
You may know the apple of sodom as a mysterious plant with the scientific names Calotropis procera and Solanum incanum. People often recognize it for its pale green leaves, thick stems, and unusual fruit, but also for its dangerous reputation.
Scientific Name | Common Names |
|---|---|
Calotropis procera | Apple of Sodom, Sodom apple, roostertree, king’s crown, small crownflower, giant milkweed, rubber bush, rubber tree |
This plant grows in dry regions and stands out for both healing uses and toxic effects. You should understand its benefits and risks before handling it.
Key Takeaways
The Apple of Sodom, known scientifically as Calotropis procera, is a shrub found in dry regions. It has unique features like pale green leaves and swollen fruit.
This plant has both medicinal uses and toxic effects. It can help with digestive issues but contains dangerous compounds that can harm humans and animals.
Always handle the Apple of Sodom with care. Wear gloves and protective clothing to avoid skin irritation and eye damage from its toxic latex.
The plant can become invasive, spreading easily and displacing native vegetation. Consider its risks before using it in landscaping or agriculture.
Consult an expert before using any part of the Apple of Sodom for medicinal purposes. Its toxicity can lead to serious health problems.
Apple of Sodom Overview

Appearance
You can identify the apple of sodom by looking at its unique features. Calotropis procera grows as a shrub that reaches up to 5 meters tall. Its stems appear straight or twisted and have a whitish color. The leaves look glaucous and almost round. You will see white flowers with purple tips grouped in clusters. The fruit stands out as a large, swollen follicle that measures between 3 and 10 centimeters. When you touch the fruit, it may dissolve into smoke or explode because it is air-filled.
Solanum incanum looks different. This plant has spiny stems and ovate leaves. It produces clusters of purple flowers. Its fruit starts green and turns yellow or orange when ripe. The branches grow thorny, and the leaves feel soft. You can compare their features in the table below:
Characteristic | Calotropis procera | Solanum incanum |
|---|---|---|
Height | Shrub, 2 to 5 m high | N/A |
Stems | Straight, sometimes tortuous, whitish | Spiny stems |
Leaves | Glaucous, sessile, oblong-obovate to orbicular | Ovate leaves |
Flowers | White with purple tips, in clusters | Purple flowers in clusters |
Fruit | Swollen follicles, 3 to 10 cm, ovoid, air-filled | Small, round berry, green to yellow/orange when ripe |
Flowering and fruiting times change by region. In Western Australia, you see flowers from January to May and August to October. In South Australia, flowering happens from October to April. The fruit is toxic in both places.
Habitat
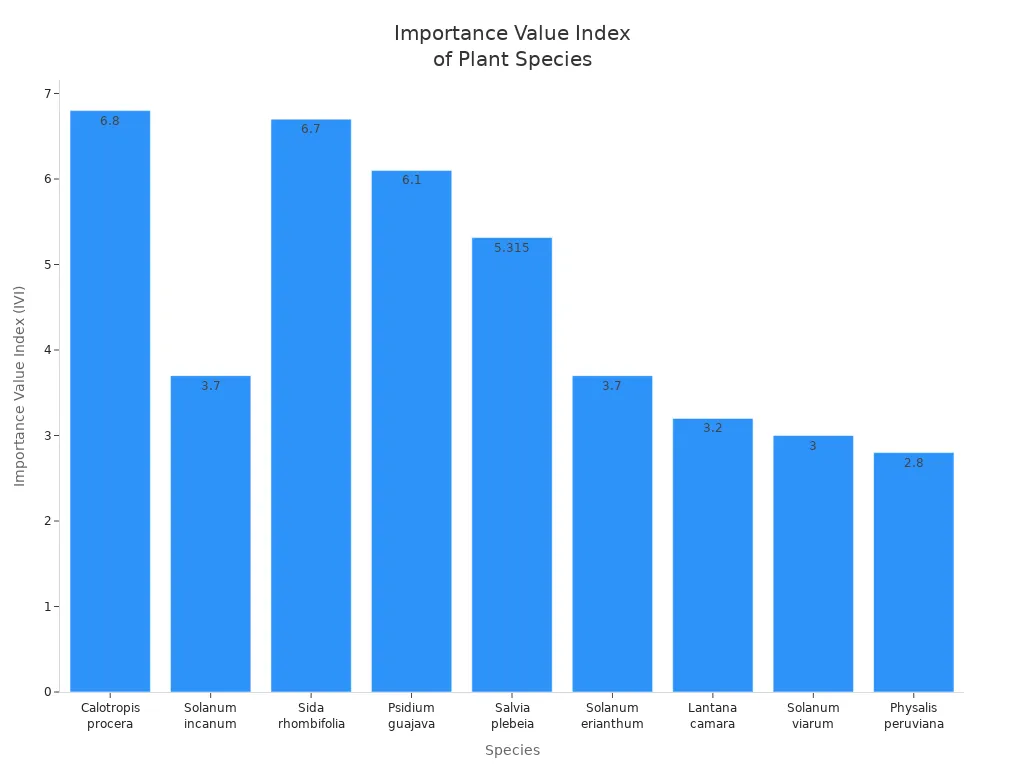
You find the sodom apple in dry and semi-arid regions. The plant grows well in continental Asia, northern Africa, and places like the Pacific Islands, Australia, and South America. Calotropis procera and solanum incanum show strong drought and salt tolerance. Their adaptations help them survive harsh climates. The chart below shows how important these species are in their habitats:
You may notice that the apple of sodom can become invasive. Its seeds spread easily by birds, water, and livestock. The plant can displace native vegetation and restrict recreational use of coastal areas. Seeds live long and help the species invade new places.
Tip: If you consider cultivation or landscaping uses, remember the invasive nature and toxic risks of this plant.
Related Species
You may hear about other related species in the solanum family. Solanum linnaeanum is closely related to solanum incanum. Taxonomists classify it in the Solanaceae family. You can see similar features in devil’s apple and narrawa burr, but their fruit color and stem hair differ. Calotropis procera belongs to a different family but shares the common name “sodom apple” due to its toxic fruit.
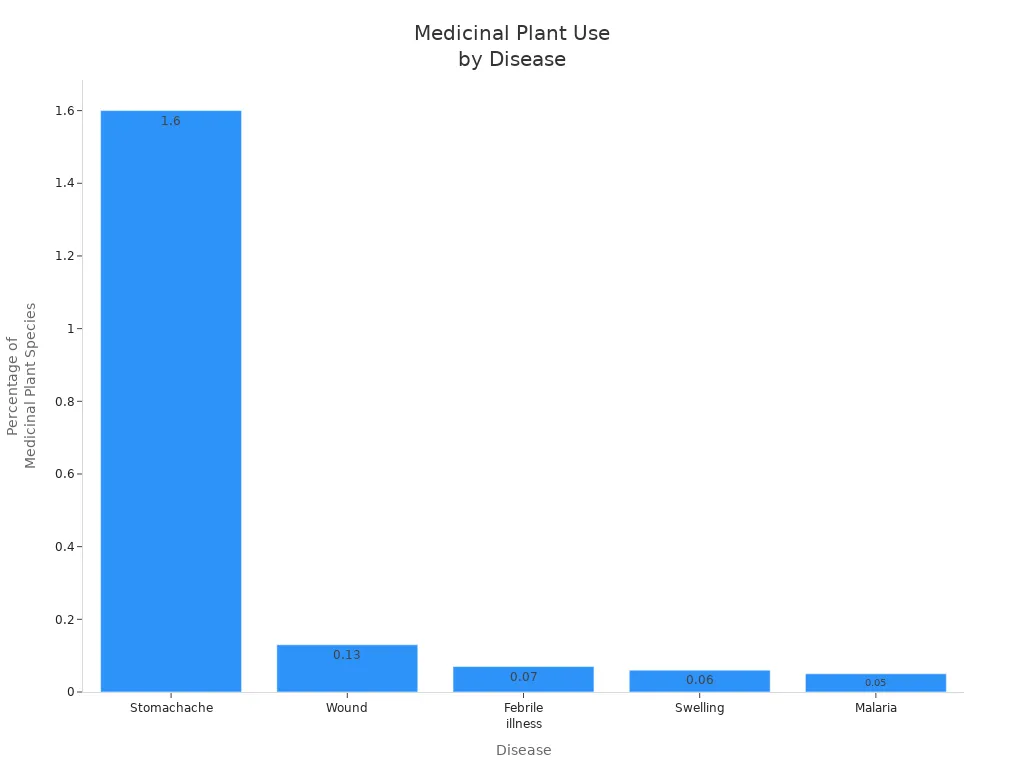
Sodom Apple Uses
Traditional Medicine
You may find the apple of sodom in many traditional medicine systems. In India, people call calotropis arka and use it for a wide range of health problems. The plant shows strong medicinal properties, especially for digestive disorders. In Ayurveda, calotropis procera helps support digestive wellness. You can use it to stimulate digestion and relieve bloating. The herb acts as a powerful laxative, helping cleanse the bowels and eliminate parasites.
You may see these common uses in Ayurveda:
Stimulate digestion
Relieve bloating
Cleanse bowels
Eliminate parasites
People in India and other regions use sodom apple for many ailments. The table below shows some traditional medicinal uses:
Medicinal Use | Region(s) of Use |
|---|---|
Snake bite | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Body pain | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Asthma | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Epilepsy | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Cancer | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Sexual disorders | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Skin diseases | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Wounds | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Scabies | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Sores | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
External infections | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Swellings | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Rheumatic pains | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Leprosy | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Toothaches | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Eczema | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Paralyzed limbs | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Cough | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Diarrhea | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Malaria | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Dysentery | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
Jaundice | India, Africa, Saudi Arabia, Yemen |
You may prepare sodom apple for medicinal use in several ways. Here is a common method:
Coat the large, sturdy leaves with a carrier oil, such as sesame or castor oil.
Warm the leaves over a flame or in a dry pan until soft and fragrant.
Apply the warm leaves directly to the painful or swollen area and secure with a cloth.
Note: You should always consult a qualified expert before using any plant for medicinal purposes.
Cultural Significance
You may notice that sodom apple holds a special place in cultural and religious stories. The fruit often appears in myths and ancient texts. In the Hebrew Bible, the Vine of Sodom is described as having toxic and bitter fruit. Josephus, a historian, wrote that the fruit looks beautiful but turns to smoke and ashes when touched. Many people believe the plant symbolizes deception and the dangers of superficial beauty.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Symbolism | Represents deception and superficial allure of sin, rooted in biblical narratives. |
Biblical Connection | Associated with the cities of Sodom and Gomorrah, symbolizing moral and spiritual corruption. |
Theological Implications | Serves as a reminder of the transient nature of worldly allurements and the emptiness of sin. |
Modern Interpretations | Continues to illustrate dangers of pursuing superficial desires that lead to spiritual emptiness. |
Source | Description |
|---|---|
Hebrew Bible | The Vine of Sodom is mentioned in Deuteronomy 32:32, describing its toxic and bitter fruit. |
Josephus | Describes the plant’s fruit as beautiful but disintegrating into smoke and ashes when touched. |
Botanical Identification | The plant is likely calotropis procera or citrullus colocynthis, both known for their attractive yet bitter fruits. |
You may see sodom apple used in rituals or as a symbol in art and literature. The plant reminds people of the risks of chasing beauty without substance.
Modern Perspectives
Today, you may find sodom apple used in medicine, agriculture, and industry. Researchers study calotropis procera for its pharmacological benefits. The plant appears in traditional medicine systems and shows promise for new treatments. In agriculture, people use sodom apple for fodder and phytoremediation. The plant helps clean contaminated soils by absorbing heavy metals. In industry, you may see uses in food, textile, and paper production. The plant also provides timber and fiber.
Field | Uses |
|---|---|
Medicine | Explored for potential pharmacological applications and widely used in traditional medicine systems. |
Agriculture | Utilized as fodder and for phytoremediation. |
Industry | Applications in food, textile, and paper industries; also used for timber and fiber production. |
You may use sodom apple in compost and land management. Calotropis procera can accumulate heavy metals from soil, which helps manage pollution. The plant uses mechanisms like phytoextraction and rhizo-filtration to clean soil and water. However, heavy metal accumulation can cause health problems, so you should manage soil contamination carefully.
Evidence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Phytoaccumulation | Calotropis procera can accumulate heavy metals from contaminated soils, impacting soil health. |
Mechanisms | Plants use phytoextraction, rhizo-filtration, and phyto-stabilization to manage heavy metals. |
Health Implications | Heavy metal accumulation can lead to diseases, so managing soil contamination is important. |
Tip: If you consider sodom apple for landscaping or environmental uses, you should weigh the benefits against possible risks to health and the ecosystem.
Toxicity and Precautions

Toxic Compounds
You will find that the apple of sodom contains several dangerous chemicals. The most important group is glycoalkaloids. These are nitrogen-containing steroidal glycosides. Glycoalkaloids are common in plants from the Solanum genus. They are biologically active and can cause serious problems for humans and animals.
Evidence | Description |
|---|---|
Toxicity | The Sodom apple contains steroidal glycoalkaloids that are toxic to humans and livestock. |
Physiological Effects | These glycoalkaloids can cause gastrointestinal irritation and nervous system impacts, potentially leading to severe symptoms and death. |
You should know that glycoalkaloids are more poisonous than other types of plant alkaloids. Both humans and livestock can get sick from eating sodom apple fruit or leaves. Glycoalkaloids do not absorb well in the stomach, but large amounts can still cause poisoning. The latex from calotropis procera is also a strong irritant. It can harm your skin and eyes if you touch it.
Health Risks
You face many risks if you touch or eat parts of this plant. The toxicity of sodom apple affects people, pets, and farm animals. Even small amounts can cause trouble. You may see symptoms like stomach pain, vomiting, and diarrhea. In some cases, the toxins affect the nervous system and can cause confusion, weakness, or even death.
A 2011 study on sheep showed that eating sodom apple led to:
Emphysema
Pneumonia
Bleeding ulcers
Brain swelling
Death
Reports from hospitals describe 29 patients who got latex from calotropis procera in their eyes. Most had sudden, painless loss of vision, red eyes, and swelling of the cornea. Some developed iridocyclitis and secondary glaucoma. Over 80% had vision worse than 20/60.
Children, pets, and livestock are at the highest risk. You should keep them away from the plant at all times. The latex acts as a strong irritant and can cause severe reactions on contact.
⚠️ Warning: Never eat any part of the apple of sodom. Avoid touching the latex or sap with bare skin.
Safe Handling
You must take special precautions when dealing with this plant. Wear gloves and protective clothing if you need to remove or handle sodom apple. Wash your hands and tools after contact. If you get latex on your skin or in your eyes, rinse with plenty of water and seek medical help right away.
Safe disposal methods include:
Burning, slashing, or crushing old plants.
Spraying young shoots with 2,4-D herbicide at the flowering stage.
You should never compost sodom apple in a regular garden pile. The toxins can remain in the soil and harm other plants or animals. Always consult a local expert before using any part of the plant for medicinal or other uses.
Note: Proper handling and disposal protect you, your family, and the environment from the dangers of this toxic plant.
You learned what makes the apple of sodom unique and dangerous.
This plant, called calotropis in many regions, grows as a perennial shrub in dry areas.
You can spot it by its pale leaves and swollen fruit.
The plant contains toxic compounds like cardenolides and alkaloids, which can harm your organs and nervous system.
Always handle the apple of sodom with care. You should ask an expert before using or touching any part of this plant.
FAQ
What is the main danger of touching the Apple of Sodom?
You risk skin irritation and eye damage if you touch the latex or sap. The plant contains toxic chemicals that can harm you quickly. Always wear gloves and wash your hands after handling.
What does the fruit of calotropis look like?
You see large, swollen, air-filled pods. The fruit measures about 3 to 10 centimeters. When you touch it, the pod may burst or dissolve into smoke. The fruit looks attractive but is highly toxic.
What should you do if a child or pet eats part of the plant?
You need to seek medical help right away. The toxins can cause vomiting, diarrhea, and confusion. Quick action helps prevent serious health problems.
What are the traditional uses of the Apple of Sodom?
You find the plant used in Ayurveda and folk medicine. People use it for digestive issues, skin diseases, and pain relief. Always consult an expert before trying any remedy.
What makes the Apple of Sodom invasive?
You notice the seeds spread easily by birds, water, and livestock. The plant grows fast and can take over dry regions. It often replaces native plants and disrupts local habitats.

