
Poppy seeds, though tiny and unassuming, possess a dual nature. They offer impressive Poppy Seeds Nutrition, yet significant public concerns persist regarding their opioid content. The Center for Science in the Public Interest (CSPI) has even submitted a regulatory petition to the FDA, drawing attention to cases like Elizabeth Dominguez’s, who experienced distress after unknowingly consuming poppy seeds. These small poppy seeds provide rich nutrition, including essential minerals and fiber, and are used in many culinary applications. Understanding their safety remains crucial. This discussion aims to offer a balanced, informative perspective for enjoying poppy seeds safely and beneficially.
Key Takeaways
Poppy seeds are very nutritious. They have important minerals, fiber, protein, and healthy fats.
Poppy seeds can cause a positive drug test. This is because they have small amounts of opioid chemicals.
You can make poppy seeds safer. Wash, soak, or bake them to lower the opioid content.
Poppy seeds are good for your health. They help make bones strong and keep your heart healthy.
Eat poppy seeds in small amounts. This way, you can enjoy their benefits safely.
Key Nutritional Information of Poppy Seeds

Poppy seeds offer a remarkable nutritional value for their small size. Understanding their nutritional information reveals a rich profile of essential macronutrients and micronutrients. A 100-gram serving of poppy seeds provides a significant amount of energy and vital building blocks for the body.
Nutrient | Value per 100g |
|---|---|
Calories | 533 |
Fat | 44.7g |
Carbohydrates | 23.69g |
Protein | 18.04g |
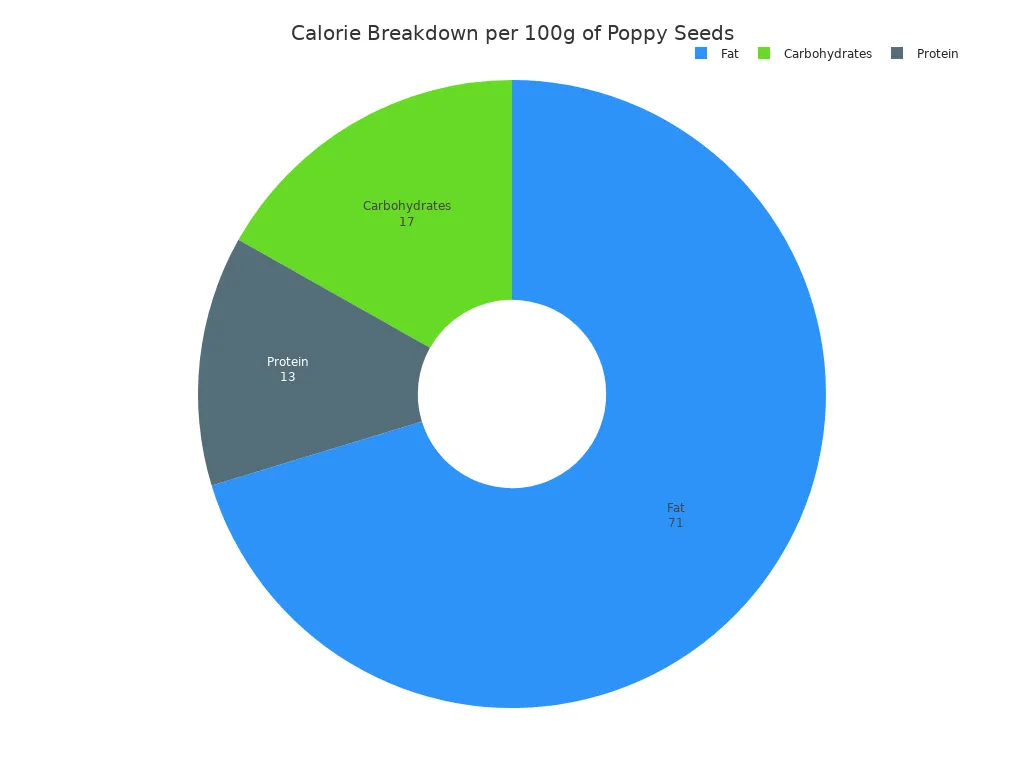
The calorie breakdown shows that fats contribute the most energy. About 71% of the calories come from fat, 17% from carbohydrates, and 13% from protein.
Essential Minerals
Poppy seeds are a powerhouse of valuable vitamins and minerals. They contain many micronutrients crucial for various bodily functions.
Nutrient | Quantity | %DV† |
|---|---|---|
Vitamins | ||
Thiamin (B1) | 0.85 mg | 56% |
Riboflavin (B2) | 0.1 mg | 8% |
Niacin (B3) | 0.9 mg | 6% |
Vitamin B6 | 0.25 mg | 19% |
Folate (B9) | 82 μg | 21% |
Vitamin C | 1.0 mg | 1% |
Vitamin E | 1.77 mg | 12% |
Minerals | ||
Calcium | 1438 mg | 144% |
Copper | 1.63 mg | 82% |
Iron | 9.76 mg | 75% |
Magnesium | 347 mg | 98% |
Manganese | 6.71 mg | 319% |
Phosphorus | 870 mg | 124% |
Potassium | 719 mg | 15% |
Selenium | 0 μg | 0% |
Sodium | 26 mg | 1% |
Zinc | 7.0 mg | 64% |
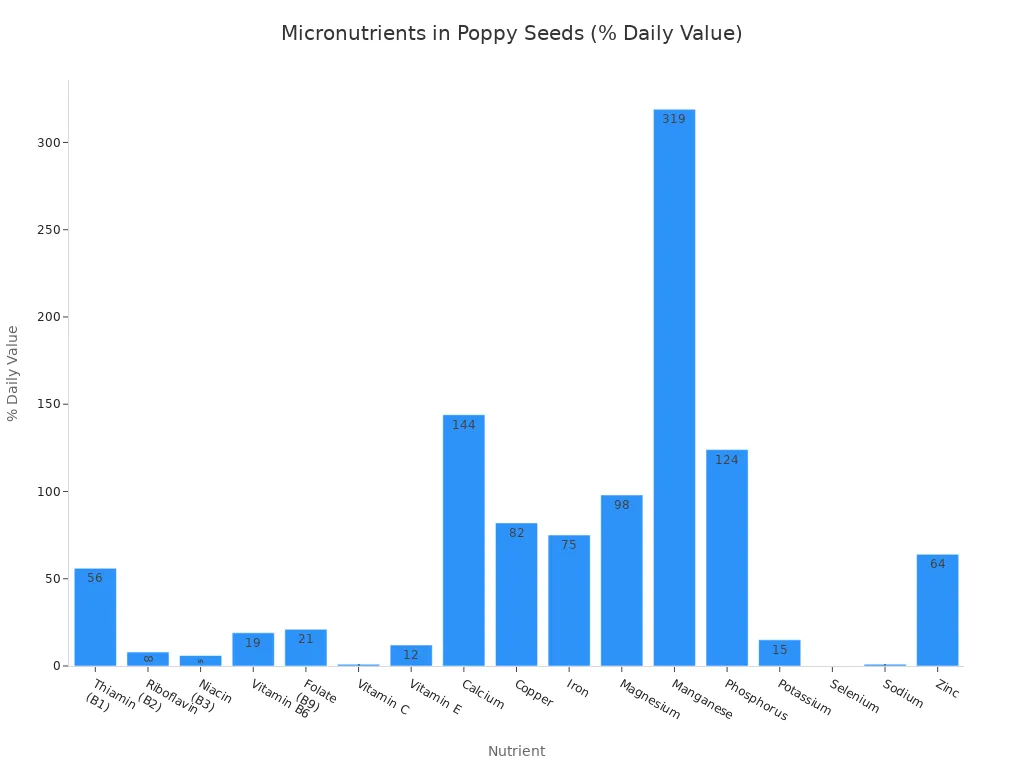
Poppy seeds are an excellent source of calcium and magnesium. A 100-gram serving provides 1438 mg of calcium, which is 144% of the daily recommended value. This makes them a significant contributor to bone health. They also supply substantial amounts of magnesium, zinc, iron, and manganese. Manganese plays several important roles in the body. It acts as a cofactor for various enzymes involved in reproductive function. Manganese also supports digestion by helping metabolize amino acids, cholesterol, glucose, and carbohydrates.
Fiber and Digestion
Poppy seeds are rich in fiber. They contain 19.5 grams of dietary fiber per 100 grams. This high in fiber content offers numerous health benefits. Dietary fiber is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. It adds bulk to stool, which helps promote regular bowel movements. This can prevent constipation and support overall gut health.
The fiber in poppy seeds also helps regulate blood sugar levels. It slows down the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream. Furthermore, poppy seeds contain fermentable complex carbohydrate polymers. These complex carbohydrates escape digestion in the upper digestive tract. They reach the colon where gut microbiota ferment them. This process produces short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like acetate, propionate, and butyrate. These SCFAs are beneficial for metabolic health and help maintain a balanced gut microbiota composition. This rich in fiber content truly makes poppy seeds a great food for digestive health.
Protein and Healthy Fats
Poppy seeds provide a good amount of protein, with 18.04 grams per 100 grams. Protein is vital for building and repairing tissues, making enzymes, and supporting overall body function.
These tiny seeds are also a source of healthy fats. A 100-gram serving contains 44.7 grams of total fat. Most of these fats are polyunsaturated.
Fat Type | Amount per 100g |
|---|---|
Total fat | 42g |
– Saturated | 4g |
– Monounsaturated | 6g |
– Polyunsaturated | 29g |
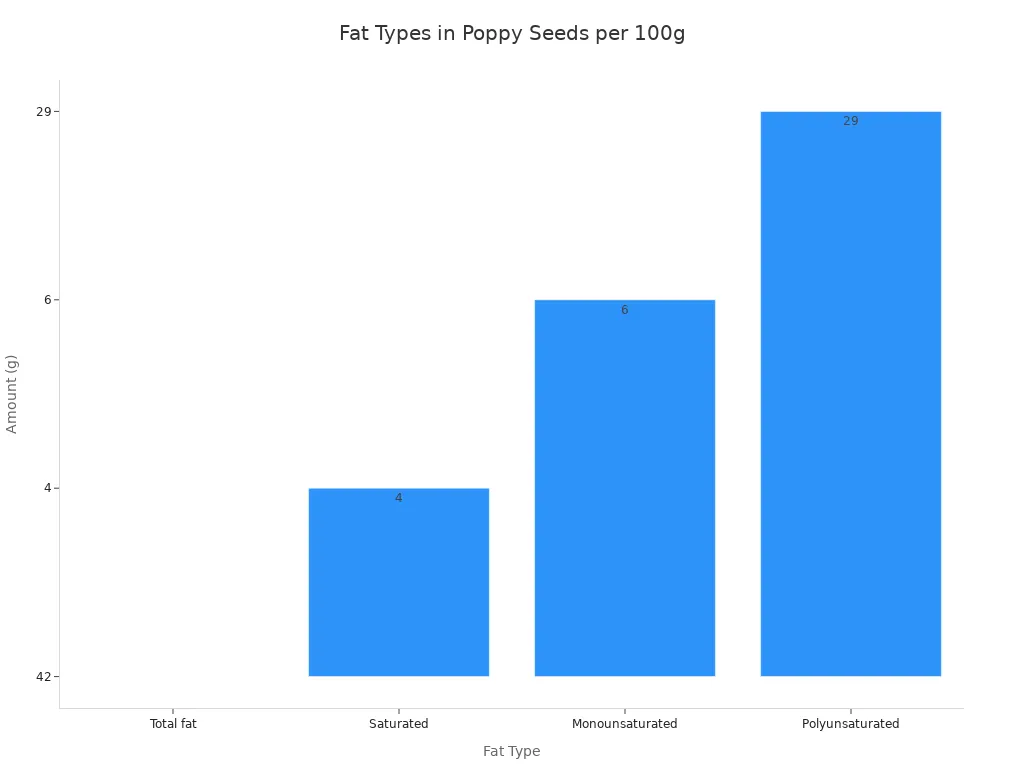
Poppy seeds are particularly rich in omega-6 and omega-9 fatty acids. They also contain small amounts of alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), an essential omega-3 fat. These healthy fats contribute to heart health and help maintain a balanced lipid profile. The overall poppy seeds nutrition profile makes them a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Culinary Uses of Poppy Seeds

Poppy seeds offer diverse culinary applications across many global cuisines. They enhance the flavor and texture of various dishes. People use them in baked goods, sauces, salads, and plant-based cooking. Their versatile nature makes them a popular ingredient worldwide. They also function as a thickening agent and texturizer due to their high soluble fiber content.
Baking and Desserts
Poppy seeds are a staple in many sweet treats. They are essential in European pastries like poppy seed rolls (Mohnstrudel) and American muffins. Many bakers use them as a popular filling for sweet buns and pastries, especially in Slavic countries. Recipes like Sweet Buns with Poppy Seed Filling are common. These buns often feature a versatile sweet yeast bread dough. Other popular desserts include Poppy Seed Cake with Dulce de Leche Buttercream and Poppy Seed Baked French Toast Casserole. An Easy Lemon Poppy Seed Cake offers a convenient option for home bakers. This cake often combines a lemon or yellow cake mix with instant vanilla pudding and poppy seeds.
Savory Dishes
Poppy seeds also find their way into many savory preparations. They are a crucial component of Everything bagel seasoning, which enhances various foods from crackers to salads. In Polish cuisine, people prepare Kluski z makiem, noodles with poppy seeds, often for Christmas. Obwarzanek krakowski, a ring-shaped bread from Kraków, gets sprinkled with poppy seeds before baking. Poppy seed bagels are also a well-known savory item. Chefs incorporate them into noodle dishes, such as Hungarian-Style Cabbage Noodles, for added texture and flavor. They can also provide a unique textural element when used in coatings for proteins.
Traditional Applications
Different cultures have unique traditional uses for poppy seeds. In Hungary, people enjoy Mákos guba, a bread dessert with leftover sweet white bread and crushed poppy seeds. Austrian strudels, both sweet and savory, often feature poppy seed paste. Czech koláče and Slovak makovník also use poppy seeds as a filling. In India, pulverized white poppy seeds thicken and flavor curries and stews. They are widely used in Andhra, Bengali, Oriya, and Malabar cuisines for thickening, texture, and flavor. A popular Bengali dish is aloo posto, made with potatoes and poppy seeds. Historically, ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Romans used poppy seeds for medicinal purposes, including as a sedative and pain reliever.
Poppy Seeds and Opioid Concerns
Many people worry about the opioid content in poppy seeds. This concern comes from the fact that poppy plants produce opioid alkaloids. These alkaloids can transfer to the seeds. Understanding these issues helps people make informed choices about poppy seed consumption.
Opioid Contamination
Opioid contamination in poppy seeds primarily comes from the natural presence of opiates. These opiates include morphine, codeine, and thebaine. They exist in the latex of maturing opium poppies. During harvesting, these opiates transfer onto the surface of the poppy seeds. Poor harvesting practices also contribute to contamination. For example, if insects damage the poppy plants, latex rich in opium alkaloids can touch the seeds. This increases the opioid content.
The levels of opioid alkaloids in commercially available poppy seeds vary greatly. Many factors influence these levels. These factors include the sub-varieties of Papaver somniferum L., the season, and weather conditions. Fertilizer type, country of origin, and specific growing conditions like shade or direct sunlight also play a role. Contamination from opium latex during growth and mixing seeds from different fields also cause wide variations.
Here is a look at typical alkaloid levels:
Alkaloid | Store-purchased (mg/kg) | Local Producers (mg/kg) | Other Studies (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
Morphine | 12.46–102.86 (highest 533) | 1.1–110.1 | 0.2–241, 3.6–261, 0.9–12.58, 30.55–57.94 |
Codeine | 0.25–37.05 | 1.3–24.3 | 0.39–6.14, 4.46–10.88, <0.1–348 |
Oripavine | 0.37–0.39 | <LOQ–5.7 | 5.3–9.1 |
Papaverine | <LOQ–4.21 | Not detected | 5.17–12.06, <0.1–3.8 |
Thebaine | <LOQ–32.67 | 1.1–68.8 | 7.59–21.03, 0.37–37.22, <0.1–106 |
Noscapine | 0.31–4.54 | 0.4–29.4 | 8.0–39.7, 0.3–6.83, 0.1–6.0 |
Morphine often appears at the highest concentration, typically between 30 and 45 mg/kg. Thebaine also shows relatively high levels, around 15–23 mg/kg, in both store-bought and locally sourced poppy seeds. Codeine content usually ranges from 5 to 10 mg/kg. Papaverine and oripavine are present in smaller amounts. Noscapine is found at about 15 mg/kg in seeds from local producers.
Another study shows these ranges:
Alkaloid | Source #2 (ng/g) | Source #7 (ng/g) |
|---|---|---|
Morphine | 2,638–63,994 | ND–4,754 |
Codeine | 474–23,307 | 2,361–14,607 |
Thebaine | 1,977–133,493 | N/A |
Noscapine | N/A | Highest levels |
Papaverine | Detected, but not quantifiable | N/A |
Several factors influence the level of opioid contamination in poppy seeds:
Geographical location where poppies grow.
Methods used to wash and process the seeds.
Terroir, which includes climate, soil, amount of sunshine, topography, and harvest time.
The specific variety or cultivar of the plant.
Processing methods like washing, cooking, or baking.
Cultivation and harvesting techniques.
Drug Test Implications
Even small amounts of opioid alkaloids from poppy seeds can lead to positive drug test results. This happens because drug tests detect the presence of these compounds. The amount of alkaloids varies widely in raw poppy seeds. Therefore, consuming foods with poppy seeds can sometimes cause false positives on drug screenings. This is a significant concern for individuals who undergo regular drug testing.
Safe Consumption Guidelines
To minimize risks, people should follow safe consumption guidelines for poppy seeds. European authorities consider 20 milligrams of morphine per kilogram of poppy seeds a safe level. The European Union set this standard in 2021. It established maximum opiate limits in poppy seeds and related products.
The United States is still developing its guidance. They expect to release it by December 2025. Currently, no specific limit exists in the U.S.
Country/Region | Regulatory Limit (Opiate Alkaloids) |
|---|---|
European Union | 20 milligrams per kilogram |
United States | Guidance under development, expected by December 2025 (no specific limit yet) |
People can also reduce the opioid content in poppy seeds through preparation. Washing, soaking, or grinding poppy seeds can reduce opiate content by 25% to 73%. Baking further degrades opiates. This process can lead to losses of up to 80-90% of the original opiate content. Oxidation and heat cause this reduction.
Experts generally recommend that foods containing up to about 50 grams of poppy seed can be eaten safely. This helps people enjoy the nutritional benefits of poppy seeds without undue concern. Always choose poppy seeds from reputable sources. This helps ensure better quality and lower contamination levels.
Health Benefits of Poppy Seeds
Poppy seeds offer many health benefits. Their rich nutrient and antioxidant profile provides specific advantages for the body.
Bone Health
Poppy seeds are excellent for bone health. They contain calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus. These minerals are crucial for strong bones and teeth. Calcium is a main part of bones. Phosphorus works with calcium to build and keep bone tissue. This helps prevent bone density loss as people get older. Magnesium also helps bones form. It makes sure calcium absorbs correctly. This makes bones stronger. Bones store about 60% of the body’s magnesium. This shows magnesium’s vital role in bone development. The combination of these minerals in poppy seeds supports strong and healthy bones. This helps reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
Heart Health
Poppy seeds offer many heart benefits. They contain healthy fats like polyunsaturated fatty acids (omega-6 and omega-3). These fats help manage bad cholesterol. They support a balanced lipid profile. This leads to better cardiovascular health. Research shows diets high in unsaturated fats can reduce heart attack and stroke risk by up to 17%. Magnesium in poppy seeds relaxes artery muscles. This improves blood flow. Potassium helps keep blood pressure healthy by balancing sodium. Dietary fibers also reduce harmful cholesterol. They link to healthy blood pressure levels. Oleic acid, an omega-9 fat, can also help moderate blood pressure. These components contribute to overall heart health.
Antioxidant Properties
Poppy seeds are rich in antioxidants. These compounds protect the body from cell damage. They can also guard against various diseases. Poppyseed oil, with its mono- and polyunsaturated fats, may benefit skin health. It can help wound healing. It may also prevent scaly skin when applied to the skin. The polyphenols in poppy seeds are rich in antioxidants. They may lower the risk of heart disease. These health benefits make poppy seeds a valuable addition to a balanced diet. Poppy seeds nutrition provides these protective elements.
Poppy seeds offer significant poppy seeds nutrition. They provide essential minerals, ample fiber, and healthy fats. People must understand the implications of poppy seed consumption, especially regarding opioid contamination and drug tests. Enjoy poppy seeds in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Always consider sourcing and preparation for optimal health. These versatile seeds enhance many dishes, adding both flavor and health value.
FAQ
What are poppy seeds?
Poppy seeds are tiny, oil-rich seeds from the opium poppy plant. People use them widely in cooking and baking. They add a nutty flavor and crunchy texture to many dishes.
What nutrients do poppy seeds provide?
Poppy seeds offer many nutrients. They contain essential minerals like calcium, magnesium, and iron. They also provide dietary fiber, protein, and healthy fats.
Can poppy seeds cause a positive drug test?
Yes, poppy seeds can cause a positive drug test. They contain trace amounts of opioid alkaloids. These alkaloids can show up on drug screenings.
How can people reduce opioid content in poppy seeds?
People can reduce opioid content by washing, soaking, or grinding poppy seeds. Baking also helps. These methods can lower the opiate levels significantly.
Are poppy seeds safe to eat?
Yes, poppy seeds are safe to eat in moderation. Experts recommend consuming up to about 50 grams safely. Always choose seeds from reputable sources.

