferous vegetables like brussels sprouts. They are not antioxidants themselves. However, they hydrolyze into active products. These derivatives increase the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes. Examples include superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and catalase. These enzymes are crucial for neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS). They maintain cellular redox balance.
Glutathione synthesis enzymes: Glucosinolate derivatives also enhance enzymes involved in the synthesis of glutathione (GSH). Glutathione is a powerful endogenous antioxidant. It plays a vital role in detoxifying harmful compounds. It protects cells from oxidative damage, including oxidative DNA damage.
These antioxidants contribute significantly to your health benefits.
Cancer-Fighting Potential
Research suggests a link between brussels sprouts consumption and a reduced risk of certain cancers. You can potentially lower your risk by including these sprouts in your diet. A study on Dutch adults found that men and women with the highest intake of cruciferous vegetables had a significantly lower likelihood of developing colon cancer. This was compared to those with the lowest intake.
Research indicates that a compound in brussels sprouts may help inhibit tumor growth. It blocks aggressive enzymes that promote cancer progression. These enzymes typically weaken tumor-suppressing genes. The compound in brussels sprouts allows these suppressors to function effectively. Brussels sprouts also contain chlorophyll. A 2018 study on pancreatic cancer cells suggested chlorophyll could act as an antioxidant against compounds involved in pancreatic cancer development.
Consider these findings:
Lung Cancer: Population research indicates that consuming larger amounts of brussels sprouts and broccoli associates with a lower risk of developing lung cancer.
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Some population studies suggest that women who consume more brussels and similar vegetables have a reduced risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Prostate Cancer: Population research shows that individuals who eat larger quantities of brussels sprouts and related vegetables have a lower risk of developing prostate cancer.
Pancreatic Cancer: Conversely, some population research indicates that higher consumption of brussels sprouts does not lead to a lower risk of pancreatic cancer.
These findings highlight the potential cancer-fighting benefits of these amazing sprouts. You make a great choice for your health by including them in a healthy diet.
Easy and Delicious: Simple Brussel Uses

You now know the many health benefits of brussels sprouts. You might wonder how to prepare them. These small vegetables are versatile. You can easily add them to your meals. Here are some simple ways to enjoy brussels.
Roasting for Crispy Texture
Roasting transforms brussels sprouts. It gives them a delicious, crispy texture. You simply toss them with olive oil, salt, and pepper. Then, you roast them in a hot oven. This method brings out their natural sweetness. It makes them a favorite side dish.
Sautéing with Flavor
Sautéing is another quick way to cook brussels sprouts. You can enhance their taste with many flavor pairings. Consider adding crispy bacon or pancetta for a savory touch. Caramelized onions add richness. Toasted almonds or pecans give a delightful crunch. For a sweet tang, try balsamic glaze or maple syrup. Garlic and Parmesan create a savory, umami-packed side. You can also use red pepper flakes for a pleasant heat. Mustard, thyme, and smoked paprika are also great seasonings for your sautéed sprouts.
Quick Steaming Methods
Steaming is an excellent cooking method. It helps retain the vitamins and minerals in your brussels sprouts. The National Library of Medicine supports this. You can use a steamer basket. Add water to a saucepan. Place the sprouts in the basket. Steam them for 5 to 10 minutes until they are fork-tender. You can also microwave them. Place halved brussels sprouts in a bowl with water. Microwave for about 5 minutes. For a skillet method, arrange them in a single layer. Add a little water. Steam for 3 to 5 minutes. An Instant Pot also works. Cook brussels for 2 minutes on high pressure.
Adding to Salads
Brussels sprouts are great in salads. You can use them raw or cooked. Shaved raw brussels sprouts add a fresh crunch. Try them with pickled onions and roasted cashews. A miso dressing with white miso paste and toasted sesame oil complements this well. For a different salad, combine shaved brussels sprouts with dried cranberries, pumpkin seeds, and walnuts. A Dijon dressing with olive oil, lemon juice, and Dijon mustard works perfectly. You can also use cooked brussels sprouts in salads.
Creative Recipe Ideas
You can get creative with your brussels sprouts recipes. Try a Brussels Sprouts Slaw. This cook-free recipe uses shredded sprouts as a base. A Fried Brussels Sprout Salad offers a unique twist. You can also make Bright Brussels Sprouts Fettuccine. This pasta dish combines sautéed sprouts with lemon and Parmesan. A Brussels Sprouts Gratin with Walnut Crumble is a rich, cheesy option. For an appetizer, try Parmesan Pastry-Wrapped Brussels Sprouts. Buffalo Brussels Sprouts offer savory and spicy flavors. These ideas show the versatility of brussels.
You now understand the impressive nutritional facts and many health benefits of brussels sprouts. These small brussels offer great advantages. You can easily add these versatile brussels sprouts to any meal. From roasting to salads, you have many ways to enjoy these delicious sprouts. Give brussel sprouts a try! You will discover their great taste and numerous benefits. Make smart, healthy choices for your well-being. Your body will thank you for these amazing brussels. Embrace these powerful sprouts for better health. These brussels are truly beneficial sprouts.
Make brussels sprouts a regular part of your diet. You will enjoy their deliciousness and boost your overall health.
FAQ
Are brussels sprouts good for weight loss?
Yes, they are. Brussels sprouts are low in calories. They are also high in fiber. Fiber helps you feel full longer. This can reduce your overall calorie intake.
Can brussels sprouts cause gas?
Sometimes, yes. Brussels sprouts contain raffinose. This is a type of fiber. Your body can find raffinose hard to digest. This may cause gas or bloating for some people.
How often should I eat brussels sprouts?
You can enjoy brussels sprouts several times a week. They offer many nutrients. Aim for a varied diet. This ensures you get all essential vitamins and minerals.
Are raw brussels sprouts safe to eat?
Yes, you can eat raw brussels sprouts. Many people enjoy them shredded in salads. Raw sprouts keep all their nutrients. Always wash them thoroughly before eating.
Tip: If you are new to eating brussels sprouts, start with small portions. This helps your digestive system adjust.

