
Discover black currants, vibrant berries with a unique taste. These powerful superfruits offer exceptional vitamin C. They provide many other significant health benefits. This blog explores their nutritional profile. It also details their specific health advantages. Readers will find practical ways to enjoy black currants. These potent berries can enhance a diet. They contribute to a healthier lifestyle. Blackcurrants are a true health gem.
Key Takeaways
Black currants are very rich in Vitamin C. One cup gives you more than double your daily need.
These berries boost your immune system. They help your body fight off sickness.
Black currants are good for your heart and eyes. They also help reduce swelling in your body.
You can eat black currants fresh, frozen, or dried. Add them to many foods like smoothies or desserts.
Black currants have more Vitamin C than many other fruits. They also have special nutrients not found in other berries.
Black Currant Nutrition

Black currants are a nutritional powerhouse. They offer a wide array of vitamins, minerals, and beneficial plant compounds. Understanding their composition helps explain their significant health benefits.
Vitamin C Content
Black currants stand out for their exceptionally high concentration of vitamin C. A single cup of these berries provides 203 milligrams of vitamin C. This amount delivers an impressive 226% of the daily value. This makes black currants an excellent source of this vital nutrient. Vitamin C plays a crucial role in supporting the immune system. It also helps with collagen production, which is essential for healthy skin, bones, and connective tissues.
Consider how black currants compare to other common sources of vitamin C:
Food Item | Vitamin C Content (mg/100g) |
|---|---|
Blackcurrant | 183 |
Parsley | 178 |
Red Pepper | 120 |
Kiwi | 90 |
Lemon | 53 |
Orange | 50 |
Strawberry | 50 |
Cauliflower | 48 |
Potato | 20 |
Apple | 10 |
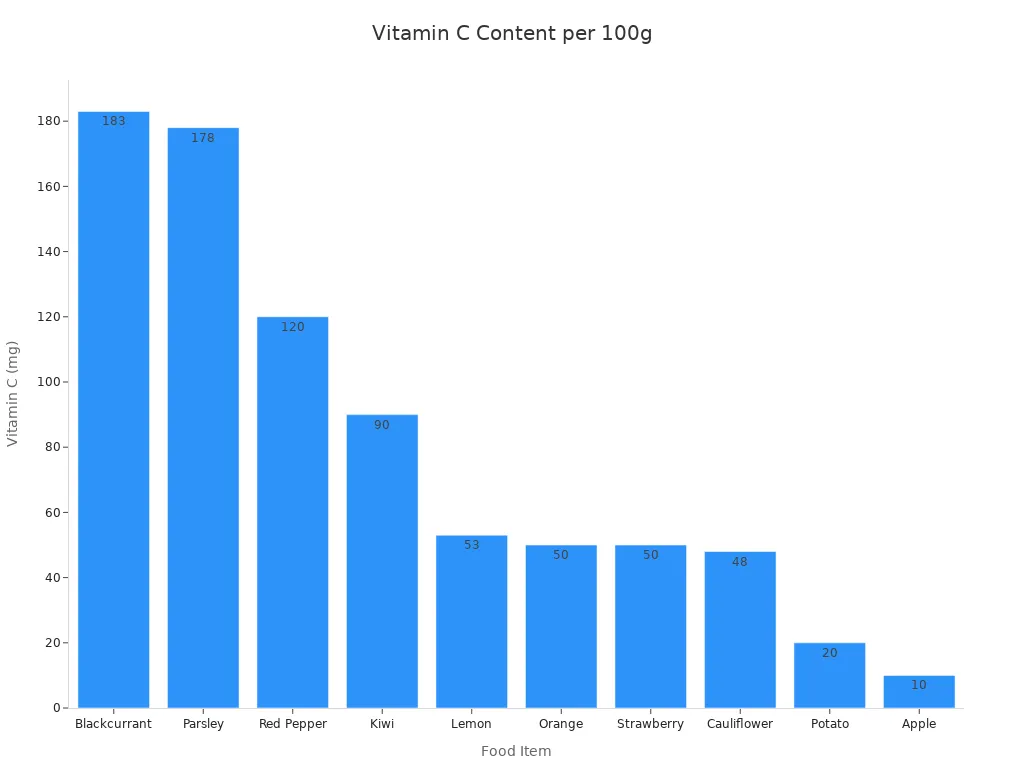
An 80-gram serving of blackcurrants provides 200% of a person’s daily vitamin C needs. Even a half-cup (56g) of black currants offers 113% of the daily value for vitamin C. Fresh black currants, at 100 grams, can provide more than 300% of the daily recommended intake values of vitamin C, specifically 301% for 181mg of vitamin C.
Other Key Nutrients
Beyond their remarkable vitamin C content, black currants are rich in nutrients. They offer a good source of vitamins and minerals vital for overall health.
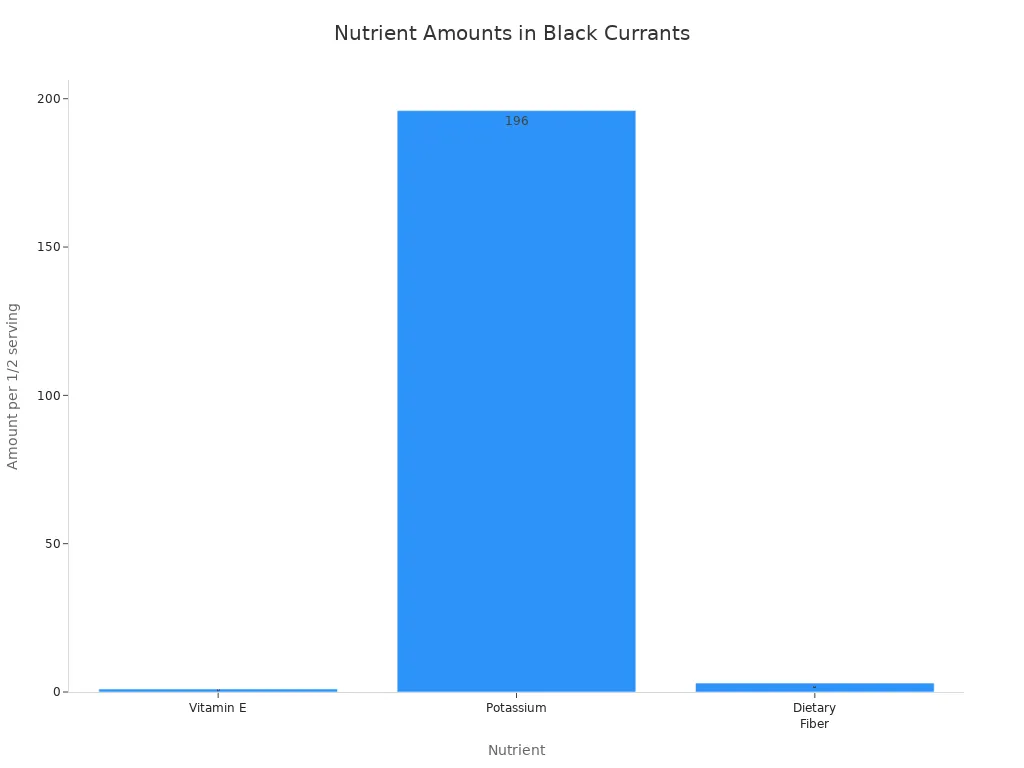
A typical serving of black currants provides:
Vitamin E: This vitamin acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage. A half-cup serving contains 1 mg of vitamin E.
Potassium: This mineral is important for maintaining healthy blood pressure and fluid balance. A cup (112g) of black currants contains 361 mg of potassium. A half-cup serving provides 196 mg. Dried black currants provide 14% of the daily requirements for potassium for adults.
Fiber: Black currants are a good source of dietary fiber. A cup contains 4.4 grams of fiber, which is 16% of the daily value. Fiber aids digestion and helps maintain gut health. A 1/2 cup serving of dried black currants provides approximately 20% of the recommended daily allowance of fiber.
Calcium: This mineral is crucial for strong bones and teeth.
Iron: Black currants contain iron, with 1.54 grams per cup. Iron is essential for oxygen transport in the blood.
Protein: A cup of black currants provides 1.6 grams of protein.
Carbohydrates: They contain 17 grams of carbohydrates per cup (112g), providing energy.
Here is a summary of some key nutrients in a half-cup serving:
Nutrient | Amount per 1/2 serving |
|---|---|
Vitamin E | 1 mg |
Potassium | 196 mg |
Dietary Fiber | 3 g |
Phytochemicals and Antioxidants
The vibrant color and potent health benefits of black currants come from their rich array of phytochemicals and antioxidants. These compounds protect the body from oxidative stress and inflammation.
Primary phytochemicals present in black currants include:
Polyphenols
Anthocyanins
Flavonoids
Flavonols (quercetin, myricetin, kaempferol)
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (linoleic acid, oleic, γ‐linolenic, α‐linolenic, stearidonic)
Tannins
Organic acids (citric acid)
The antioxidant content of blackcurrants is particularly impressive. They contain a variety of powerful antioxidant compounds:
Anthocyanins
Vitamin C
Catechins
Sinapinic acid
Rutin
Hesperidin
p-Coumaric acid
Ferulic acid
Caffeic acid
Myricetin
Quercetin
Isorhamnetin
Kaempferol
These compounds work together to provide comprehensive protection for the body. They contribute to the overall health-promoting properties of these amazing berries.
Health Benefits of Black Currants
Black currants offer many impressive health benefits. These small berries pack a powerful nutritional punch. They support various body systems. Understanding these advantages shows why black currants are a true superfruit.
Immune System Boost
Black currants are excellent for strengthening the body’s defenses. They help boost the immune system. Their high vitamin C content is a major factor. Vitamin C helps the body fight off illnesses.
Specific compounds in black currants also play a role. A polysaccharide from black currant, called CAPS, strengthens the immune system. It does this by stimulating dendritic cells. This process activates immune responses and releases important immune signals. Black currant seed oil (BCSO) also enhances immune responses, especially in older adults. It improves how T cells function. This leads to better immune reactions in the body.
Several studies support these immune-boosting effects:
A study looked at black currant seed oil. It found the oil helped the immune response in healthy older people.
Research showed blackcurrant extract has anti-inflammatory properties. It changes how immune cells called macrophages behave.
Scientists found blackcurrant anthocyanins can reduce allergic airway inflammation.
Another study showed blackcurrant extract helps manage stress from exercise. It also reduces inflammatory responses.
These findings show how black currants effectively boost the immune system.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Black currants possess strong anti-inflammatory properties. These properties help reduce inflammation throughout the body. This can be beneficial for various conditions.
Black currants are rich in natural compounds that fight inflammation. They contain anthocyanins, which are powerful anti-inflammatory agents. They also provide gamma-linolenic acid (GLA). GLA is a beneficial omega-6 fatty acid found in the seeds. Both anthocyanins and GLA work together to support a healthy inflammatory response. This can help with joint and muscle pain. These bioactive compounds make black currants effective in helping the body reduce inflammation.
Heart Health Support
Black currants may help improve heart health. They contain compounds that support the cardiovascular system. Anthocyanins from blackcurrants have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. These properties are vital for preventing chronic diseases, including heart disease. Eating black currants can reduce oxidative stress. They can also improve blood fat levels. These effects lower the risk of heart disease.
Blackcurrants contain important polyphenols. These include four main anthocyanins:
Cyanidin-3-glucoside
Cyanidin-3-rutinoside
Delphinidin-3-glucoside
Delphinidin-3-rutinoside
Cyanidin-3-rutinoside and delphinidin-3-rutinoside are the main ones. These compounds improve how blood vessels work. They increase nitric oxide production, which helps blood vessels relax. They also stop the production of endothelin-1, a substance that narrows blood vessels.
However, research on blood pressure is mixed. A review of ten studies looked at blackcurrant and raspberry consumption. It found that blackcurrant consumption did not significantly lower blood pressure. More studies are needed to fully understand its impact on blood pressure.
Vision and Eye Health
Black currants offer significant benefits for eye health. They contain several nutrients that protect the eyes.
Key nutrients in black currants for eye health include:
Anthocyanins: These compounds give black currants their deep color. They improve night vision. They also protect against eye strain from screens and pollution. Anthocyanins fight oxidative stress in the retina.
Vitamin C: This natural antioxidant supports overall eye health.
Vitamin E: This vitamin is also known for its role in eye health.
Gamma-linolenic acid (GLA): This omega-6 fatty acid helps with conditions like dry eye. It helps the eyes produce more tears, keeping them moist and comfortable. It may help with dry eyes.
Studies show black currant extract can protect retinal cells from damage. It reduces harmful reactive oxygen species. It also stops the buildup of lipofuscin, a waste product linked to eye aging. These findings suggest black currant extract may help prevent and treat dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD). The berries’ antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties can improve retinal health. They may slow AMD progression.
Digestive Health
Black currants contribute to a healthy digestive system. They are a good source of dietary fiber.
Here is the fiber content:
Serving Size | Fiber Content |
|---|---|
1 cup (fresh) | Around 4g (approximately 16% of daily recommended intake) |
1/2 cup (dried) | Approximately 20% of daily recommended allowance |
Fiber is essential for regular bowel movements. It also supports a healthy gut.
Black currants can also influence the gut microbiome. One study found blackcurrants led to more short-chain fatty acids in the gut. These acids are beneficial for gut health. Another study showed daily blackcurrant consumption changed gut bacteria. It increased specific bacteria linked to bone mineral density. This suggests black currants can improve health through specific changes in gut bacteria.
Incorporating Black Currants
People easily add black currants to their daily diet. They come in various forms. This makes them versatile for many uses.
Fresh, Frozen, and Dried Options
Black currants are available fresh during their season. People can also enjoy them year-round in other forms. Freezing is a simple way to preserve them. Remove leaves and wash the berries. Store them in lidded containers for quick freezing. They keep their taste well. Jam and jelly are common preservation methods. For long-term storage at room temperature, people can process black currants by washing them. Then, cover them with water and blend them into a slurry. Screen this through a food mill. Place the mixture in one-liter jars for pressure canning. Use 15 PSI for 15 minutes. Drying black currants also extends their shelf life. Use a dehydrator or an oven. Dried berries work well in desserts, snacks, and drinks.
Culinary Uses and Recipes
Black currants offer a unique flavor. They enhance many dishes. People use them in savory main courses. Examples include quick peppered duck with black currant sauce or roast chicken with black currant gravy. Blackcurrants also appear in drinks. Try old fashioned black currant lemonade or homemade black currant liqueur. Black currant juice is popular in Italian sodas. Blackcurrant fruit juice makes a great hot drink for colds. For breakfast, people enjoy black currant doughnuts, pancakes, or muffins. Desserts like black currant shortbread bars, pavlova, and ice cream are also favorites. A black currant powder can also be added to smoothies for a nutritional boost.
Black Currant Supplements
For those seeking a concentrated form, black currant supplements are available. These often come as capsules or black currant powder. Supplements offer a convenient way to get the berries’ benefits. They provide a consistent dose of nutrients.
Blackcurrants vs. Other Berries

Blackcurrants offer a unique nutritional profile. They stand out among other popular berries. This section compares blackcurrants to common berries. It highlights their distinct advantages.
Vitamin C Comparison
Blackcurrants are true champions for vitamin C content. They contain a very high amount of this essential vitamin. Blackcurrant has 50 to 280 mg of ascorbic acid per 100 grams. This makes them an exceptional source.
Consider how blackcurrants compare to other popular berries:
Berry Type | Vitamin C Content |
|---|---|
Black Currant | Very High (~200mg) |
Blueberry | Moderate (~14mg) |
Raspberry | Less than half of fresh/frozen (when dried) |
Dried black currants have less than half the vitamin C of fresh or frozen ones. Frozen black currants offer a high-bioavailable way to exceed daily needs. Blackcurrants contain 203 mg of vitamin C per cup. Oranges are a well-known source of vitamin C. However, blackcurrants provide a higher amount per serving.
Unique Antioxidant Profiles
Black currants also boast a powerful antioxidant profile. Their deep color comes from anthocyanins. These compounds provide strong antioxidant benefits. The ORAC value measures antioxidant capacity. Blackcurrants have a high ORAC value.
Berry Type | ORAC Value |
|---|---|
Elderberry | 14,697 |
Haskap | 11,000? |
Wild Blueberry | 9,621 |
Cranberry | 9,090 |
Black Currant | 7,957 |
Blackberry | 5,905 |
Jostaberry | 5,650? |
Red Raspberry | 5,065 |
Blueberry | 4,669 |
Strawberry | 4,302 |
Red Currant | 3,387 |
Gooseberry | 3,332 |
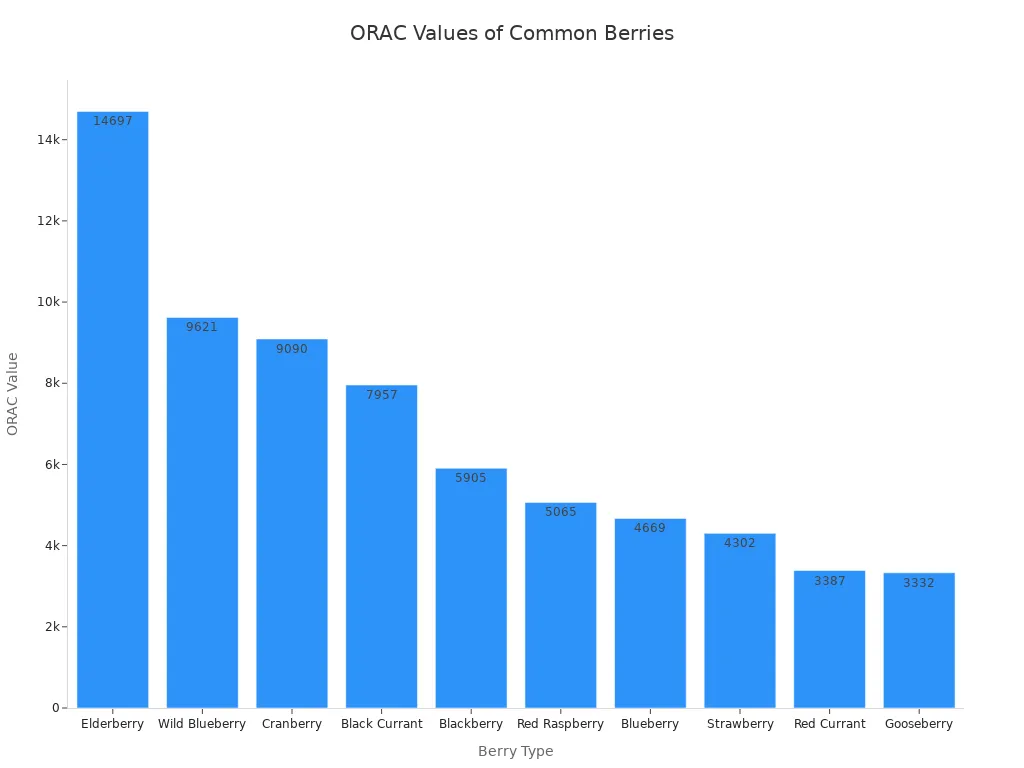
Black currants rank high among berries for antioxidant power.
Overall Nutritional Advantages
Blackcurrants offer several nutritional advantages. They surpass many other berries in key areas.
Nutritional Aspect | Black Currants (per cup) | Strawberries (comparison) |
|---|---|---|
Vitamin C | 203 mg (226% DV) | Significantly lower than black currants; black currants have more than twice the vitamin C of a large orange, and surpass many other berries. |
Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA) | Rich source | Not mentioned as a significant component |
Antioxidants | Rich in anthocyanins, polyphenols | Rich in antioxidants, but GLA is a unique advantage of black currants. |
Blackcurrants are remarkably rich in vitamin C. They surpass many other berries, including popular choices like blackberries and raspberries. They also provide Gamma-Linolenic Acid (GLA). This is a unique fatty acid not commonly found in other berries.
Comparing blackcurrants to cranberries shows further differences:
Nutrient | Cranberry (per 100g) | Currant (per 100g) |
|---|---|---|
Calories | 46 | 56 |
Total Carbs | 12g | 13.8g |
Dietary Fiber | 3.6g | 4.3g |
Sugar | 4.3g | 7.4g |
Protein | 0.46g | 1.4g |
Saturated Fat | 0.01g | 0.02g |
Vitamin C | 14mg | 41mg |
Vitamin A | 3ug | 2ug |
Vitamin E | 1.3mg | 0.1mg |
Vitamin K | 5ug | 11ug |
Thiamin (B1) | 0.012mg | 0.04mg |
Riboflavin (B2) | 0.02mg | 0.05mg |
Niacin (B3) | 0.101mg | 0.1mg |
Pantothenic Acid | 0.295mg | 0.064mg |
Vitamin B6 | 0.057mg | 0.07mg |
Folate (B9) | 1ug | 8ug |
Calcium | 8mg | 33mg |
Iron | 0.23mg | 1mg |
Potassium | 80mg | 275mg |
Beta-carotene | 38ug | 25ug |
Lutein + Zeaxanthin | 91ug | 47ug |
Alpha Linoleic Acid (Omega-3) | 0.022g | 0.035g |
Linoleic Acid (Omega-6) | 0.033g | 0.053g |
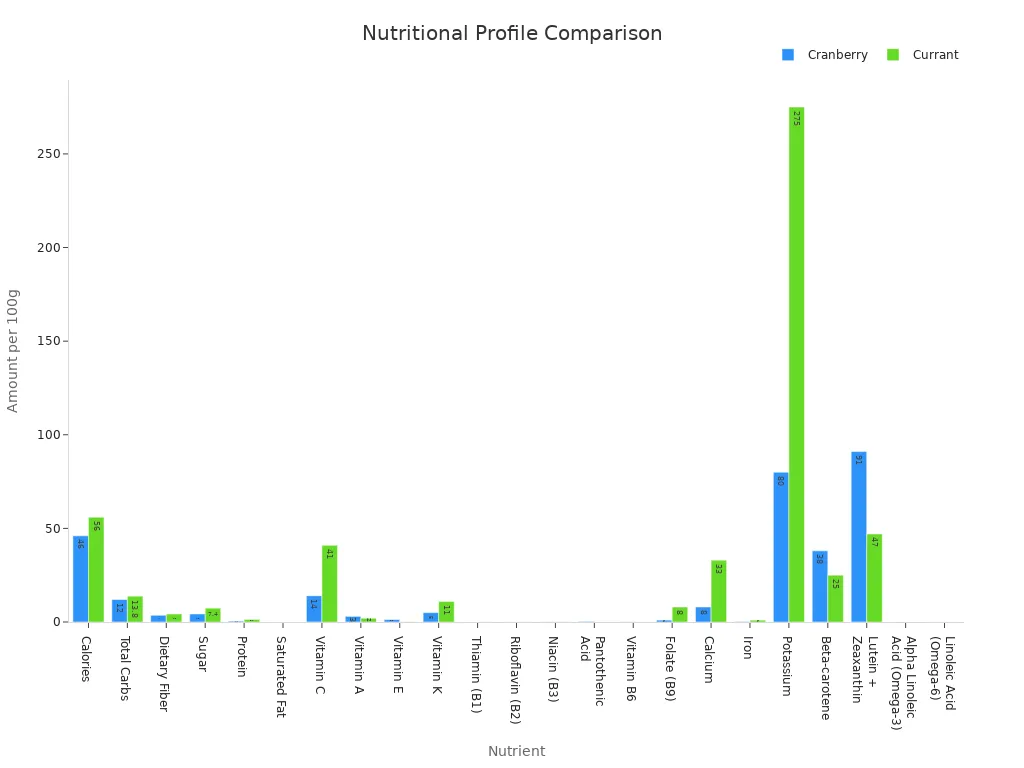
Both cranberries and black currants are rich in vitamin C and dietary fiber. Black currants generally contain more thiamin, riboflavin, and folate. They are a notable source of potassium, calcium, and iron. Black currants offer a comprehensive nutritional advantage.
Black currants are a nutritional powerhouse. They offer many health benefits. Their high vitamin C content is especially notable. This essential vitamin supports overall health. Incorporate these nutrient-dense berries into a balanced diet. This enhances immunity, reduces inflammation, and promotes overall well-being. Explore the versatility of blackcurrants in your culinary endeavors. Embrace these powerful berries for a healthier lifestyle. The benefits of blackcurrants are clear.

