
Cheonggukjang is a traditional Korean fermented soybean paste. It features a distinct rapid fermentation process and a strong, unique aroma compared to other soybean pastes. This Korean fermented bean paste holds significant cultural importance. People recognize cheonggukjang for its growing health benefits. The global market for fermented bean paste products shows strong growth.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
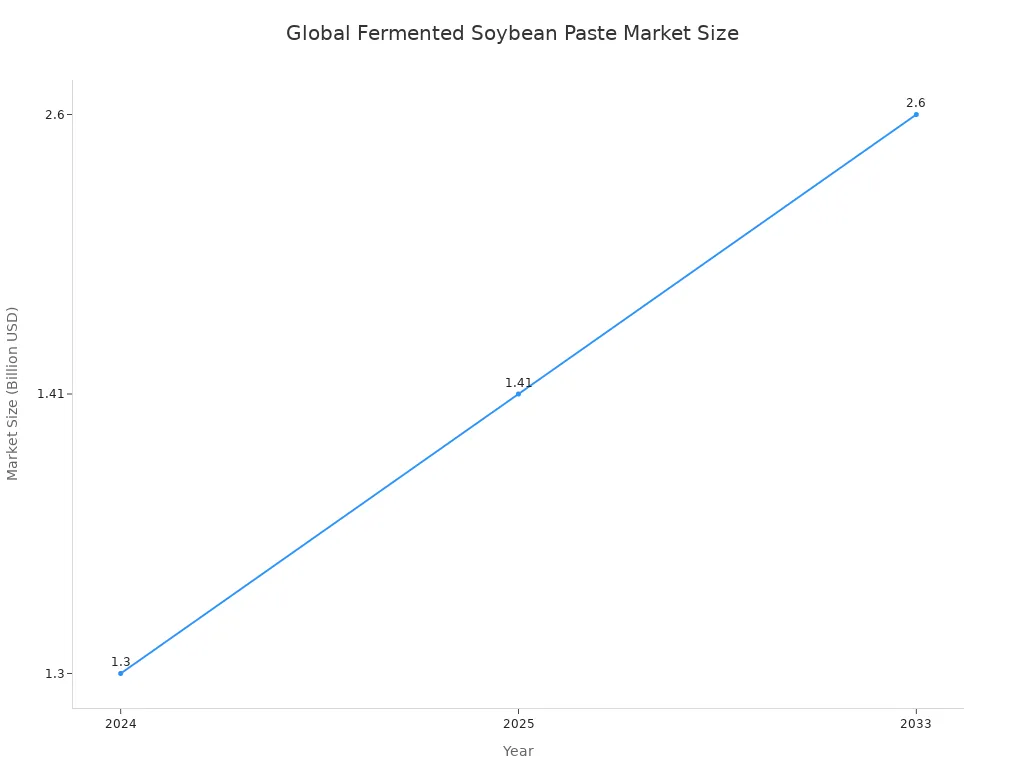
Global Fermented Bean Paste Market Size (2024) | USD 6.21 billion |
Projected CAGR (2025-2033) | 5.8% |
Estimated Market Value (2033) | USD 10.37 billion |
Experts estimate this market size at USD 6.21 billion in 2024. They project it to reach USD 10.37 billion by 2033. The broader global soybean paste market also grows steadily, with cheonggukjang contributing to this expansion.
Key Takeaways
Cheonggukjang is a Korean fermented soybean paste. It has a strong smell and a rich, savory taste.
Making Cheonggukjang involves soaking and boiling soybeans. Then, special bacteria ferment them quickly.
Cheonggukjang is often used in stews. It adds a unique flavor to Korean dishes.
Eating Cheonggukjang is good for your health. It helps your gut, boosts your immune system, and can help manage weight.
What is Cheonggukjang: A Fermented Soybean Paste

Cheonggukjang stands out as a unique Korean fermented soybean paste. Its distinct characteristics come from a rapid fermentation process. This process gives it a strong, earthy aroma. People often recognize cheonggukjang for this powerful smell. It also offers a rich, savory flavor.
How Cheonggukjang is Made
Making cheonggukjang involves a specific method. First, people soak soybeans in water. Then, they boil the soybeans until they become soft. After boiling, they drain the soybeans and place them in a warm, humid environment. This environment encourages rapid fermentation.
The fermentation process relies on specific microorganisms. Bacillus strains are the main microbes involved. Scientists have detected a vast diversity of Bacillus species. Bacillus thermoamylovorans is often the most abundant. Other important species include Bacillus licheniformis, Bacillus glycinifermentans, and Bacillus subtilis. These probiotic Bacillus strains are crucial. They produce enzymes like proteases and lipases. These enzymes enhance the flavor and nutritional value of the fermented soybean paste.
The fermentation time for cheonggukjang is relatively short. Some recipes suggest a maximum of three days. However, some people extend this to four or five days. A scientific study observed moisture content increasing within the first 48 hours of fermentation. Microorganisms from rice straw often transfer naturally to the boiled soybeans. Bacillus subtilis is a primary bacterium driving this fermentation. Other Bacillus species, such as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and Bacillus circulans, also contribute.
Cheonggukjang vs. Doenjang
Cheonggukjang and Doenjang are both Korean fermented soybean pastes. They share soybeans as their main ingredient. However, their fermentation processes and resulting characteristics differ significantly.
Component | Cheonggukjang | Doenjang |
|---|---|---|
Protein | Higher | Lower |
Fat | Higher | Lower |
Isoflavone | Higher | Lower |
Isoflavone Bioavailability | Excellent | N/A |
Cheonggukjang typically has higher levels of protein, fat, and isoflavones. Its isoflavones also show excellent bioavailability.
The starter cultures for these two pastes are different. For cheonggukjang, microorganisms from rice straw or the air naturally ferment the boiled soybeans. Bacillus subtilis is a key bacterium in this process. Doenjang fermentation begins with meju. Meju is a block of fermented soybeans. It contains diverse microorganisms. Initially, Weissella is common before meju fermentation. Then, Bacillus becomes dominant in high-temperature meju. Lactic acid bacteria like Weissella and Latilactobacillus dominate in low-temperature meju. During the final Doenjang fermentation, Leuconostoc, Logiolactobacillus, and Tetragenococcus become prevalent. Fungi like Mucor and Debaryomyces also play roles.
Cheonggukjang undergoes a rapid, short-term fermentation. This process gives it a strong, pungent aroma. Doenjang, on the other hand, ferments for a longer period. This results in a milder, more savory flavor and a less intense smell. People often use cheonggukjang in stews. Doenjang finds use in a wider range of dishes, including soups, marinades, and dipping sauces.
Uses of Cheonggukjang in Cooking

Cheonggukjang plays a central role in Korean cuisine. People value its deep, savory flavor and unique aroma. It adds a distinct character to many dishes.
Cheonggukjang Stew
Cheonggukjang is most frequently used to prepare a stew. This stew is often simply called ‘cheonggukjang’. To avoid confusion, people may also refer to it as ‘cheonggukjang jjigae’. This hearty stew is a staple in Korean homes. It offers a comforting and nutritious meal.
A typical cheonggukjang stew includes various ingredients. People often use 190g of cheonggukjang as the base. They add beef, about 190g, for richness. Other common components include soybean paste, crushed garlic, and half an onion. Shiitake mushrooms, anchovies, and Cheongyang red pepper provide depth and spice. Young squash and tofu also find their way into the stew. Some recipes also call for chopped kimchi and kimchi brine. These ingredients create a complex and satisfying flavor profile.
Other Culinary Applications
While stew is its most famous application, people use cheonggukjang in other ways. Some cooks incorporate it into marinades for meat. Its strong flavor can tenderize and season effectively. Others mix it into dipping sauces. This adds a pungent, umami kick to fresh vegetables or grilled items. People also experiment with cheonggukjang in stir-fries. It can provide a unique fermented taste to various vegetable and meat combinations.
Cooking Tips
When cooking with cheonggukjang, consider its strong aroma. Some people find it intense. To reduce the smell, you can cook it in a well-ventilated area. You can also add aromatic vegetables like garlic and onions. These help balance the flavor. Always taste the cheonggukjang before adding salt. Its natural saltiness varies. A little goes a long way due to its concentrated flavor.
Tip: For a milder flavor, combine cheonggukjang with a small amount of doenjang in your stew. This can introduce a familiar taste while still enjoying the benefits of cheonggukjang.
Health Benefits of Cheonggukjang
Cheonggukjang offers many health advantages. Its unique fermentation process creates a powerhouse of nutrients and beneficial compounds. People recognize the health benefits of cheonggukjang for its positive impact on various bodily systems.
Gut Health and Digestion
Cheonggukjang significantly supports gut health. It contains beneficial bacteria from its fermentation. These microbes improve gut microbiota composition. They increase helpful bacteria and decrease harmful ones. Studies show that digested cheonggukjang influences human microbiota. Researchers assess this through in vitro fecal fermentation.
Cheonggukjang supplementation improves gut microbiota. It increases beneficial bacteria. It also decreases harmful bacteria. A reduction in the Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio has been noted. This change is not always statistically significant. Cheonggukjang consumption changes gut microbiota composition. It also alters isoflavone-metabolite profiles. These changes depend on an individual’s enterotype. People with a Ruminococcaceae-rich enterotype show more changes. This highlights the need for personalized nutritional guidance. Cheonggukjang is excellent for aiding in digestion.
Immune System Support
Cheonggukjang boosts the immune system. Polysaccharides from cheonggukjang (PSCJ) show immunostimulatory activity. This suggests a positive impact on immune function. A study showed that cheonggukjang intake enhanced immunity. It increased cytokine secretion, NK cell activity, and splenocyte proliferation. This occurred in immunosuppressed rats.
Cheonggukjang promotes the production of several immune markers:
IL-2
IL-12
IFN-γ
IgG
Cheonggukjang consumption enhances immunity. It increases levels of cytokines, including IL-2, IFN-γ, and TNF-α. It also recovers or increases IgG levels. These effects were observed in immunosuppressed conditions. This indicates a positive impact on these immune markers.
Immune Marker | Effect in CP-treated group (without Cheonggukjang) | Effect with Cheonggukjang consumption (S1-S4) |
|---|---|---|
IL-2 | Significantly decreased | Levels returned to normal or decrease suppressed |
IFN-γ | Significantly decreased | Levels returned to normal or decrease suppressed |
TNF-α | Significantly decreased | Levels returned to normal or decrease suppressed (except S2 for TNF-α) |
IgG | Significantly decreased | Levels returned to normal or decrease suppressed |
PSCJ-treated groups showed a significant increase in T- and B-lymphocyte proliferation. Previous research indicated PSCJ enhances proliferation. It also increases IL-2 and IFN-γ productions in primary cultured splenocytes. PSCJ stimulates the complement system. It significantly increases nitric oxide (NO) and immunostimulatory cytokines (IL-6 and IL-12) production. This occurs in primary cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. PSCJ induces mRNA expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). It does this by activating nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) in RAW 264.7 macrophages. This leads to increased NO and TNF-α production.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Cheonggukjang helps regulate blood pressure. Unlike other pastes, people can make cheonggukjang without salt. This is beneficial for blood pressure management. Excessive refined salt consumption links to increased high blood pressure. Cheonggukjang reduces blood pressure. It also shows anti-cancer and hypocholesterolemic effects.
Cheonggukjang regulates blood pressure by inhibiting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). ACE degrades bradykinin. Bradykinin is a peptide known for its blood pressure-lowering effects. Cheonggukjang blocks ACE. This helps maintain higher levels of bradykinin. It contributes to reduced blood pressure. ACE inhibition is a recognized strategy for managing hypertension.
Weight Management and Glycemic Control
Cheonggukjang can help with weight management. Cheonggukjang fermented with Bacillus licheniformis-67 prevented weight gain in mice. These mice ate a high-fat diet. It led to a reduction in body weight. It also reduced epididymal fat pad weight. Serum and hepatic lipid profiles decreased. Blood glucose, insulin, and leptin levels improved. The fermentation decreased lipid anabolic genes. It increased lipid catabolic genes.
A study observed a significant decrease in blood glucose levels. This occurred in the CKB group (cheonggukjang fermented with B. licheniformis-67). This happened after 120 and 180 minutes of oral glucose administration. This group also showed lower overnight fasting blood glucose. This started from the 7th week onward. This was compared to high-fat diet (HD) and unfermented soybean (SS) groups. This suggests improved glucose clearance and higher insulin sensitivity in the CKB group.
Improved glucose clearance and insulin sensitivity link to the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Isoflavones and poly-gamma glutamic acid (PGA) in cheonggukjang potentially mediate this activation. These compounds promote glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity. In animal models, cheonggukjang supplementation substantially reduced blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels. It also improved insulin resistance. This makes it a great health food for diabetics. However, a human clinical trial showed no improvement in blood glucose or insulin index after cheonggukjang pill administration. This indicates potential differences between animal and human studies or specific formulations.
Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Effects
Cheonggukjang contains powerful antioxidants. These compounds help protect the body from damage. They contribute to anti-aging effects.
Key antioxidant compounds include:
Isoflavone aglycones: daidzein, glycitein, and genistein. These increase after fermentation.
Total phenolic content: Higher with increasing ratios of mountain-cultivated ginseng and fermentation.
Total flavonoid content: Higher with increasing ratios of mountain-cultivated ginseng and fermentation.
Ginsenosides: Rg3 and compound K. These increase after fermentation, especially with mountain-cultivated ginseng supplementation.
A study revealed significant improvements in nail thickness and smoothness. This highlights its potential role in maintaining nail health. This suggests broader anti-aging benefits.
Essential Nutrients and Protein
Cheonggukjang is a nutrient-dense food. It provides essential nutrients and protein.
Nutrient | Amount per 100g serving |
|---|---|
Protein | 12.35 g |
Nutrient | Amount per 38-gram serving (Pulmuone brand) |
|---|---|
Protein | 6 g |
Cheonggukjang offers easily digestible protein. It also contains vitamin E, vitamin K, magnesium, and potassium. These nutrients contribute to overall health. Its rich nutritional profile makes it beneficial for women’s health. Studies have shown that cheonggukjang can impact the development of colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. This suggests a potential role in preventing this condition.
Cheonggukjang stands as a powerful, flavorful fermented soybean paste. It shows great versatility in Korean cooking. Its impressive health benefits span from gut health to potential disease prevention. We encourage you to explore this unique and beneficial fermented soybean paste. Discover its rich taste and positive impact on your well-being.
FAQ
What gives Cheonggukjang its strong aroma?
Bacillus strains, especially Bacillus subtilis, drive Cheonggukjang’s rapid fermentation. These microorganisms produce enzymes and volatile compounds. These compounds create the paste’s distinct, pungent smell. This aroma is a hallmark of its unique fermentation process.
What are the primary health benefits of eating Cheonggukjang?
Cheonggukjang offers many health benefits. It supports gut health and digestion. It also boosts the immune system. People consume it for cardiovascular benefits and weight management. It provides antioxidants and essential nutrients like protein, vitamin E, and vitamin K.
What is the best way to store Cheonggukjang?
People should store Cheonggukjang in an airtight container. Refrigeration is essential to maintain its freshness. Proper storage helps preserve its unique flavor and beneficial properties. This also prevents spoilage and extends its shelf life.
What does Cheonggukjang taste like?
Cheonggukjang has a rich, savory, and deeply umami flavor. It often carries an earthy and slightly pungent taste. Its unique profile comes from the rapid fermentation of soybeans. This makes it a distinctive ingredient in Korean cuisine.

