You might wonder what makes up a healthy diet. It means eating a variety of foods from different groups so your body gets all the nutrients it needs. Studies show that when you include more whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, you boost your chances of meeting your vitamin and mineral needs. Take a look at the table below to see how different eating patterns affect your health. If you feel short on time or motivation, try simple swaps and plan quick meals to make healthy eating fit your routine.
Dietary Pattern | Associated Risks | Protective Effects |
|---|---|---|
Western Diet | Elevated metabolic risks, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes | N/A |
Mediterranean Diet | N/A | Protective effects against cardiometabolic diseases |
High Sodium Intake | Hypertensive effects, exacerbates obesity and inflammation | N/A |
High Dietary Fiber | N/A | Attenuates pro-inflammatory effects of red meat |
Ultra-Processed Foods | Violates dietary guidelines, increases chronic disease risk | N/A |
Traditional Diets | N/A | Consistent protective effects against chronic diseases |
Key Takeaways
A healthy diet includes a variety of foods from different groups. Focus on whole grains, fruits, and vegetables to meet your nutrient needs.
The Mediterranean diet is a great example of healthy eating. It emphasizes plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins, promoting heart health and longevity.
Pay attention to portion sizes. Use visual cues to estimate servings and avoid overeating, even with healthy foods.
Limit processed foods high in sugar and sodium. Cooking at home and reading labels can help you make better choices.
Meal planning simplifies healthy eating. Prepare ingredients in advance and choose recipes that use similar items to save time and reduce waste.
Healthy Diet Basics

What Is a Healthy Diet
You might ask yourself, “What does a healthy diet really mean?” According to the World Health Organization, a healthy diet is essential for your health, well-being, and growth. It helps you avoid malnutrition and lowers your risk of diseases like diabetes, cancer, and heart problems. When you focus on healthy eating, you give your body the fuel it needs to work its best every day.
A healthful diet includes a mix of foods from different groups. Nutrition experts recommend you eat plenty of plant-based foods, such as vegetables, fruits, legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. You also need enough protein, which can come from both animal and plant-based sources. Try to choose whole and minimally processed foods. Limit foods high in saturated fats, added sugars, and sodium. Balance and variety matter most, so you get all the nutrients your body needs.
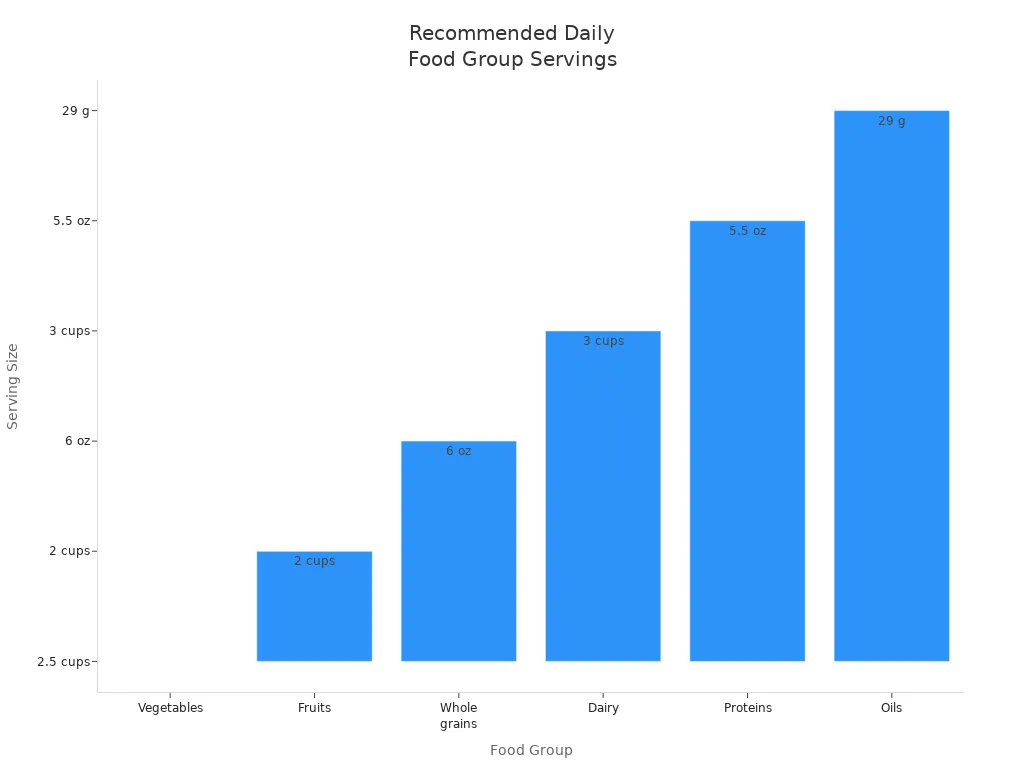
Here’s a quick look at the recommended daily servings for each food group:
Food Group | Recommended Serving Size |
|---|---|
Vegetables | 2 ½ cups equivalent |
Fruits | 2 cups equivalent |
Whole grains | 6 ounce equivalent |
Dairy | 3 cups equivalent |
Proteins | 5 ½ ounce equivalent |
Oils | 29 grams (2 ⅓ TBSP) |
You might notice that many healthful diets, like the Mediterranean diet, focus on plant-based foods. The Mediterranean diet encourages you to eat lots of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts, and olive oil. It also includes fish and lean proteins. This eating pattern is popular because it supports heart health and helps you feel full and satisfied.
Tip: Try to fill half your plate with vegetables and fruits at every meal. This simple habit makes healthy eating easier.
A healthful diet also means paying attention to micronutrients. Your body needs nearly 30 vitamins and minerals that it cannot make on its own. If you do not get enough of these, you might face serious health problems like heart disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer, or osteoporosis. That’s why nutrition guidelines always stress the importance of variety and balance.
Cultural traditions shape what you eat, too.
Cultural values and beliefs guide your food choices and how you prepare meals.
Some foods have special meaning and are saved for holidays or family gatherings.
Food habits can be hard to change because they connect to your emotions and social life.
When you look at different cultures, you see many ways to enjoy a healthful diet. The Mediterranean diet is just one example. People in other parts of the world also build their meals around plant-based foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Why It Matters
You might wonder why you should care about a healthy diet. The answer is simple: healthy eating helps you live longer and feel better. Research shows that eating a diet rich in plant-based foods and low in processed foods can help you live a longer life. For example, foods like garlic and olive oil, which are common in the Mediterranean diet, may help you stay healthy as you age. Mindful eating and eating fewer calories can also boost your lifespan.
A large study in the UK found that following healthy eating patterns, like those in the Mediterranean diet, can add almost 10 years to your life. People who ate more whole grains, nuts, and fruits—and less sugar and processed meat—lived longer. The Mediterranean diet stands out because it is full of plant-based foods and healthy fats, making it both tasty and healthful.
“Obesity and diabetes are increasing in prevalence worldwide. Despite excessive dietary consumption, obese individuals have high rates of micronutrient deficiencies. Deficiencies of specific vitamins and minerals that play important roles in glucose metabolism and insulin signaling pathways may contribute to the development of diabetes in the obese population.”
“The only study, from Guatemala, in which an intervention designed to improve linear growth has been examined with respect to diabetes prevalence, found that diabetes prevalence was lower in those exposed to improved nutrition during the first 1000 days.”
If you do not pay attention to nutrition, you might face problems like obesity and diabetes. Even if you eat a lot, you can still miss out on important vitamins and minerals. This can make it harder for your body to control blood sugar and stay healthy. Eating a healthful diet, like the Mediterranean diet, helps you avoid these risks.
The Mediterranean diet is famous for its healthful benefits. It is rich in plant-based foods, healthy fats, and lean proteins. People who follow this diet often have lower rates of heart disease, diabetes, and some cancers. The Mediterranean diet also supports healthy weight and strong bones.
You do not have to live near the Mediterranean Sea to enjoy this way of eating. You can add more plant-based foods, olive oil, and fish to your meals wherever you live. The Mediterranean diet is flexible and fits many lifestyles. It is a great example of how a healthful diet can be both delicious and good for you.
To sum up, a healthy diet gives you energy, protects you from disease, and helps you live your best life. The Mediterranean diet shows how plant-based foods, healthy fats, and mindful eating can make a big difference. When you choose a healthful diet, you invest in your future.
Balanced Diet Essentials
Food Groups
When you want to build a balanced diet, you need to know the main food groups. These groups help you get the right mix of nutrients every day. The Dietary Guidelines for Americans highlight the following food groups:
Fruits
Vegetables
Grains
Protein Foods
Dairy
Oils (not a food group, but still important for a healthy eating pattern)
You see these same groups in other healthy eating plans, like the Mediterranean Diet and the DASH eating plan. Both focus on eating more plant-based foods and less processed food. Here’s a quick look at how these diets compare:
Food Group | DASH Diet | Mediterranean Diet |
|---|---|---|
Fruits | High consumption | High consumption |
Vegetables | High consumption | High consumption |
Nuts/Seeds/Legumes | High consumption | High consumption |
Lean Meats/Fish/Poultry | High consumption | Moderate consumption |
Dairy | Low- or non-fat dairy | Regular dairy, less emphasis on fat |
Sweets | Low consumption | Moderate consumption |
Saturated Fats | Low consumption | Moderate consumption |
Alcohol | Low consumption (restricted) | Moderate consumption |
Fats | Emphasis on low saturated fats | Emphasis on olive oil (monounsaturated) |
You notice that both diets encourage you to eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. They also suggest you limit sweets and saturated fats. This approach gives your meals more nutritional value and helps you feel your best.
Tip: Try to include at least three different food groups in every meal. This habit makes your plate more colorful and boosts the nutritional value of your food.
Daily Servings
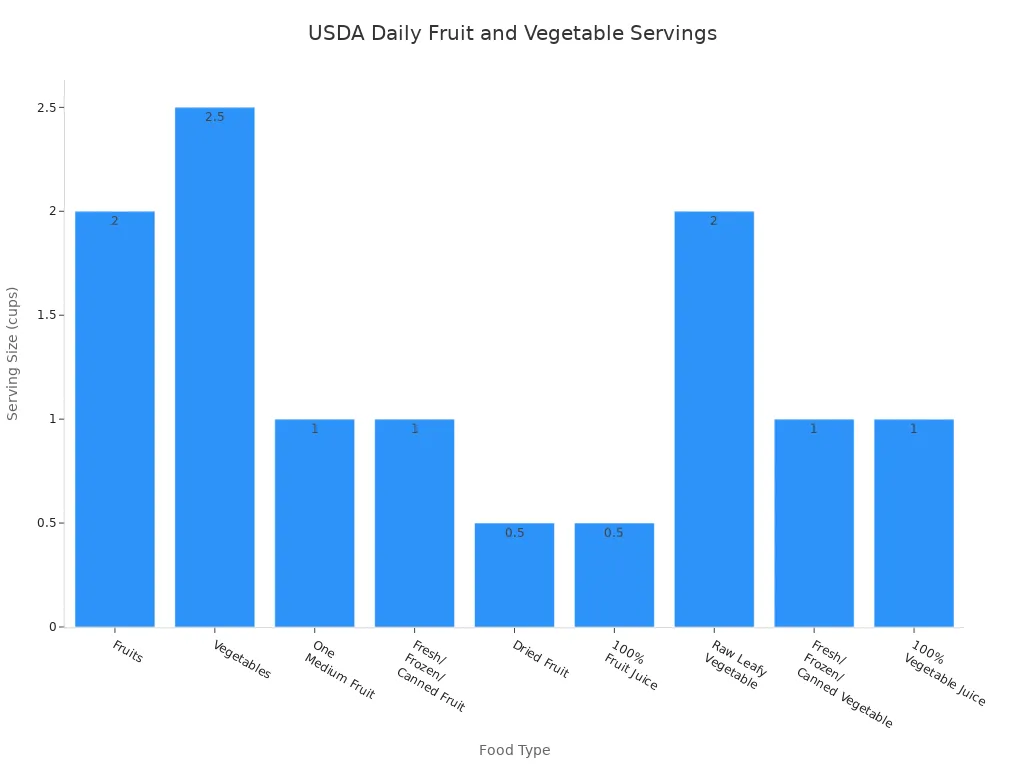
Knowing what to eat is only part of the story. You also need to know how much to eat from each group. The dietary guidelines give you clear daily goals. Here’s a table to help you plan your balanced diet:
Food Type | Daily Serving Size |
|---|---|
Fruits | 2 cups |
Vegetables | 2 1/2 cups |
One Medium Fruit | about the size of your fist |
Fresh/Frozen/Canned Fruit | 1 cup |
Dried Fruit | 1/2 cup |
100% Fruit Juice | 1/2 cup |
Raw Leafy Vegetable | 2 cups |
Fresh/Frozen/Canned Vegetable | 1 cup |
100% Vegetable Juice | 1 cup |
For whole grains and lean proteins, the recommendations look like this:
Food Group | Daily Servings/Equivalents | Examples of Serving Size |
|---|---|---|
Whole Grains | 3 to 6 servings (3 to 6 oz) | One slice whole-grain bread, ½ cup cooked brown rice, 3 cups popped popcorn |
Lean Proteins | 1 to 2 servings (5½ oz) | ¼ cup cooked beans, 1 ounce cooked seafood, one egg |
You can see that whole grains play a big role in a balanced diet. Try to make at least half your grains whole grains. This means choosing foods like brown rice, whole-wheat bread, and oatmeal. These foods give you more fiber and keep you full longer.
Dairy is also important. Aim for 3 cups of low-fat or fat-free dairy each day. If you do not eat dairy, you can choose fortified soy milk or yogurt. Oils, like olive oil, add healthy fats to your meals. Use them in small amounts for cooking or salad dressings.
Most dietary guidelines around the world agree on these basics. They all encourage you to eat more plant-based foods and cut back on salt, sugar, and alcohol. Some countries, like Italy, give even more detailed advice based on your age and activity level.
Portion Tips
Even when you eat the right foods, you need to watch your portions. Eating too much of anything—even healthy foods—can lead to weight gain. Here are some simple strategies to help you manage your portions:
Portion Control Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
Pre-portioned Foods | Meals structured around single-serving main dishes, which can help limit energy intake. |
Tools for Portion Selection | Using tools like food scales to choose portions based on energy density. |
Structuring the Eating Environment | Limiting exposure to large portions by using pre-portioned foods packaged for single eating occasions. |
Household Measures for Portion Guidance | Utilizing common objects or household measures to estimate recommended portion sizes. |
You do not always need a scale or measuring cup. You can use visual cues to estimate serving sizes:
Protein: Palm of your hand ≈ 3–4 oz serving (about the size of a deck of cards)
Carbohydrates & Starches: Fist or cupped hand ≈ ½ to 1 cup cooked cereal, pasta, or starchy vegetables (like a hockey puck)
Vegetables: Both hands cupped together ≈ 2 cups raw vegetables or 1 cup cooked (about the size of a baseball)
Fats: Thumb tip ≈ 1 tablespoon oil, butter, mayonnaise, or nut butter (like a pair of dice)
Snacks: Thumb measure ≈ 1 oz of nuts, cheese, or chips
Note: If you eat out, ask for a to-go box and put half your meal away before you start eating. This trick helps you avoid oversized portions.
A balanced diet is not just about what you eat, but also how much you eat. When you use these portion tips, you make it easier to stick to your healthy diet and get the most nutritional value from every meal. Remember, whole grains, lean proteins, and fresh fruits and vegetables should fill most of your plate. Oils and fats add flavor, but you only need a little.
If you follow these simple steps, you will find that a balanced diet fits easily into your daily life. You will feel more energized, and your body will thank you for the good nutrition.
Making Smart Choices
Limit Processed Foods
You might not realize how much processed food sneaks into your meals. These foods often have extra sugar, salt, and chemicals that your body does not need. In fact, about 60% of what Americans eat comes from processed foods, which means you get more sodium and sugar than you think. Over 70% of your sodium intake comes from these foods, not from the salt shaker.
Eating too many processed foods can lead to health problems. Take a look at this table to see what studies have found:
Study Description | Findings |
|---|---|
Large study of 100,000 adults | 10% increase in heart disease risk for every 10% more ultra-processed food eaten |
Study of almost 20,000 adults | 18% higher risk of death for each extra serving of processed food daily |
You also face a higher risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and missing out on important nutrients. Processed foods often contain added sugars and artificial chemicals that do not support good nutrition.
Tip: Try to cook more meals at home and read labels when you shop. Small changes can help you cut back on processed foods.
Healthy Swaps
You do not have to give up your favorite foods to follow a healthy diet. You can make simple swaps that boost your nutrition and lower your calorie intake. Here are some easy ideas:
High-Calorie Food | Healthy Swap | Description |
|---|---|---|
Butter | Olive or canola oil | Healthier fats for cooking and baking |
Canned foods (high sodium) | No salt added or low-sodium options | Rinse to remove extra salt |
Store-bought dressings | Homemade vinaigrette | Mix olive oil, vinegar, and herbs |
Refined grains | Whole grains | Look for “whole” as the first ingredient |
Fatty meats | Lean meats and poultry | Trim visible fat before cooking |
When you choose whole foods over processed ones, you get more vitamins, minerals, and fiber. These swaps help you manage your weight and keep your body strong.
Snack Ideas
Smart snacks can keep your energy up and help you feel full between meals. Dietitians recommend snacks that give you protein, fiber, and healthy fats. Here are some tasty options:
Apple or pear with nut butter
Popcorn
Roasted chickpeas
Beet chips
Walnuts
Cottage cheese with fruit or veggies
Greek yogurt
Chia pudding
These snacks fill in nutrition gaps and help you avoid energy crashes. Pairing fiber-rich foods with protein or healthy fats, like an apple with peanut butter, keeps you satisfied longer. Healthy eating does not mean you have to feel hungry—just make smart choices that support your goals.
Simple Meal Ideas

Quick Recipe
You want dinner to be easy, tasty, and good for you. Try these quick meal ideas that fit healthy eating guidelines. You can make them in less than 30 minutes, and they use simple ingredients you probably have at home.
Caprese chicken breasts: Cook chicken with tomatoes, mozzarella, and basil. You get protein and antioxidants in one pan.
Sheet pan pork chops and sweet potatoes: Roast pork chops, sweet potatoes, and apples together. This meal gives you vitamins and keeps cleanup simple.
Healthy mac and cheese (with veggies): Make classic mac and cheese, but add broccoli or spinach for extra nutrition.
Taco salad: Use ground beef or beans, lettuce, tomatoes, and a yogurt dressing. You get fiber and protein, and you can customize it.
Slow cooker beef and broccoli: Toss beef and broccoli in a slow cooker. You get iron and vitamin B12, and you can prep it in the morning.
Easy chickpea curry: Cook chickpeas with tomatoes and spices. This dish is full of plant-based protein and fiber.
Tip: If you prep ingredients ahead of time, you can mix and match these recipes all week. Try chopping veggies or cooking grains in advance.
Easy Planning
Meal planning helps you eat better and saves you time. You do not have to spend hours in the kitchen. Just follow these steps to make healthy eating simple:
Make a plan: Pick a few easy recipes for the week. Write down what you need for each meal.
Pick a method: Double recipes or batch-cook ingredients. Store leftovers in the fridge or freezer for quick meals.
Think about repurposing: Use cooked chicken in salads, wraps, or pasta. This trick reduces waste and keeps meals interesting.
Prep wisely: Chop veggies, cook grains, or portion snacks ahead of time. You will spend less time cooking each day.
Meal planning gives you more variety. You eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. You also avoid impulse eating and save money by shopping with a list. Weekly meal plans help you manage your time and keep healthy ingredients on hand, so you skip fast food and stick to your goals.
Planning meals can lower stress and help you feel more confident about your food choices. You set yourself up for success with just a little effort.
Choosing a healthy diet brings real rewards. You might notice more energy, better mood, and even a stronger body over time. People who make small, steady changes—like eating more veggies or swapping meat for beans—see big improvements in health and well-being.
Health Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
Resilience to disease | Helps prevent diabetes and heart problems |
Positive feelings | Makes meals enjoyable and boosts motivation |
Start with simple steps. Reflect on your habits, try new foods, and celebrate every win. Healthy eating is a journey, not a race!
FAQ
What makes some diets healthier than others?
You see many diets online. Some focus on whole foods, while others rely on processed meals. Diets with fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats help your body work better. Diets high in sugar or saturated fat can raise health risks.
How do diets affect your energy levels?
Diets with balanced nutrients give you steady energy. You feel less tired when you eat whole grains, lean proteins, and fresh produce. Diets with lots of sugar or processed foods can make your energy crash. Choose diets that support your daily activities.
Can you follow diets if you have food allergies?
You can find diets that fit your needs. Many diets offer options for allergies, like gluten-free or dairy-free choices. You should read labels and ask your doctor about safe diets. Diets with simple ingredients make it easier to avoid allergens.
Are plant-based diets better for your health?
Plant-based diets often help you lower disease risk. You get more fiber, vitamins, and minerals from these diets. Diets with less meat and more plants support heart health. You can try diets like the Mediterranean or DASH diets for better results.
How do you stick to healthy diets every day?
You can plan meals and snacks ahead. Diets work best when you keep healthy foods ready. You might use a shopping list or prep ingredients on weekends. Diets become easier when you set small goals and celebrate progress. Stay flexible and enjoy your food.

