
Bell peppers are vibrant, versatile, and exceptionally healthy vegetables. You get outstanding Bell Peppers Nutrition from these colorful gems. They are packed with vitamin C and powerful antioxidants. For example, half a cup of raw red bell pepper gives you 106% of your daily vitamin C. This helps your immune system and prevents conditions like scurvy. Bell peppers also provide other key nutrients. These include Vitamin A, B6, and Folate, all vital for your body’s functions. Understanding this exceptional Bell Peppers Nutrition helps you appreciate their role in a healthy lifestyle.
Key Takeaways
Bell peppers are rich in Vitamin C. This nutrient boosts your immune system.
Bell peppers contain many antioxidants. These protect your cells from damage.
Red bell peppers offer the most Vitamin A and C. They also have lycopene.
Eating bell peppers helps your eyes. They contain nutrients good for vision.
Bell peppers are low in calories. They support healthy weight management.
Bell Peppers Nutrition: What’s Inside

Bell peppers offer you a treasure trove of essential nutrients. You get a good source of vitamin C, vitamin A, and fiber from these colorful vegetables. Understanding the bell pepper nutrition helps you make smart dietary choices.
Vitamin C in Bell Peppers: Immune Support
Bell peppers are an excellent source of vitamin C. This nutrient is vital for your overall health. A medium-sized red bell pepper provides an impressive 159% of your daily recommended intake for vitamin C. This makes it one of the richest sources available.
Vitamin C plays a crucial role in supporting your immune system. It stimulates white blood cell activity, which strengthens your immune defense. For example, vitamin C enhances the function of phagocytes, a type of white blood cell. These cells engulf and neutralize harmful pathogens. It also boosts the production of cytokines, which are communication proteins for your immune cells. Furthermore, vitamin C helps maintain the viability of T-lymphocytes, essential for cell-mediated immunity. It also aids in the multiplication of both T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, which are critical for fighting infections.
You can see the recommended daily intake for adults in the chart below:
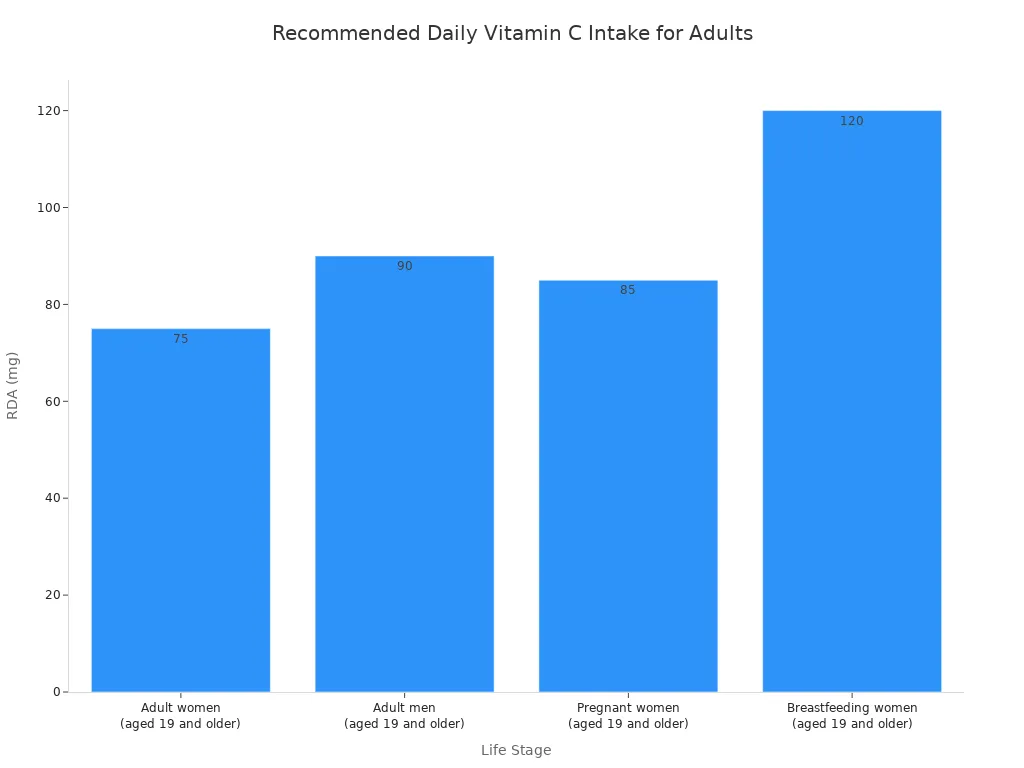
The recommended Daily Value (DV) for vitamin C for adults and children aged 4 and above increased to 90 mg in January 2020. This DV helps you understand the percentage of nutrients in a single serving on food labels.
Antioxidants in Bell Peppers: Cell Protection
Beyond vitamin C, bell peppers are packed with antioxidants. These include carotenoids, polyphenols, and other phytochemicals. These antioxidants are powerful compounds. They destroy free radicals in your body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage your cells. This damage can lead to chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
The antioxidants in bell peppers work by reducing ferric ions to ferrous ions. This reducing capacity shows their strong antioxidant activity. They also prevent the oxidation of essential fatty acids. This protection is important for optimal brain function. You get a powerful antioxidant capacity from bell peppers. This helps to protect against oxidative damage.
Different colors of bell peppers contain various carotenoids. For example, yellow/orange bell peppers have violaxanthin, cis-violaxanthin, antheraxanthin, beta-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin. Red bell peppers contain capsanthin-5,6-epoxide and cucurbitaxanthin. Beta-carotene is a common hydrocarbon carotenoid in bell peppers. It is a precursor for the orange and red carotenoids. Beta-cryptoxanthin is also present. Both contribute to the orange color of bell peppers. These antioxidant properties make bell peppers a great source of antioxidants.
Other Essential Vitamins and Minerals
The bell pepper nutrition profile extends beyond vitamin C and antioxidants. You also get other significant vitamins. These include vitamin A, vitamin B6, vitamin E, and vitamin K. These vitamins support various bodily functions. Vitamin A is crucial for vision. Vitamin B6 helps with metabolism. Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant. Vitamin K is important for blood clotting.
Fiber for Digestive Health
Bell peppers also provide dietary fiber. Fiber is essential for your digestive health. It helps keep your bowel movements regular. Fiber also supports a healthy gut microbiome. This contributes to overall well-being.
Red Bell Peppers: Nutrient Powerhouse
Among all the colors, red bell peppers stand out as a nutrient powerhouse. They contain the highest amount of vitamins, especially vitamin A and vitamin C. One medium-sized red bell pepper gives you a significant boost in these nutrients. Red bell peppers also contain lycopene. Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that contributes to their vibrant red color.
Bell Pepper Color | Lycopene Content (mcg) |
|---|---|
Green | 0 |
Yellow | 0 |
Orange | 0 |
Red | 7,300 |
As you can see, red bell peppers are the only ones with lycopene. This makes the nutritional value of bell peppers even more impressive, especially for the red variety.
Health Benefits of Bell Peppers
You gain many significant health benefits of bell peppers when you include them in your diet. These vibrant vegetables offer more than just color. They provide crucial support for your body’s functions.
Immune System Support
You know bell peppers are rich in vitamin C. This high vitamin C content boosts your immunity. It helps you fight illness. A study on bell pepper leaf extract showed anti-inflammatory effects. It inhibited inflammatory cytokine production. It also suppressed cell proliferation without cytotoxicity. This extract reduced inflammatory protein expression. These findings suggest components in bell pepper leaf extract have anti-inflammatory activity. They also show an immunosuppressive effect. This happens by inhibiting T-cell activation through the NF-κB pathway. Remember, this was an in vitro study using mouse cells. It was not a direct human clinical study. Still, it points to the potential for bell peppers to support your immune system and improve immunity.
Bell Peppers for Eye Health
Bell peppers offer significant health benefits for your eyes. The vitamin C and other antioxidants in bell peppers are important for eye health. They can help prevent or delay eye problems. This includes age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Orange bell peppers contain the carotenoid zeaxanthin. This carotenoid increases pigment density in your macula.
It lowers your risk of AMD. Bell peppers are excellent sources of lutein and zeaxanthin. These carotenoids are beneficial for eye health. Daily lutein supplements can increase macular pigment optical density (MPOD). They improve visual function for people with early signs of ARMD. A diet rich in lutein and zeaxanthin reduces your risk of ARMD. Bell peppers are exceptionally high in these nutrients. This shows the power of bell pepper nutrition for your vision.
Bell peppers are an excellent source of vitamin C. Its concentration increases as the fruit ripens. Studies show vitamin C levels increase from green to red bell peppers. It might decrease in advanced ripening because of its antioxidant role. All analyzed bell pepper varieties in one study exceeded the recommended daily dosage (60 mg/100 g) of vitamin C. Some varieties, like Janette/Terrano, contributed up to 218% of the Recommended Daily Dosage (RDD). Other studies report contributions from 25% to 461% of the RDD. Humans cannot make vitamin C. This is due to genetic mutations. Dietary sources like bell peppers are essential for many biological functions. This includes its role as an antioxidant.
Cardiovascular Health Benefits
Antioxidants in bell peppers contribute to better heart health. Bell peppers contain lycopene. This natural plant compound is especially high in red bell peppers. A report in the journal ‘Nutrients’ says lycopene fights free radicals. These free radicals damage body cells. This reduces your risk of cardiovascular issues.
Bell peppers are rich in quercetin and luteolin. These compounds protect against LDL oxidation. Japanese researchers found luteolin and quercetin effectively inhibit LDL oxidation. This was among ten tested flavonoids. Another study in the Journal of Food Science showed bell pepper extracts reduced cholesterol oxidation during heating. This resulted in 84% unoxidized cholesterol compared to 19% for the control.
Folate-rich foods like bell peppers link to a lower risk of heart attacks. The Kuopio Ischemic Heart Disease Risk Factor Study looked at 1,980 men over 10 years. It found men with the highest folate intake were 55% less likely to have a heart attack. Folate also helps with antihypertensive health benefits. It synthesizes nitric oxide. This dilates endothelial cells and improves blood flow. Circulation Research reported this. Alpha-carotene is present in bell peppers. It may decrease your risk of mortality from all causes. This includes cardiovascular disease. The NHANES III study showed people with the highest blood levels of alpha-carotene had a 39% reduced risk of death from all causes.
You can see how bell pepper compounds impact heart health:
Antioxidant/Compound | Heart Health Marker | Study Finding |
|---|---|---|
Quercetin & Luteolin | LDL Oxidation | Japanese researchers found luteolin ranked first and quercetin fourth in inhibiting LDL oxidation among ten tested flavonoids. |
Bell Pepper Extracts | Cholesterol Oxidation (during heating) | A study in the Journal of Food Science showed bell pepper extracts resulted in 84% unoxidized cholesterol during heating, compared to 19% for the control. |
Alpha-carotene | Mortality from Cardiovascular Disease | Associated with a reduced risk of mortality from all causes, including cardiovascular disease. |
Skin Health and Radiance
Vitamin C helps heal and rejuvenate tissues. This includes cartilage. It contributes to healthy skin. Vitamin C, found in bell peppers, plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis for skin health. It acts as a co-factor for enzymes like proline and lysine hydroxylases. These are essential for stabilizing the collagen molecule’s tertiary structure. Vitamin C also promotes collagen gene expression. It stimulates collagen mRNA production in fibroblasts. Fibroblasts are cells that form collagen in your skin’s dermis. Studies with fibroblast cells in vitro show collagen hydroxylase enzymes depend on Vitamin C. They show decreased total synthesis and crosslinking when Vitamin C is absent. This highlights its vital role in forming the basement membrane and dermal collagen matrix.
Research indicates ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) enhances type 1 and type 4 collagen expression. It also enhances SVCT2 in cultured human skin fibroblasts. This directly helps synthesize different types of collagen. These are important for skin structure and health. A compelling argument for Vitamin C‘s vital role in skin health is its deficiency. Deficiency links to losing important skin functions. Poor wound healing is a rapid and extreme consequence. It directly links to impaired collagen formation. You see this in Vitamin C-deficient individuals. This shows you need enough Vitamin C for healthy collagen synthesis.
Beyond promoting collagen synthesis, Vitamin C increases dermal fibroblast proliferation and migration. These functions are critical for effective wound healing. This further shows Vitamin C‘s comprehensive contribution to skin health. It impacts collagen-producing cells.
Clinical studies show red bell pepper xanthophylls inhibited UV-induced skin damage. They improved facial skin moisture in volunteers. This shows bell pepper compounds directly protect and hydrate your skin. Bell peppers are rich in bioactive compounds. These include carotenoids, vitamin C and E, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds. These compounds show antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. They alleviate inflammatory responses. They restore skin functionality after photodamage. They prevent solar UV-induced skin disorders. Orange sweet pepper has many carotenoids. These include lutein, β-cryptoxanthin, α-carotene, and zeaxanthin.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
The antioxidants in bell peppers help reduce chronic inflammation. Bell peppers are rich in flavonoids. Flavonoids are known for their anti-inflammatory activities. Luteolin is one such flavonoid. Luteolin glycosides, luteolin 7-O-(2″-O-apiosyl)glucoside, and luteolin 7-O-apiosylmalonylglucoside are present. They show anti-inflammatory effects. They inhibit the release of TNF-α and IL-6. Apigenin is another flavonoid in bell peppers with anti-inflammatory properties. Quercetin 3-O-glucoside (isoquercitrin) and Quercetin 3-O-rhamnoside (quercitrin) are also identified. Capsaicinoids are compounds responsible for pungency in some peppers. They also have anti-inflammatory effects. This aspect of bell pepper nutrition contributes to overall well-being.
Weight Management Support
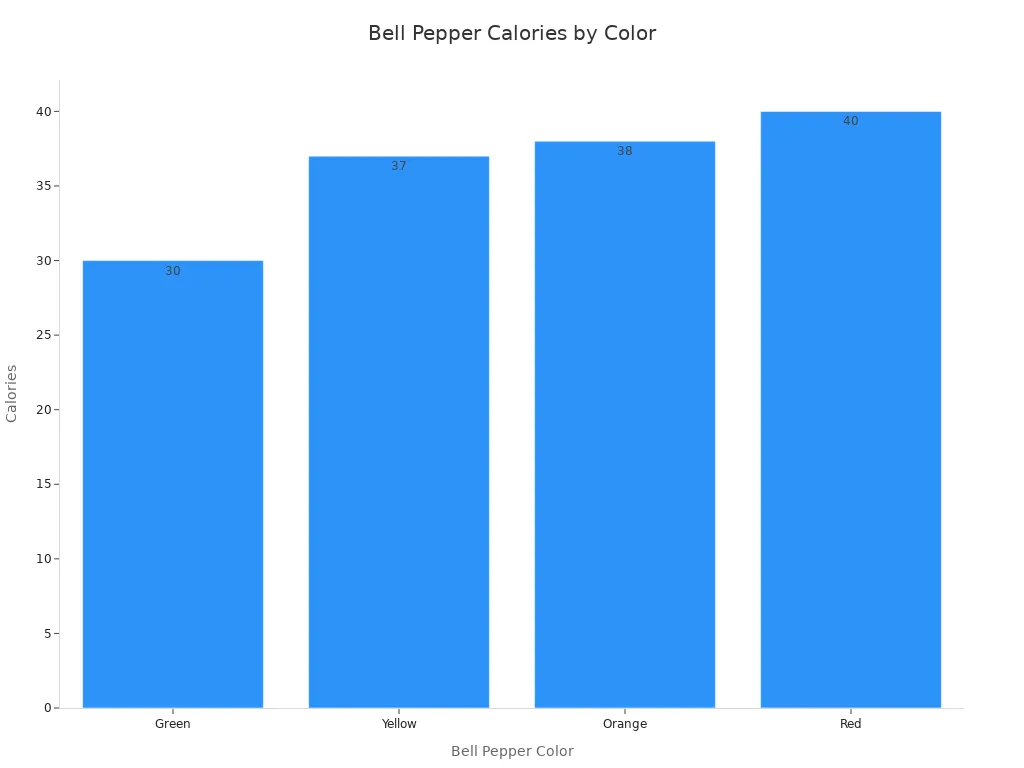
Bell peppers are a low-calorie, nutrient-dense food. This makes them a great choice for weight management. A typical medium bell pepper weighs about 119 grams. It contains about 24-40 calories. The calorie count changes with color. Green bell peppers have around 30 calories. Red, yellow, and orange varieties range from 35-40 calories. This is because they have higher natural sugar content as they ripen. While bell peppers contribute to overall digestive health through fiber, their direct impact on weight management is primarily through their low-calorie density.
You can see the calorie count for different bell pepper colors:
Bell Pepper Color | Calories (per medium pepper) |
|---|---|
Green | 30 |
Yellow | 37 |
Orange | 38 |
Red | 40 |
Capsaicinoids are found in pungent peppers. They can help with weight management. They suppress appetite. They increase metabolism. They reduce fat storage. However, bell peppers are generally non-pungent. Clinical studies have not shown a significant influence of non-pungent capsinoids on human weight and obesity. This suggests limited direct support for bell peppers‘ role in weight management based on these findings. One study by Reinbach et al. (2009) did investigate ‘CH-19 sweet pepper’ (a non-pungent cultivar). It looked at its effects on appetite and energy intake in humans.
Culinary Uses of Bell Peppers

Selecting and Storing Bell Peppers
When you choose bell peppers, look for shiny skin and vibrant colors. Avoid dull colors; they show overripeness. The skin should be smooth. Wrinkly skin means the pepper is old and dry. Check the stem; it should be green. A brown stem means the pepper is dying. Fresh bell peppers feel firm when you gently squeeze them. Soft peppers are overripe.
To store bell peppers, keep them whole in your refrigerator’s vegetable bin. This maximizes their shelf life. Once you cut them, seal them in a plastic bag. Use them within a few days. For longer storage, you can freeze chopped peppers. Spread them on a cookie tray first. Then transfer them to a freezer-safe bag. Defrosted peppers will be soft. They work best for cooking. Refrigeration in humidity-controlled drawers extends shelf life to 10-14 days. Separate bell peppers from fruits like tomatoes. Tomatoes produce ethylene, which can spoil peppers faster. Never wash bell peppers before storage. Wash them just before you use them. This prevents decay. Store whole peppers stem-side down. This reduces moisture buildup.
Raw Delights: Salads, Dips, and Snacks
You can enjoy bell peppers raw in many ways. Slice them into colorful salads. Use them as crunchy dippers for hummus or guacamole. They make a great healthy snack on their own.
Cooked Creations: Roasting, Stir-Frying, and Grilling
Bell peppers are also delicious when cooked. Roast them for a sweet, smoky flavor. Add them to stir-fries for extra crunch and color. Grill them alongside your favorite meats or vegetables. If you wonder how to use red bell pepper, try roasting it. Roasting brings out its natural sweetness.
Bell Peppers in Global Cuisine
Many cultures use bell peppers. You find them in Mediterranean dishes. They appear in Asian stir-fries. Mexican cuisine often features them in fajitas or salsas.
Color Matters: Nutritional Differences
Different colors of bell peppers offer slightly different nutrients. Red bell peppers, for example, have more Vitamin A and C. You can easily add them to your diet by choosing your favorite color. Each color brings unique benefits and flavors to your meals.
Common Questions About Bell Peppers
You might have some questions about bell peppers. Here, you find answers to common inquiries.
Are There Any Side Effects or Allergies?
Most people enjoy bell peppers without issues. However, some individuals can experience allergies or sensitivities.
Common Allergens: Proteins like profilin (found in all peppers) and Lipid Transfer Proteins (LTPs) can cause reactions.
General Symptoms: You might experience itching or tingling in your mouth, hives, eczema, or swelling of your lips, face, tongue, or throat. Digestive issues like abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting can also occur. Some people feel dizzy, wheeze, or have difficulty breathing.
Severe Symptoms: Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening reaction. It requires immediate medical attention.
Bell peppers belong to the nightshade family. For some, consuming nightshades can lead to gut irritation or increased inflammation. An intolerance might cause digestive issues. An allergy could result in more severe symptoms like breathing problems or a rash. A skin prick test can help confirm a bell pepper allergy.
Optimal Consumption: Raw vs. Cooked
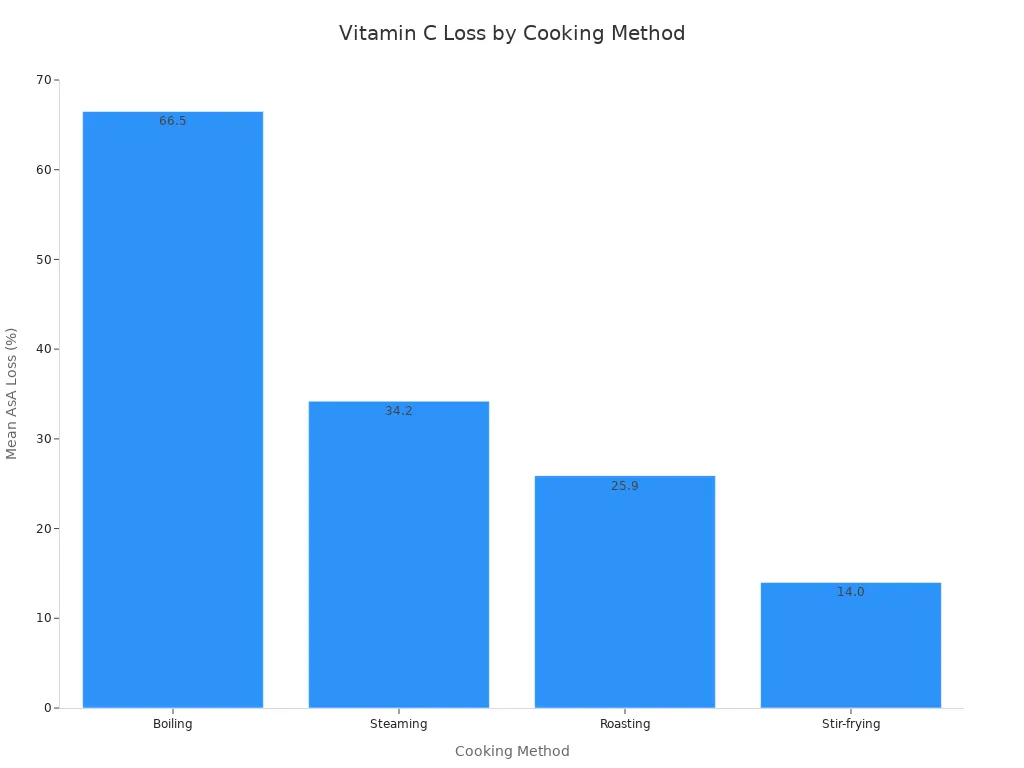
You might wonder if eating bell peppers raw or cooked is better. Cooking methods affect nutrient content, especially Vitamin C.
Cooking Method | Mean AsA Loss (15 min) |
|---|---|
Boiling | 66.5% |
Steaming | 34.2% |
Roasting | 25.9% |
Stir-frying | 14.0% |
Several factors influence Vitamin C loss:
The cooking method you choose.
The heating temperature.
How long you cook them.
Enzymatic oxidation during preparation.
The surface area exposed to water and oxygen.
You see no significant loss of Vitamin C in microwave-heated and stir-fried peppers after 5 minutes. However, boiled peppers show a significant loss after 5 minutes. This happens because antioxidant compounds leach into the cooking water due to prolonged exposure to water and heat. Eating bell peppers raw or lightly cooked helps you retain more Vitamin C.
Organic vs. Conventional Bell Peppers
You might consider organic bell peppers. Organic bell peppers contain higher concentrations of certain minerals. These include calcium (Ca), copper (Cu), potassium (K), and phosphorus (P) in both ripe and unripe stages. Conversely, conventional bell peppers show greater protein content.
Some research indicates organic bell peppers may have higher levels of bioactive compounds. These include flavonoids, carotenoids, and vitamin C. For instance, studies found more vitamin C, carotenoids, and polyphenols in organic sweet peppers. However, other studies show mixed results. One American study found only one of two organic pepper cultivars had more vitamin C. The other had higher vitamin C when grown conventionally. You find higher flavonol content in conventionally grown peppers, except for quercetin in one organic variety. Conventional bell peppers also contain higher levels of micronutrients like zinc (Zn) and iron (Fe). They generally have a greater overall mineral content.
You now understand the amazing bell peppers nutrition. These vibrant bell peppers offer significant vitamin C and antioxidants. This bell pepper nutrition supports your immune system, protects your eyes, and boosts overall well-being. You can easily add these colorful vegetables to your diet often. Embrace the excellent bell pepper nutrition for a healthier life. Enjoy the benefits of bell pepper nutrition.
FAQ
Are bell peppers good for weight loss?
Yes, bell peppers are excellent for weight loss. They are low in calories and high in nutrients. You can enjoy them as a satisfying snack or add them to meals. This helps you feel full without consuming many calories.
Can you eat bell pepper seeds?
You can eat bell pepper seeds. They are not harmful. Most people remove them for texture or appearance. The seeds do not offer significant nutritional benefits.
Do bell peppers cause gas or bloating?
Bell peppers rarely cause gas or bloating. Some sensitive individuals might experience mild digestive discomfort. This is due to their fiber content. If you have a sensitive stomach, try eating them cooked.
Which bell pepper color is the healthiest?
Red bell peppers are generally the healthiest. They contain the highest amounts of Vitamin A and Vitamin C. You also get more lycopene from red bell peppers. Each color offers great nutrition, but red stands out.
